这次来学习下单链表的一些常见操作,链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。
创建链表
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {5,2,7,4,9,3,1}; SingleLinkedList singleLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList(); for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ singleLinkedList.add(arr[i]); } singleLinkedList.deleteNode(1); singleLinkedList.printLink(); System.out.println(); //int len = singleLinkedList.length(); //System.out.println(len); } } class SingleLinkedList{ public Node head = new Node(); //head为头节点不存放任何的数据,只是充当一个指向链表中真正存放数据的第一个节点的作用 class Node{ public int value; public Node next; public Node() {} public Node(int value) { this.value = value; this.next = null; } } public void add(int value) {//增加节点 尾插法 if(head.next == null) { head.next = new Node(value); return; } Node tempNode = head; while(tempNode.next!=null) { tempNode = tempNode.next; } tempNode.next = new Node(value); } public void printLink() {//遍历链表 Node tempNode = head; while(tempNode.next!=null) { tempNode = tempNode.next; System.out.print(tempNode.value+" "); } } public void deleteNode(int value) {//根据值删除节点 Node tempNode = head; while(tempNode.next!=null) { if(tempNode.next.value == value) { tempNode.next = tempNode.next.next; }else { tempNode = tempNode.next; } } } public int length(){ int length = 0; Node temp = head; while (temp.next!=null){ length++; temp = temp.next; } return length; } }
运行结果如下:
翻转链表
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {5,2,7,4,9,3,1}; SingleLinkedList singleLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList(); for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ singleLinkedList.add(arr[i]); } singleLinkedList.reverseList(); singleLinkedList.printLink(); } } class SingleLinkedList{ public Node head = new Node(); //head为头节点不存放任何的数据,只是充当一个指向链表中真正存放数据的第一个节点的作用 class Node{ public int value; public Node next; public Node() { this.next = null; } public Node(int value) { this.value = value; this.next = null; } } public void add(int value) {//增加节点 尾插法 if(head.next == null) { head.next = new Node(value); return; } Node tempNode = head; while(tempNode.next!=null) { tempNode = tempNode.next; } tempNode.next = new Node(value); } public void printLink() {//遍历链表 Node tempNode = head; while(tempNode.next!=null) { tempNode = tempNode.next; System.out.print(tempNode.value+" "); } } public void reverseList() { Node preNode = null; Node curNode = head; while(curNode!=null) { Node tempNode = curNode.next; curNode.next = preNode; preNode = curNode; curNode = tempNode; } Node newHeadNode = new Node(); newHeadNode.next = preNode; head = newHeadNode; } }
中间元素
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {5,2,7,4,9,3,1}; SingleLinkedList singleLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList(); for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ singleLinkedList.add(arr[i]); } int midvalue = singleLinkedList.findMiddle(); System.out.println(midvalue); } } class SingleLinkedList{ public Node head = new Node(); //head为头节点不存放任何的数据,只是充当一个指向链表中真正存放数据的第一个节点的作用 class Node{ public int value; public Node next; public Node() { this.next = null; } public Node(int value) { this.value = value; this.next = null; } } public void add(int value) {//增加节点 尾插法 if(head.next == null) { head.next = new Node(value); return; } Node tempNode = head; while(tempNode.next!=null) { tempNode = tempNode.next; } tempNode.next = new Node(value); } public int findMiddle(){ Node slowNode = head; Node fastNode = head; while(fastNode!=null&&fastNode.next!=null) { fastNode = fastNode.next.next; slowNode = slowNode.next; } return slowNode.value; } }
运行如下:
判断是否为循环链表
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {5,2,7,4,9,3,1}; SingleLinkedList singleLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList(); for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ singleLinkedList.add(arr[i]); } Boolean hasCycle = singleLinkedList.hasCycle(); System.out.println(hasCycle); } } class SingleLinkedList{ public Node head = new Node(); //head为头节点不存放任何的数据,只是充当一个指向链表中真正存放数据的第一个节点的作用 class Node{ public int value; public Node next; public Node() { this.next = null; } public Node(int value) { this.value = value; this.next = null; } } public void add(int value) {//增加节点 尾插法 if(head.next == null) { head.next = new Node(value); return; } Node tempNode = head; while(tempNode.next!=null) { tempNode = tempNode.next; } tempNode.next = new Node(value); } public void printLink() {//遍历链表 Node tempNode = head; while(tempNode.next!=null) { tempNode = tempNode.next; System.out.print(tempNode.value+" "); } } public boolean hasCycle() { if(head == null) { return false; } Node slowNode = head; Node fastNode = head; while(slowNode!=null&&fastNode!=null&&fastNode.next!=null) { slowNode = slowNode.next; fastNode = fastNode.next.next; if(slowNode == fastNode) { return true; } } return false; } }
运行结果如下:
链表排序
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {5,2,7,4,9,3,1}; SingleLinkedList singleLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList(); for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ singleLinkedList.add(arr[i]); } singleLinkedList.sortList(); singleLinkedList.printLink(); } } class SingleLinkedList{ public Node head = new Node(); //head为头节点不存放任何的数据,只是充当一个指向链表中真正存放数据的第一个节点的作用 class Node{ public int value; public Node next; public Node() { this.next = null; } public Node(int value) { this.value = value; this.next = null; } } public void add(int value) {//增加节点 尾插法 if(head.next == null) { head.next = new Node(value); return; } Node tempNode = head; while(tempNode.next!=null) { tempNode = tempNode.next; } tempNode.next = new Node(value); } public void printLink() {//遍历链表 Node tempNode = head; while(tempNode.next!=null) { tempNode = tempNode.next; System.out.print(tempNode.value+" "); } } public void sortList() { quickSort(head, null); } private void quickSort(Node low, Node high) { if(low == high) { return; } Node pt = partition(low,high); quickSort(low,pt); quickSort(pt.next,high); } private Node partition(Node low, Node high) { int pivotKey = low.value; Node p1 = low; Node p2 = low.next; while(p2!=high) { if(p2.value < pivotKey) { p1 = p1.next; int temp = p1.value; p1.value = p2.value; p2.value = temp; } p2 = p2.next; } if(p1!=head) { int temp = p1.value; p1.value = low.value; low.value = temp; } return p1; } }
运行结果如下: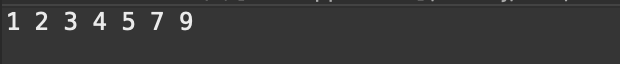
合并两个已排序链表
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr1 = {1,4,7}; int[] arr2 = {2,3,5}; SingleLinkedList singleLinkedList1 = new SingleLinkedList(); SingleLinkedList singleLinkedList2 = new SingleLinkedList(); for(int i=0;i<arr1.length;i++){ singleLinkedList1.add(arr1[i]); } for(int i=0;i<arr2.length;i++){ singleLinkedList2.add(arr2[i]); } Node newNode = singleLinkedList1.merge(singleLinkedList1.head.next,singleLinkedList2.head.next); while(newNode!=null) { System.out.print(newNode.value+" "); newNode = newNode.next; } } } class Node{ public int value; public Node next; public Node() { this.next = null; } public Node(int value) { this.value = value; this.next = null; } } class SingleLinkedList{ public Node head = new Node(); //head为头节点不存放任何的数据,只是充当一个指向链表中真正存放数据的第一个节点的作用 public void add(int value) {//增加节点 尾插法 if(head.next == null) { head.next = new Node(value); return; } Node tempNode = head; while(tempNode.next!=null) { tempNode = tempNode.next; } tempNode.next = new Node(value); } public Node merge(Node head1,Node head2) { if(head1 == null){ return head2; } if(head2 == null){ return head1; } Node newhead = null; if(head1.value <= head2.value){ newhead = head1; newhead.next = merge(head1.next,head2); }else{ newhead = head2; newhead.next = merge(head1,head2.next); } return newhead; } }
运行结果为: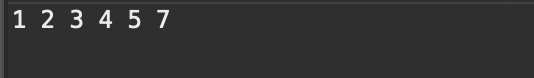
删除倒数第N个节点
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {5,2,7,4,9,3,1}; SingleLinkedList singleLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList(); for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ singleLinkedList.add(arr[i]); } singleLinkedList.removeNthFromEnd(2); singleLinkedList.printLink(); } } class SingleLinkedList{ public Node head = new Node(); //head为头节点不存放任何的数据,只是充当一个指向链表中真正存放数据的第一个节点的作用 class Node{ public int value; public Node next; public Node() { this.next = null; } public Node(int value) { this.value = value; this.next = null; } } public void add(int value) {//增加节点 尾插法 if(head.next == null) { head.next = new Node(value); return; } Node tempNode = head; while(tempNode.next!=null) { tempNode = tempNode.next; } tempNode.next = new Node(value); } public void printLink() {//遍历链表 Node tempNode = head; while(tempNode.next!=null) { tempNode = tempNode.next; System.out.print(tempNode.value+" "); } } public void removeNthFromEnd(int n) { if(n<=0) { return; } Node dummyNode = head.next; Node preDeleteNode = head; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { if(dummyNode == null) { return; } dummyNode = dummyNode.next; } while(dummyNode!=null) { dummyNode = dummyNode.next; preDeleteNode = preDeleteNode.next; } preDeleteNode.next = preDeleteNode.next.next; } }
运行结果:
判断两个链表是否相交
public Node getIntersectionNode(Node headA, Node headB) { if (headA == null || headB == null) { return null; } Node currA = headA; Node currB = headB; int lengthA = 0; int lengthB = 0; // 让长的先走到剩余长度和短的一样 while (currA != null) { currA = currA.next; lengthA++; } while (currB != null) { currB = currB.next; lengthB++; } currA = headA; currB = headB; while (lengthA > lengthB) { currA = currA.next; lengthA--; } while (lengthB > lengthA) { currB = currB.next; lengthB--; } // 然后同时走到第一个相同的地方 while (currA != currB) { currA = currA.next; currB = currB.next; } // 返回交叉开始的节点 return currA; }