1、关于set
C++ STL之所以得到广泛的赞誉,也被很多人使用,不只是提供了像vector,string,list等方便的容器,更重要的是STL封装了许多复杂的数据结构算法和大量常用数据结构操作。vector封装了数组,list封装了链表,map和set封装了二叉树等。在封装这些数据结构的时候,STL按照程序员的使用习惯,以成员函数方式提供的常用操作,如:插入、排序、删除、查找等。
关于set,必须说明的是set关联式容器。set作为一个容器也是用来存储同一数据类型的数据类型。set中每个元素的值都唯一,而且系统能根据元素的值自动进行排序。C++ STL中标准关联容器set,multiset,map,multimap内部采用的就是一种非常高效的平衡检索二叉树:红黑树,也称为RB树(Red-Black Tree)。RB树的统计性能要好于一般平衡二叉树,所以被STL选择作为了关联容器的内部结构。
(1)为何map和set的插入删除效率比用其它序列容器高?
因为对于关联容器来说,不需要做内存拷贝和内存移动。set容器内的所有元素都是以节点的方式来存储,其节点结构和链表差不多,指向父节点和子节点。结构图如下:
A
/
B C
/ /
D E F G
因此插入的时候只需要稍作变换,把节点的指针指向新的节点就可以了。删除的时候类似,稍作变换后把指向删除节点的指针指向其它节点就OK了。这里的一切操作都是指针换来换去,和内存移动没有关系。
(2)为何每次insert之久,以前保存的iterator不会失效?
iterator这里就相当于指向节点的指针,内存没有变,指向内存的指针怎么会失效呢?(当然被删除的那个元素本身已经失效了)相对于vector来说,每一次删除和插入,指针都有可能失效,调用push_back在尾部插入也是如此。因为为了保证内部数据的连续存放,iterator指向的那块内存在删除和插入过程中可能已经被其它内存覆盖或内存已经被释放了。即使是push_back的时候,容器内部空间可能不够,需要一块新的更大的内存,只有把以前的内存释放,申请新的更大的内存,复制已有的数据元素元素到新的内存,最后把需要插入的元素放到最后,那么以前的内存指针自然就不可用了。特别是在和find等算法在一起使用时,牢记:不要使用过期的iterator。
(3)当数据元素增多时,set的插入和搜索速度变化如何?
在set中查找是使用二分查找,复杂度是log2n。也就是说,如果有16个元素,最多需要比较4次就能找到结果,有32个元素,最多比较5次。那么有100000个呢?最多比较的次数为log10000,最多为14次,如果是200000个元素呢?最多不过15次。当数据量增大一倍的时候,搜索次数只不过多了1次,多了1/14的搜索时间而已。
2、set中常用的方法
begin() ,返回一个迭代器,返回的值为set容器的第一个元素
end() ,返回一个迭代器,返回的值为set容器的最后一个元素
clear() ,删除set容器中的所有的元素
empty() ,判断set容器是否为空
max_size() ,返回set容器可能包含的元素最大个数
size() ,返回当前set容器中的元素个数
rbegin() ,返回一个逆迭代器,返回的值和end()相同
rend() ,返回一个逆迭代器,它指向容器c的第一个元素前面的位置
count() ,用来查找set中某个某个键值出现的次数。这个函数在set并不是很实用,因为一个键值在set只可能出现0或1次,这样就变成了判断某一键值是否在set出现过了。
erase(iterator) ,删除定位器iterator指向的值
erase(first,second) ,删除定位器first和second之间的值,包含first指向的值,不包含second指向的值,即左闭右开
erase(key_value) ,删除键值key_value的值
试试erase的用法:
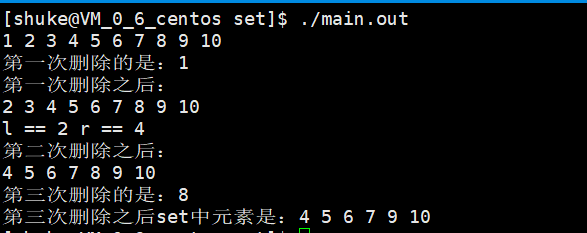
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <set> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main(int argc,char* argv[]) 7 { 8 set<int> s; 9 set<int>::iterator iter; 10 set<int>::const_iterator const_iter; 11 set<int>::iterator first; 12 set<int>::iterator second; 13 14 for(int i = 1; i <= 10; ++i) 15 { 16 s.insert(i); 17 cout << i << " "; 18 } 19 cout << endl; 20 iter = s.begin(); 21 cout << "第一次删除的是:" << *iter << endl; 22 s.erase(s.begin()); 23 cout << "第一次删除之后:" << endl; 24 for(const_iter = s.begin();const_iter != s.end();++const_iter) 25 { 26 cout << *const_iter << " "; 27 } 28 cout << endl; 29 first = s.begin(); 30 second = s.begin(); 31 second++; 32 second++; 33 cout << "l == " << *first << " r == " << *second << endl; 34 s.erase(first,second); 35 cout << "第二次删除之后:" << endl; 36 for(const_iter = s.begin();const_iter != s.end();++const_iter) 37 { 38 cout << *const_iter << " "; 39 } 40 cout << endl; 41 42 s.erase(8); 43 cout << "第三次删除的是:8" << endl; 44 cout << "第三次删除之后set中元素是:" ; 45 for(const_iter = s.begin();const_iter != s.end();++const_iter) 46 { 47 cout << *const_iter << " "; 48 } 49 cout << endl; 50 return 0; 51 }
运行结果:
find() ,返回给定值的定位器,如果没找到则返回end()。
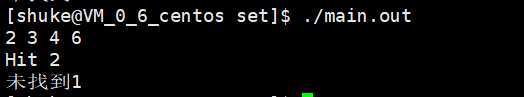
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <set> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main(int argc,char* argv[]) 7 { 8 int a[] = {4,6,2,3}; 9 set<int> s(a,a + 4); 10 set<int>::iterator iter; 11 for(iter = s.begin();iter != s.end();iter++) 12 { 13 cout << *iter << " "; 14 } 15 16 cout << endl; 17 if((iter = s.find(2)) != s.end()) 18 cout<< "Hit " << *iter << endl; 19 if((iter = s.find(1)) != s.end()) 20 cout << "Hit " << *iter << endl; 21 else 22 cout <<"未找到1" << endl; 23 24 return 0; 25 }
运行结果:
insert(key_value); 将key_value插入到set中 ,返回值是pair<set<int>::iterator,bool>,bool标志着插入是否成功,而iterator代表插入的位置,若key_value已经在set中,则iterator表示的key_value在set中的位置。
inset(first,second); 将定位器first到second之间的元素插入到set中,返回值是void.
示例代码:
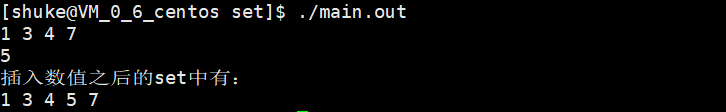
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <set> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 int a[] = {1, 4, 3, 7}; 9 set<int> s; 10 set<int>::iterator iter; 11 s.insert(a,a + 4); 12 for(iter = s.begin() ; iter != s.end() ; ++iter) 13 { 14 cout<<*iter<<" "; 15 } 16 cout<<endl; 17 pair<set<int>::iterator,bool> pr; 18 pr = s.insert(5); 19 if(pr.second) 20 { 21 cout<<*pr.first<<endl; 22 } 23 cout << " 插入数值之后的set中有:" << endl; 24 for(iter = s.begin() ; iter != s.end() ; ++iter) 25 { 26 cout<<*iter<<" "; 27 } 28 cout<<endl; 29 30 return 0; 31 }
运行结果:
lower_bound(key_value) ,返回第一个大于等于key_value的定位器
upper_bound(key_value),返回第一个大于key_value的定位器
示例代码:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <set> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main(int argc,char* argv[]) 7 { 8 int a[] = {1,3,5,4,6}; 9 set<int> s; 10 s.insert(a,a + 5); 11 set<int>::iterator iter; 12 for(iter = s.begin();iter != s.end();++iter) 13 { 14 cout << *iter << " "; 15 } 16 cout << endl; 17 cout << "第一个大于等于2的值是: "; 18 cout << *s.lower_bound(2) << endl; 19 cout << "第一个大于等于3的值是: "; 20 cout << *s.lower_bound(3) << endl; 21 cout << "第一个大于3的值是: "; 22 cout << *s.upper_bound(3) << endl; 23 return 0; 24 }
运行结果:

3、自定义比较函数
3.1重载<操作符
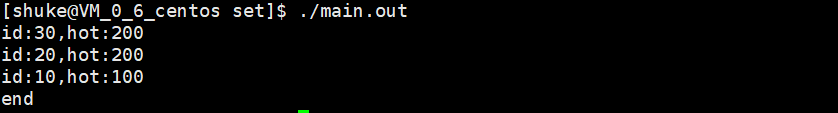
1 class song 2 { 3 public: 4 song(int id,int hot) 5 { 6 this->m_id = id; 7 this->m_hot = hot; 8 } 9 bool operator<(const class song & right)const //重载<运算符 10 { 11 if(this->m_id == right.m_id) //根据id去重 12 return false; 13 if(this->m_hot != right.m_hot) 14 return this->m_hot > right.m_hot; //按热度降序 15 else 16 return this->m_id > right.m_id; //热度相同,按id降序 17 } 18 int m_id; 19 int m_hot; 20 }; 21 int main(int argc,char* argv[]) 22 { 23 set<song> mySet; 24 song s1(10,100); 25 song s2(20,200); 26 song s3(20,300); 27 song s4(30,200); 28 mySet.insert(s1); //插入s1 29 mySet.insert(s2); //插入s2 30 mySet.insert(s3); //s3和s2的id相同,不插入 31 mySet.insert(s4); //插入s4 32 for(auto it : mySet) 33 { 34 cout << "id:" << it.m_id << ",hot:" << it.m_hot << endl; 35 } 36 cout << "end" << endl; 37 return 0; 38 }
运行结果:
3.2重载()运算符
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <set> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 class song 6 { 7 public: 8 song(int id,int hot) 9 { 10 this->m_id = id; 11 this->m_hot = hot; 12 } 13 /* 14 bool operator<(const class song & right)const //重载<运算符 15 { 16 if(this->m_id == right.m_id) //根据id去重 17 return false; 18 if(this->m_hot != right.m_hot) 19 return this->m_hot > right.m_hot; //按热度降序 20 else 21 return this->m_id > right.m_id; //热度相同,按id降序 22 } 23 */ 24 int m_id; 25 int m_hot; 26 }; 27 class comp 28 { 29 public: 30 bool operator()(class song left,class song right) //重载()运算符 31 { 32 if(left.m_id == right.m_id) 33 return false; 34 if(left.m_hot != right.m_hot) 35 return left.m_hot > right.m_hot; //按热度降序 36 else 37 return left.m_id > right.m_id; //热度相同,按id降序 38 } 39 }; 40 int main(int argc,char* argv[]) 41 { 42 /*自定义比较函数的用法*/ 43 /*重载<运算符的用法*/ 44 //set<song> mySet; 45 //song s1(10,100); 46 //song s2(20,200); 47 //song s3(20,300); 48 //song s4(30,200); 49 //mySet.insert(s1); //插入s1 50 //mySet.insert(s2); //插入s2 51 //mySet.insert(s3); //s3和s2的id相同,不插入 52 //mySet.insert(s4); //插入s4 53 //for(auto it : mySet) 54 //{ 55 // cout << "id:" << it.m_id << ",hot:" << it.m_hot << endl; 56 //} 57 //cout << "end" << endl; 58 //return 0; 59 60 /*重载()运算符的用法*/ 61 set<song,comp> mySet; 62 song s1(10,100); 63 song s2(20,200); 64 song s3(20,300); 65 song s4(30,200); 66 mySet.insert(s1); //插入s1 67 mySet.insert(s2); //插入s2 68 mySet.insert(s3); //s3和s2的id相同,不插入 69 mySet.insert(s4); //插入s4 70 for(auto it : mySet) 71 { 72 cout << "id:" << it.m_id << ",hot:" << it.m_hot << endl; 73 } 74 cout << "end" << endl; 75 return 0; 76 }
运行结果: