一、双指针
1. 有序数组的 Two Sum
167. Two Sum II - Input array is sorted (Easy)
2. 两数平方和
633. Sum of Square Numbers (Easy)
反转字符串中的元音字符
回文字符串
二、排序
kth element
三、贪心思想
保证每次操作都是局部最优的,并且最后得到的结果是全局最优的。
1. 分配饼干
455. Assign Cookies (Easy)
class Solution {
public int findContentChildren(int[] g, int[] s) {
if(g.length == 0 || s.length ==0){
return 0;
}
Arrays.sort(g);
Arrays.sort(s);
int num = 0;
int i=0;
int j=0;
while(i<g.length && j < s.length){
if(g[i] <= s[j]){
num++;
i++;
j++;
}else{
j++;
}
}
return num;
}
}
2. 不重叠的区间个数
435. Non-overlapping Intervals (Medium)
class Solution {
public int eraseOverlapIntervals(int[][] intervals) {
if(intervals.length == 0){
return 0;
}
Arrays.sort(intervals,Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o[1]));
int cnt = 1;
int end = intervals[0][1];
for(int i=1; i < intervals.length; i++){
if(intervals[i][0] < end){
continue;
}
end = intervals[i][1];
cnt++;
}
return intervals.length - cnt;
}
}
3. 投飞镖刺破气球
452. Minimum Number of Arrows to Burst Balloons (Medium)
题目描述:气球在一个水平数轴上摆放,可以重叠,飞镖垂直投向坐标轴,使得路径上的气球都被刺破。求解最小的投飞镖次数使所有气球都被刺破。
也是计算不重叠的区间个数,不过和 Non-overlapping Intervals 的区别在于,[1, 2] 和 [2, 3] 在本题中算是重叠区间。
class Solution {
public int findMinArrowShots(int[][] points) {
if (points.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
Arrays.sort(points, Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o[1]));
int cnt = 1, end = points[0][1];
for (int i = 1; i < points.length; i++) {
if (points[i][0] <= end) {
continue;
}
cnt++;
end = points[i][1];
}
return cnt;
}
}
四、二分查找
正常实现
Input : [1,2,3,4,5]
key : 3
return the index : 2
public int binarySearch(int[] nums, int key) {
int l = 0, h = nums.length - 1;
while (l <= h) {
int m = l + (h - l) / 2;
if (nums[m] == key) {
return m;
} else if (nums[m] > key) {
h = m - 1;
} else {
l = m + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
时间复杂度
二分查找也称为折半查找,每次都能将查找区间减半,这种折半特性的算法时间复杂度为 O(logN)。
m 计算
有两种计算中值 m 的方式:
- m = (l + h) / 2
- m = l + (h - l) / 2
l + h 可能出现加法溢出,也就是说加法的结果大于整型能够表示的范围。但是 l 和 h 都为正数,因此 h - l 不会出现加法溢出问题。所以,最好使用第二种计算法方法。
未成功查找的返回值
循环退出时如果仍然没有查找到 key,那么表示查找失败。可以有两种返回值:
- -1:以一个错误码表示没有查找到 key
- l:将 key 插入到 nums 中的正确位置
变种
二分查找可以有很多变种,实现变种要注意边界值的判断。例如在一个有重复元素的数组中查找 key 的最左位置的实现如下:
public int binarySearch(int[] nums, int key) {
int l = 0, h = nums.length - 1;
while (l < h) {
int m = l + (h - l) / 2;
if (nums[m] >= key) {
h = m;
} else {
l = m + 1;
}
}
return l;
}
该实现和正常实现有以下不同:
- h 的赋值表达式为 h = m
- 循环条件为 l < h
- 最后返回 l 而不是 -1
在 nums[m] >= key 的情况下,可以推导出最左 key 位于 [l, m] 区间中,这是一个闭区间。h 的赋值表达式为 h = m,因为 m 位置也可能是解。
在 h 的赋值表达式为 h = m 的情况下,如果循环条件为 l <= h,那么会出现循环无法退出的情况,因此循环条件只能是 l < h。以下演示了循环条件为 l <= h 时循环无法退出的情况:
nums = {0, 1, 2}, key = 1
l m h
0 1 2 nums[m] >= key
0 0 1 nums[m] < key
1 1 1 nums[m] >= key
1 1 1 nums[m] >= key
...
当循环体退出时,不表示没有查找到 key,因此最后返回的结果不应该为 -1。为了验证有没有查找到,需要在调用端判断一下返回位置上的值和 key 是否相等。
1. 求开方
69. Sqrt(x) (Easy)
public int mySqrt(int x) {
if (x <= 1) {
return x;
}
int l = 1, h = x;
while (l <= h) {
int mid = l + (h - l) / 2;
int sqrt = x / mid;
if (sqrt == mid) {
return mid;
} else if (mid > sqrt) {
h = mid - 1;
} else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}
return h;
}
2. 大于给定元素的最小元素
744. Find Smallest Letter Greater Than Target (Easy)
class Solution {
public char nextGreatestLetter(char[] letters, char target) {
int n = letters.length;
int l = 0;
int h = n - 1;
while(l <= h) {
int m = l + (h - l)/2;
if (letters[m] <= target){
l = m + 1;
}else {
h = m - 1;
}
}
return l < n ? letters[l] : letters[0];
}
}
3. 有序数组的 Single Element
540. Single Element in a Sorted Array (Medium)
class Solution {
public int singleNonDuplicate(int[] nums) {
int l = 0;
int h = nums.length - 1;
while(l < h){
int m = l + (h - l) / 2;
if(m % 2 == 1) {
m--;
}
if(nums[m] == nums[m + 1]){
l = m + 2;
} else {
h = m;
}
}
return nums[l];
}
}
五、分治
1. 给表达式加括号
241. Different Ways to Add Parentheses (Medium)
class Solution {
public List<Integer> diffWaysToCompute(String input) {
List<Integer> ways = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < input.length();i++){
char c = input.charAt(i);
if(c == '+' || c == '-' || c == '*'){
List<Integer> left = diffWaysToCompute(input.substring(0,i));
List<Integer> right = diffWaysToCompute(input.substring(i + 1));
for(int l : left) {
for(int r : right) {
switch(c) {
case '+':
ways.add(l + r);
break;
case '-':
ways.add(l - r);
break;
case '*':
ways.add(l * r);
break;
}
}
}
}
}
if(ways.size() == 0){
ways.add(Integer.valueOf(input));
}
return ways;
}
}
2. 不同的二叉搜索树
95. Unique Binary Search Trees II (Medium)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<TreeNode> generateTrees(int n) {
if(n < 1) {
return new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
}
return generateSubtrees(1, n);
}
private List<TreeNode> generateSubtrees(int s, int e) {
List<TreeNode> res = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
if (s > e) {
res.add(null);
return res;
}
for(int i = s; i <= e; ++i) {
List<TreeNode> leftSubtrees = generateSubtrees(s, i - 1);
List<TreeNode> rightSubtrees = generateSubtrees(i + 1, e);
for (TreeNode left : leftSubtrees) {
for (TreeNode right : rightSubtrees){
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(i);
root.left = left;
root.right = right;
res.add(root);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
六、搜索
深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索广泛运用于树和图中,但是它们的应用远远不止如此。
BFS
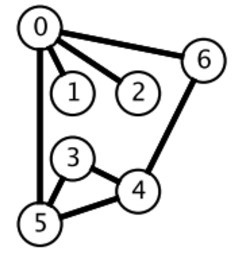
广度优先搜索一层一层地进行遍历,每层遍历都是以上一层遍历的结果作为起点,遍历一个距离能访问到的所有节点。需要注意的是,遍历过的节点不能再次被遍历。
第一层:
- 0 -> {6,2,1,5}
第二层:
- 6 -> {4}
- 2 -> {}
- 1 -> {}
- 5 -> {3}
第三层:
- 4 -> {}
- 3 -> {}
每一层遍历的节点都与根节点距离相同。设 di 表示第 i 个节点与根节点的距离,推导出一个结论:对于先遍历的节点 i 与后遍历的节点 j,有 di <= dj。利用这个结论,可以求解最短路径等 最优解 问题:第一次遍历到目的节点,其所经过的路径为最短路径。应该注意的是,使用 BFS 只能求解无权图的最短路径,无权图是指从一个节点到另一个节点的代价都记为 1。
在程序实现 BFS 时需要考虑以下问题:
- 队列:用来存储每一轮遍历得到的节点;
- 标记:对于遍历过的节点,应该将它标记,防止重复遍历。
1. 计算在网格中从原点到特定点的最短路径长度
1091. Shortest Path in Binary Matrix(Medium)
class Solution {
public int shortestPathBinaryMatrix(int[][] grid) {
if (grid == null || grid.length == 0 || grid[0].length == 0) {
return -1;
}
int[][] direction = {{1,-1}, {1,0}, {1,1}, {0,-1}, {0,1}, {0,1}, {-1,-1}, {-1,0}, {-1,1}};
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
Queue<Pair<Integer, Integer>> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new Pair<>(0, 0));
int pathLength = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
pathLength++;
while (size-- > 0){
Pair<Integer, Integer> cur = queue.poll();
int cr = cur.getKey();
int cc = cur.getValue();
if (grid[cr][cc] == 1) {
continue;
}
if (cr == m-1 && cc == n-1) {
return pathLength;
}
grid[cr][cc] = 1;
for (int[] d:direction) {
int nr = cr + d[0];
int nc = cc + d[1];
if (nr < 0 || nr >= m || nc < 0 || nc >= n) {
continue;
}
queue.add(new Pair<>(nr, nc));
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
查找最大的连通面积
数字键盘组合