在双碳目标下,具有调光功能的LED驱动电源是重要的分支。DALI通信常用在LED的数字调光控制中,下文将通过C语言与单片机结合,解释DALI的原理及实现方法。
一、通信原理
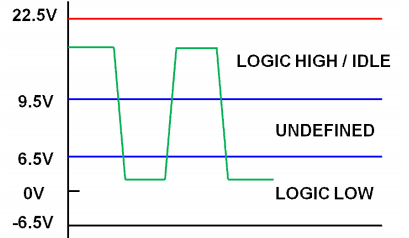

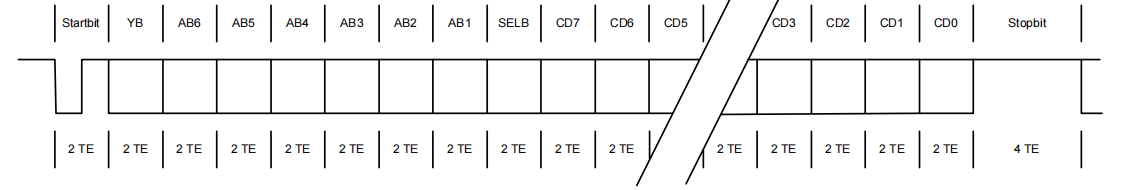
1.6 从机回复指令结构
从机向主机回复包含1个起始位、8个数据位和两个停止位。
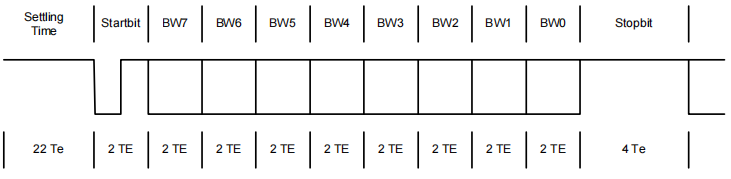
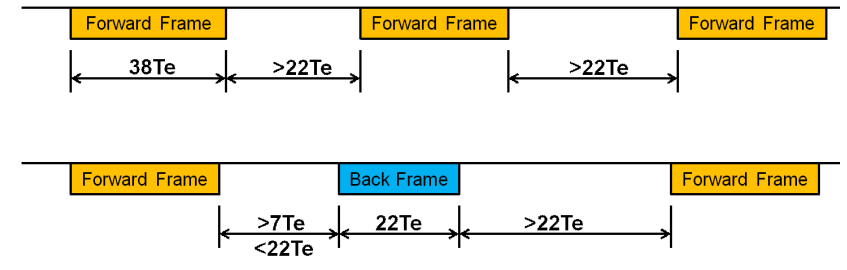
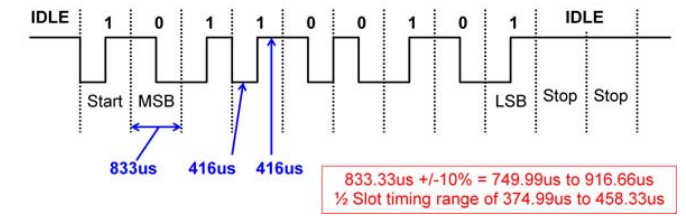
1.7 前向帧与后向帧时序约束
Te表示半个位的时间,即4.16.67uS;
两个前向帧时间间隔大于22个Te;
前向帧与后向帧之间时间间隔为7~22个Te;
后向帧与前向帧之间时间间隔大于22个Te;
1.8 主机与从机的握手
主机在发送指令后,在等候响应阶段,
如果收到从机发送的”0xFF“,就会认为从机接收成功;
如果在这个阶段处于空闲状态,就会认为从机没有接收成功;
二、实现方法
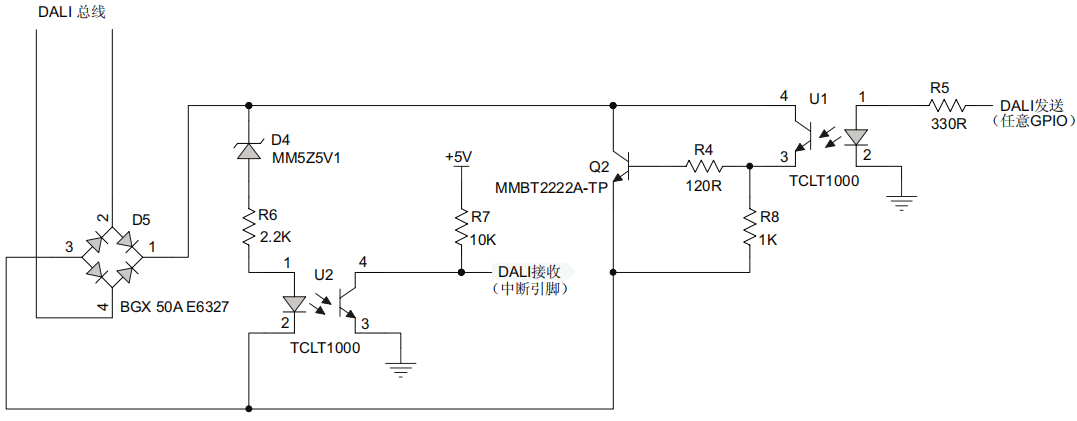
2.1 硬件原理图
下面的硬件主要是将DALI的电平信号,转为单片机能够接受的电平,下面那张是微芯公司DALI的参考通信电路。
2.1 从机接收思路及实现
本次从机的接收端,主要使用了一个边沿检测中断和一个定时器中断。
代码思路:
1)由于空闲状态,接收端的电平为高电平,产生起始信号时,需要从产生一个上升沿。于是,使用了外部下降沿触发中断,并关闭边沿触发中断;
2)检测到第一个下降沿后,定时器定时到0.75个周期,0.75个周期后读取第一位数据,并修改定时器周期为1个数据位时长。
3)第二次定时结束时读取第二位数据,依次读取后面的数据
4)当读到最后一位数据的时候,也就是LSB后的两位时,停止定时器,并初始化定时器为0.75个数据周期,然后开启边沿触发中断。
C语言程序:
1 //配置边沿触发及中断 2 void IO_Change_Init(void){ 3 4 //Set the CN2 as the IO state change flag 5 CNEN1bits.CN2IE=1;//Open the IO state interrupt 6 CNPU1bits.CN2PUE=0;//Disable the weak up 7 8 IFS1bits.CNIF=0;//Clear the interrupt flag 9 IPC4bits.CNIP=7;//Configure the interrupt level 7 10 IEC1bits.CNIE=1;//Enable this interrupt 11 } 12 //检测到第一个下降沿 13 void __attribute__ ((__interrupt__,__no_auto_psv__)) _CNInterrupt(void){ 14 15 IFS1bits.CNIF = 0; //Clear the interrupt flag 16 17 //Disable the IO State Interrupt and start the Time
18 T1CONbits.TON = 1; 19 CNEN1bits.CN2IE = 0; 20 21 } 22 //配置定时器初使周期为0.75个数据位时长 23 void Tim1_Init(void){ 24 T1CON = 0x0020; 25 26 IEC0bits.T1IE = 1; 27 IPC0bits.T1IP = 7; 28 IFS0bits.T1IF = 0; 29 30 TMR1 = 0; 31 PR1 = 390; 32 T1CONbits.TON = 0; 33 } 34 //在定时器中断里面读取数据 35 void __attribute__((__interrupt__,auto_psv,__shadow__)) _T1Interrupt(void) 36 { 37 IFS0bits.T1IF = 0; 38 39 if(LLC_DALI_Rx_Mode == 1) 40 { 41 switch(Timer_Num) 42 { 43 case 0: 44 Timer_Num++; 45 T1CONbits.TON = 0; //关闭定时器 46 PR1 = 520; //设置下一个定时时长为1个周期 47 TMR1 = 0;//初使化定时器初始值 48 T1CONbits.TON = 1;//开启定时器 49 break; 50 case 1: 51 if(_RB0 == 1 )Address_temp |= (1<<7); 52 Timer_Num++; 53 break; 54 case 2: 55 if(_RB0 == 1 )Address_temp |= (1<<6); 56 Timer_Num++; 57 break; 58 case 3: 59 if(_RB0 == 1 )Address_temp |= (1<<5); 60 Timer_Num++; 61 break; 62 case 4: 63 if(_RB0 == 1 )Address_temp |= (1<<4); 64 Timer_Num++; 65 break; 66 case 5: 67 if(_RB0 == 1 )Address_temp |= (1<<3); 68 Timer_Num++; 69 break; 70 case 6: 71 if(_RB0 == 1 )Address_temp |= (1<<2); 72 Timer_Num++; 73 break; 74 case 7: 75 if(_RB0 == 1 )Address_temp |= (1<<1); 76 Timer_Num++; 77 break; 78 case 8: 79 if(_RB0 == 1 )Address_temp |= (1<<0); 80 Timer_Num++; 81 break; 82 case 9: 83 if(_RB0 == 1 )Command_temp |= (1<<7); 84 Timer_Num++; 85 break; 86 case 10: 87 if(_RB0 == 1 )Command_temp |= (1<<6); 88 Timer_Num++; 89 break; 90 case 11: 91 if(_RB0 == 1 )Command_temp |= (1<<5); 92 Timer_Num++; 93 break; 94 case 12: 95 if(_RB0 == 1 )Command_temp |= (1<<4); 96 Timer_Num++; 97 break; 98 case 13: 99 if(_RB0 == 1 )Command_temp |= (1<<3); 100 Timer_Num++; 101 break; 102 case 14: 103 if(_RB0 == 1 )Command_temp |= (1<<2); 104 Timer_Num++; 105 break; 106 case 15: 107 if(_RB0 == 1 )Command_temp |= (1<<1); 108 Timer_Num++; 109 break; 110 case 16: 111 if(_RB0 == 1 )Command_temp |= (1<<0); 112 Timer_Num++; 113 break; 114 case 17: 115 if(_RB0 == 1 )StopBit_temp |= (1<<1); 116 Timer_Num++; 117 break; 118 case 18: 119 if(_RB0 == 1 )StopBit_temp |= (1<<0); 120 Timer_Num++; 121 break; 122 case 19: 123 T1CONbits.TON = 0;//关闭定时器 124 PR1 = 390;//设置下一个定时器周期为0.75个数据位时长 125 TMR1 = 0;//定时器计数初始值置0 126 CNEN1bits.CN2IE = 1;//开启边沿检测中断 127 //数据获取,这里还可以添加数据包检验程序 128 Command = Command_temp; 129 Address = Address_temp; 130 StopBit = StopBit_temp; 131 132 Command_temp = 0; 133 Address_temp = 0; 134 StopBit_temp = 0; 135 Timer_Num = 0; 136 break; 137 } 138 } 139 140 141
2.2 从机思路及实现
从机的回复相对较简单,只需要在每半个数据位修改输出引脚的电平。分别发送1个起始位、8个数据位和两个停止位。
代码思路:
1)接收数据完成并定时等待8Te
2)发送一个引脚低电平,并设置下一个定时周期为Te,定时器初使值为0,并开启定时器;
3)在后面的定时器中断里面,发送起始位;
4)在后面的定时器中断里面,发送数据位;
5)在后面的定时器中断里面,发送停止位;
6)初使化发送数据计数变量,初始化定时器计数值为零,关闭定时器;
7)开启边沿触发中断;
C语言程序实现
1 if(LLC_DALI_Tx_Mode == 1){ 2 switch(Timer_Num) 3 { 4 case 0: 5 //Send the Start Bit 6 _RF3 = 0; 7 T1CONbits.TON = 0; 8 PR1 = 260; 9 TMR1 = 0; 10 T1CONbits.TON = 1; 11 Timer_Num++; 12 break; 13 case 1: 14 _RF3 = 1; 15 Timer_Num++; 16 break; 17 case 2: 18 //Send the Data Bits 19 _RF3 = ((Transfer_Data & 0x80)>0)?0:1; 20 Timer_Num++; 21 break; 22 case 3: 23 _RF3 = ((Transfer_Data & 0x80)>0)?1:0; 24 Timer_Num++; 25 break; 26 case 4: 27 _RF3 = ((Transfer_Data & 0x40)>0)?0:1; 28 Timer_Num++; 29 break; 30 case 5: 31 _RF3 = ((Transfer_Data & 0x40)>0)?1:0; 32 Timer_Num++; 33 break; 34 case 6: 35 _RF3 = ((Transfer_Data & 0x20)>0)?0:1; 36 Timer_Num++; 37 break; 38 case 7: 39 _RF3 = ((Transfer_Data & 0x20)>0)?1:0; 40 Timer_Num++; 41 break; 42 case 8: 43 _RF3 = ((Transfer_Data & 0x10)>0)?0:1; 44 Timer_Num++; 45 break; 46 case 9: 47 _RF3 = ((Transfer_Data & 0x10)>0)?1:0; 48 Timer_Num++; 49 break; 50 case 10: 51 _RF3 = ((Transfer_Data & 0x08)>0)?0:1; 52 Timer_Num++; 53 break; 54 case 11: 55 _RF3 = ((Transfer_Data & 0x08)>0)?1:0; 56 Timer_Num++; 57 break; 58 case 12: 59 _RF3 = ((Transfer_Data & 0x04)>0)?0:1; 60 Timer_Num++; 61 break; 62 case 13: 63 _RF3 = ((Transfer_Data & 0x04)>0)?1:0; 64 Timer_Num++; 65 break; 66 case 14: 67 _RF3 = ((Transfer_Data & 0x02)>0)?0:1; 68 Timer_Num++; 69 break; 70 case 15: 71 _RF3 = ((Transfer_Data & 0x02)>0)?1:0; 72 Timer_Num++; 73 break; 74 case 16: 75 _RF3 = ((Transfer_Data & 0x01)>0)?0:1; 76 Timer_Num++; 77 break; 78 case 17: 79 _RF3 = ((Transfer_Data & 0x01)>0)?1:0; 80 Timer_Num++; 81 break; 82 case 18: 83 //Send the stop bit; 84 T1CONbits.TON = 0; 85 TMR1 = 0; 86 PR1 = 260<<2; 87 T1CONbits.TON = 1; 88 _RF3 = 1; 89 Timer_Num++; 90 break; 91 case 19: 92 T1CONbits.TON = 0; //关闭定时器 93 CNEN1bits.CN2IE = 1;//开启边沿检测中断 94 TMR1 = 0; //定时器初始值置0 95 PR1 = 260; //定时器周期设置为Te 96 Timer_Num = 0;//初使定时器数据位计数 97 break; 98 } 99 }
三、测试结果
3.1 从机发送测试
从机发送数据100,对应二进制为0b0110 0100,实际发送波形见下图:
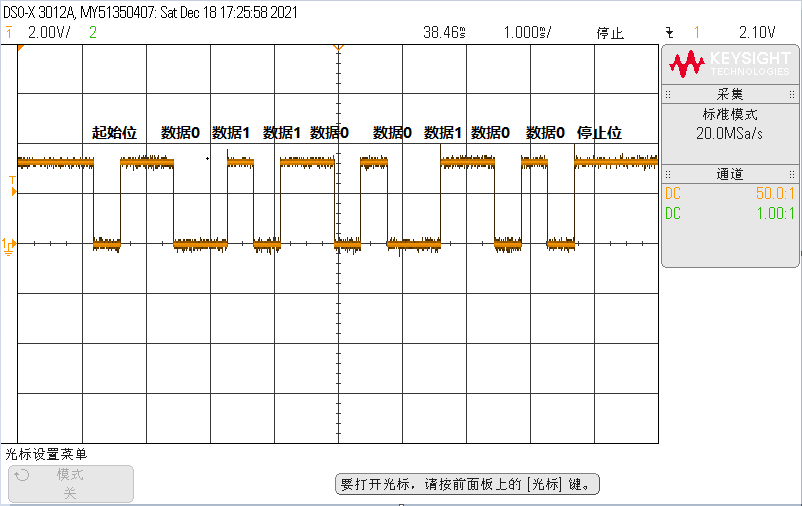
实际发送数据为0b01100100,发送正常。
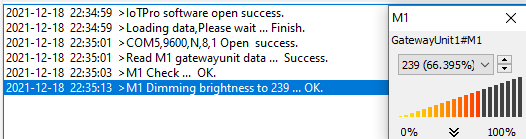
3.2 主机发送从机识别测试
主机通过上位机发送调光指令为239,从机在线调试识别出来的数据为239。接收正常。
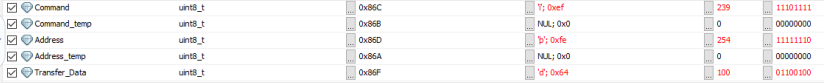
四、小结
从机的接收程序,定时器的定时步长先是1.5个Te,然后是2个Te;
从机的发送程序,定时器的定时步长为1个Te;
从机的接收程序,边沿触发只触发依次就关闭了。
从机的发送程序,发送完毕开启边沿触发。
在定时器中断里面,修改下一个定时时长,理论上可以做到每一个定时周期都不一样,这思维可以用于实现更加复杂的功能。
注意:
1)以上代码发送和接收是独立的,没有遵循通信的时序。1.7节里面有具体时序要求,根据时序稍做修改就可以啦。
2)本次代码,没有考虑到时序有10%的误差。有待改善。
五、参考资料
【1】Digital Addressable Lighting Interface (DALI) Control Devices Protocol,PART 1-2004
【2】DALI控制装置,AN1487,Microchip
【3】数字可寻址照明接口(DALI)通信,AN1465,Microchip
【4】Digital Addressable Lighting Interface (DALI) Implementation Using MSP430 Value Line Microcontrollers,TI