一、实现思想
平衡二叉树比二叉查找树升级在哪里?
平衡二叉树是在二叉查找树的属性『左小右大』的基础上做一个调整,确保每一个节点的左右子树高度差不大于1,这样在运用『左小右大』进行查找时,就可以一下子排除许多数。最直观的,平衡二叉树就不会有像二叉查找树那样一边倒的例子。
如何确保每个节点的左右子树高度差不大于1?
每插入一个节点后,我都对这棵树进行检查(这个检查正是本博客的重点),如果发现不平衡,立马做出调整。
二、实现图例
举一个例子
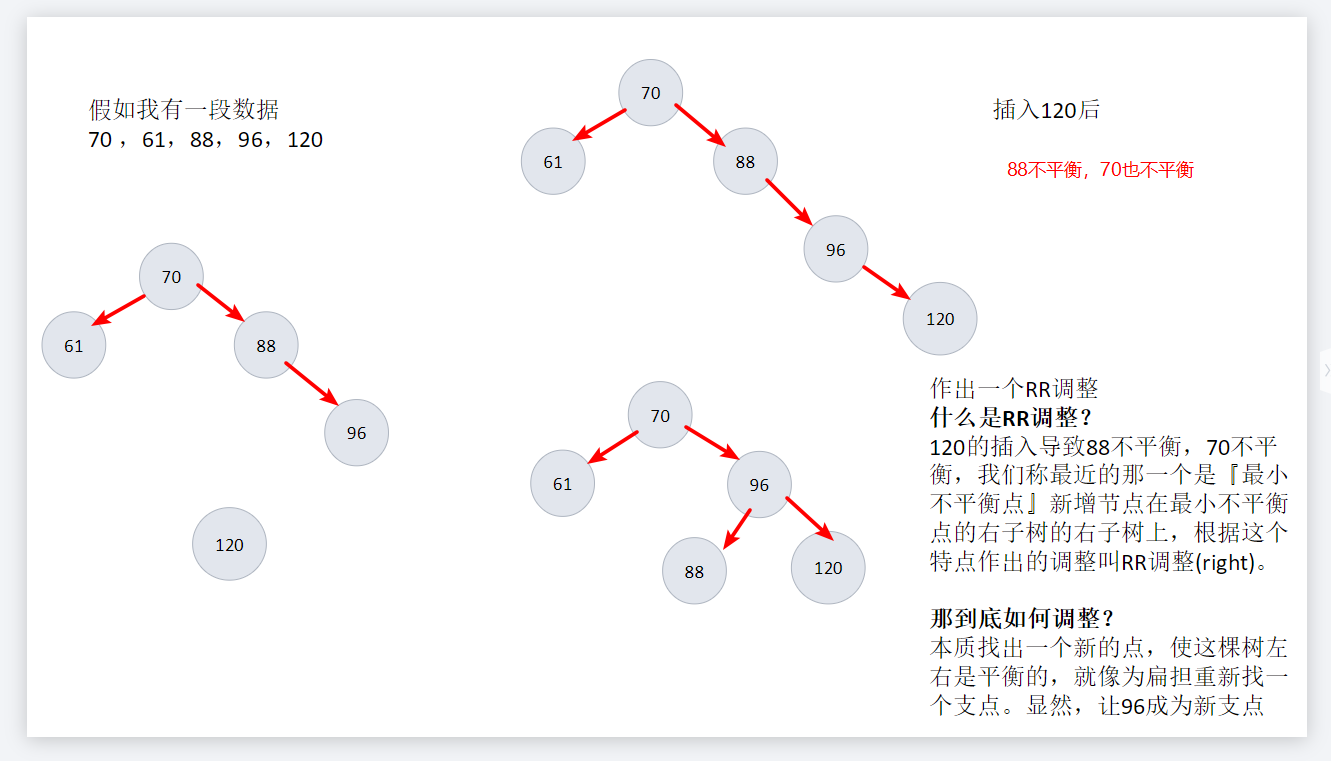
总结出四大情况
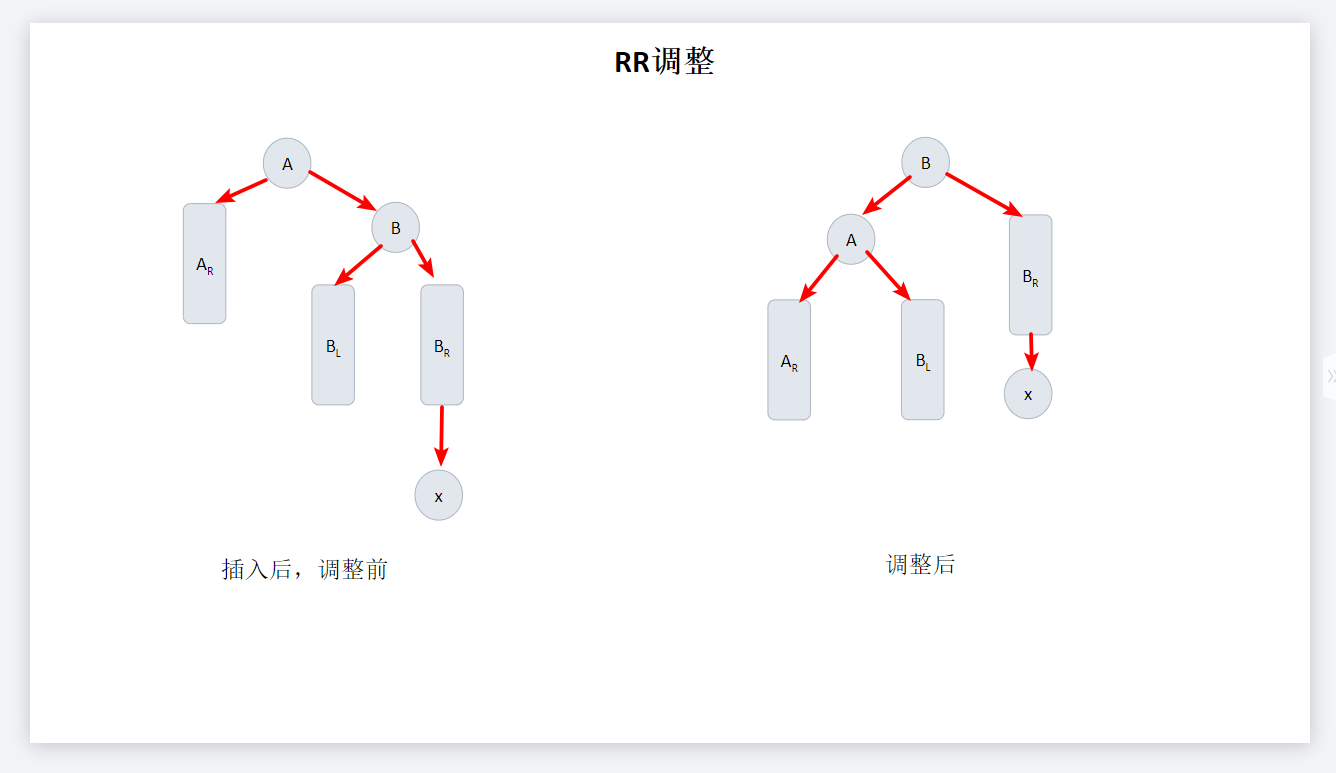
RR调整
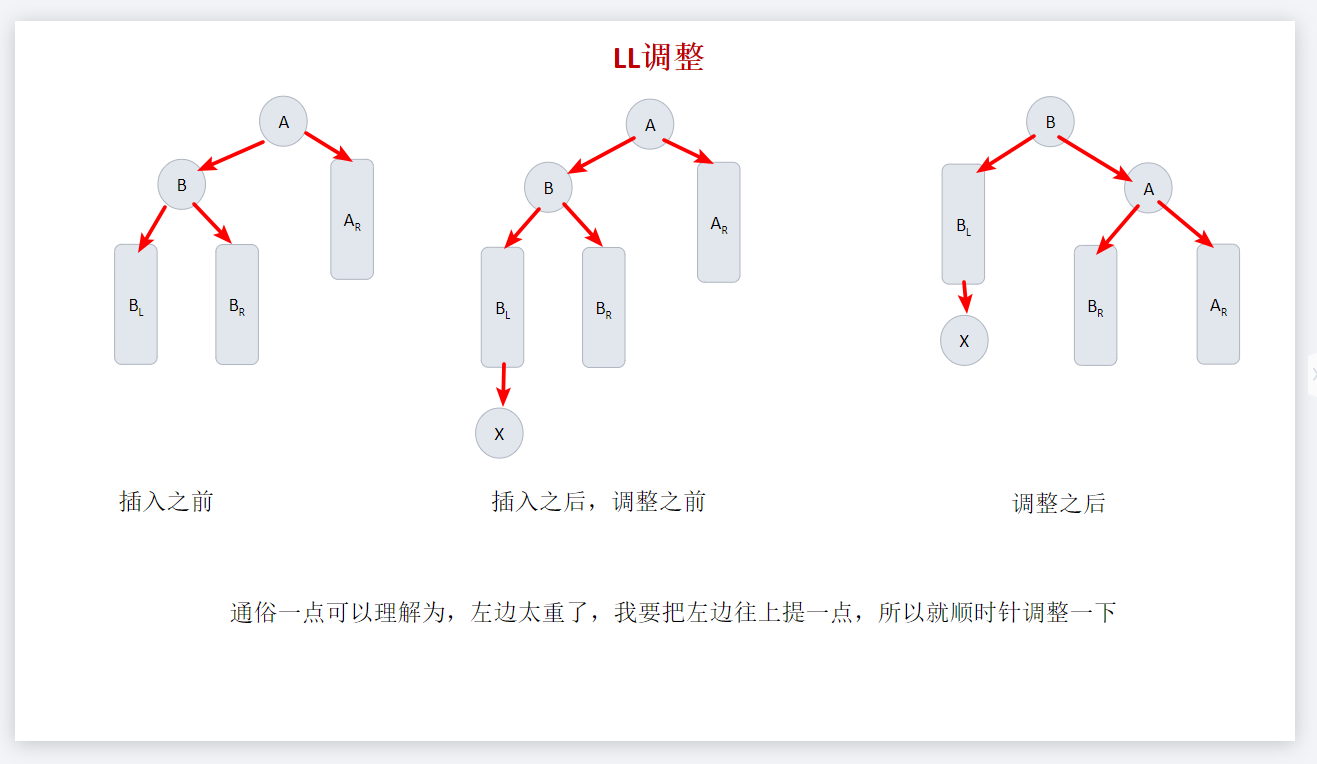
LL调整
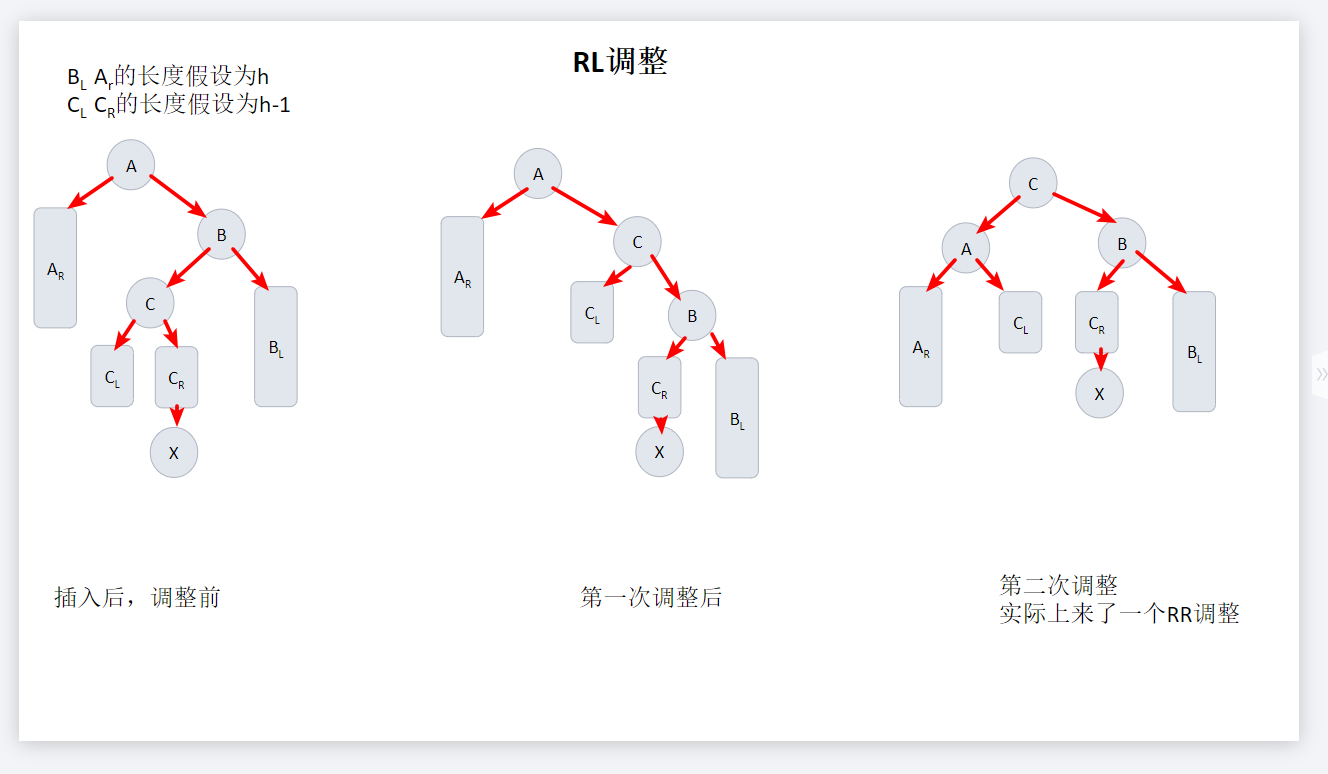
RL调整
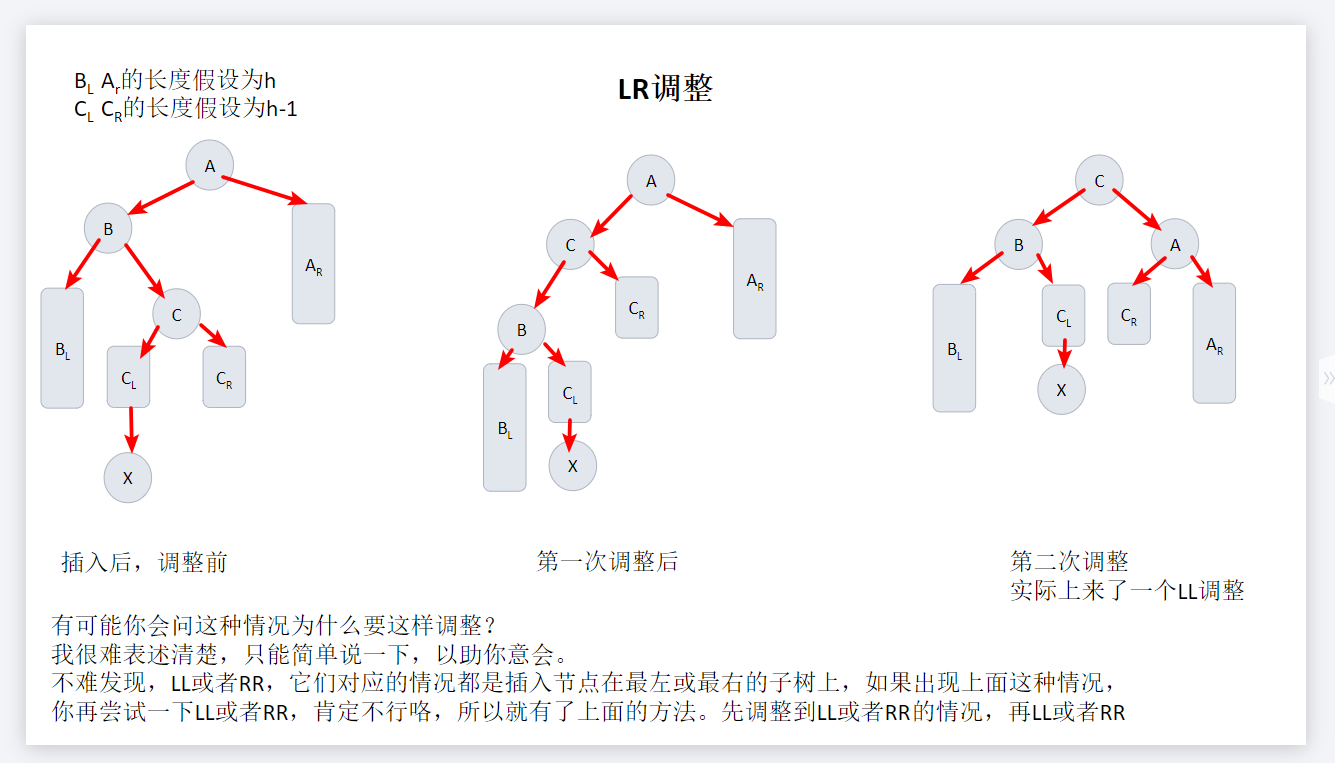
LR调整
三、实现代码
插入的函数 (其中一部分代码,这是我觉得最精华的地方,利用了递归,一次递归搞定两样事情)
- 它是递归下去寻找插入的位置
- 插入完成之后,它会层层地跳出递归,顺便检查这条路径上地节点是否平衡,不平衡则立即调整
1 //向树中插入元素 //不需要在全局寻找最小不平衡点,用递归就能统一格式地寻找 2 pTree insert(pTree root, int data) 3 { 4 5 //如果为NULL,就可以new一个节点,并且把指向返回给上一个指向 6 if (root == NULL) 7 { 8 pTree p = new Tree(); 9 p->data = data; 10 p->left = NULL; 11 p->right = NULL; 12 root = p; 13 } 14 else 15 { 16 if (data < root->data) 17 root->left = insert(root->left, data); //先是执行了插入操作,再去判断是否需要调整 18 if (height(root->left) - height(root->right) == 2) 19 { 20 //判断需要进行哪一种调整,只需要判断插入的data,相对于最小不平衡点的下一个节点,的位置。太妙了,我没有想到这样比较 21 if (data < root->left->data) 22 root = LLrotation(root); 23 else 24 root = LRrotation(root); 25 } 26 if (data >= root->data) 27 root->right = insert(root->right, data); 28 if (height(root->right) - height(root->left) == 2) 29 { 30 if (data < root->right->data) 31 root = RLrotation(root); 32 else 33 root = RRrotation(root); 34 } 35 } 36 37 return root; 38 }
判断树高的函数 (这也是我觉得比较神奇的地方,也是利用了递归)
1 //计算一个树的高度 2 int height(pTree root) 3 { 4 int hl, hr, max; 5 if (root) 6 { 7 //代码太妙了,有许多递归的用法 8 hl = height(root->left); 9 hr = height(root->right); 10 max = hl > hr ? hl : hr; 11 return max + 1; 12 } 13 else 14 return 1; 15 }
全部代码
#include <stdio.h>
typedef struct TreeNode *pTree;
typedef struct TreeNode Tree;
struct TreeNode
{
int data;
pTree left;
pTree right;
};
pTree buildTree(int a[], int len); //建立自平衡二叉树
pTree insert(pTree T, int v); //向树中插入元素
int height(pTree T); //计算一个树的高度
pTree LLrotation(pTree T); //LL旋转,左单旋转
pTree LRrotation(pTree T); //LR旋转,左右双旋
pTree RRrotation(pTree T); //RR旋转,右单旋转
pTree RLrotation(pTree T); //RL旋转,右左双旋
void middle_print(pTree T); //中序遍历
//建立自平衡二叉树
pTree buildTree(int a[], int len)
{
pTree root = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
root = insert(root, a[i]);
}
return root;
}
//向树中插入元素 //不需要在全局寻找最小不平衡点,用递归就能统一格式地寻找
pTree insert(pTree root, int data)
{
//如果为NULL,就可以new一个节点,并且把指向返回给上一个指向
if (root == NULL)
{
pTree p = new Tree();
p->data = data;
p->left = NULL;
p->right = NULL;
root = p;
}
else
{
if (data < root->data)
root->left = insert(root->left, data); //先是执行了插入操作,再去判断是否需要调整
if (height(root->left) - height(root->right) == 2)
{
//判断需要进行哪一种调整,只需要判断插入的data,相对于最小不平衡点的下一个节点,的位置。太妙了,我没有想到这样比较
if (data < root->left->data)
root = LLrotation(root);
else
root = LRrotation(root);
}
if (data >= root->data)
root->right = insert(root->right, data);
if (height(root->right) - height(root->left) == 2)
{
if (data < root->right->data)
root = RLrotation(root);
else
root = RRrotation(root);
}
}
return root;
}
//计算一个树的高度
int height(pTree root)
{
int hl, hr, max;
if (root)
{
//代码太妙了,有许多递归的用法
hl = height(root->left);
hr = height(root->right);
max = hl > hr ? hl : hr;
return max + 1;
}
else
return 1;
}
//LL旋转,左单旋转
pTree LLrotation(pTree T)
{
pTree root = T->left;
T->left = root->right;
root->right = T;
return root;
}
//LR旋转,左右双旋
pTree LRrotation(pTree T)
{
pTree b = T->left;
pTree c = b->right;
b->right = c->left;
c->left = b;
T->left = c;
T = LLrotation(T);
return T;
}
//RR旋转,右单旋转
pTree RRrotation(pTree T)
{
pTree root = T->right;
T->right = root->left;
root->left = T;
return root;
}
//RL旋转,右左双旋
pTree RLrotation(pTree T)
{
pTree b = T->right;
pTree c = b->left;
b->left = c->right;
c->right = b;
T->right = c;
T = RRrotation(T);
return T;
}
//中序遍历
void middle_print(pTree T)
{
if (T->left != NULL)
middle_print(T->left);
printf("%d
", T->data);
if (T->right != NULL)
middle_print(T->right);
}
int main(void)
{
int len = 6;
int a[] = {70, 61, 96, 88, 120, 90};
pTree root = NULL;
root = buildTree(a, len);
// printf("%d
", root->data);
middle_print(root);
return 0;
}
/*
输出
————
61
70
88
90
96
120
————
*/
四、总结
这是我第一次感觉到递归如此厉害,我之前是用一个笨方法,从全局出发寻找那个最小不平衡点,真的是太麻烦,这里的一次递归便可以完成两件事情。
补充:
这里没有讲删除节点,其实删除节点和二叉查找树删除是差不多的,只是在那个基础上多了一个调整。(这里算给自己挖一个坑吧,有机会在过来填)
2020-08-28