有时候把Python函数调用的命名参数都收集到一个dict中可以更方便地做参数检查,或者直接由参数创建attribute等。更简单的理解就是def foo(*args, **kwargs): pass可以接受所有的参数,其中kwargs就是命名参数字典,那么直接在函数外面套个foo却不能达到目的,一个比较简单的实现是这样的:
def annotation(**annotations):
"""
A decorator to collect all named args to function.__namedargs__,
all anonymous args to function.__unnamedargs__,
decorator's args to function.__annotations__.
"""
def func_decorator(func):
@functools.wraps(func)
def func_wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
argspec = inspect.getargspec(func)
namedargs = inspect.getcallargs(func, *args, **kwargs)
# def foo(a, b=0, *c, **d): pass
# foo(1, b=2, c=3, d=4) will convert c=3 to namedargs.
unnamedargs = namedargs.pop(argspec.varargs, ())
namedargs.update(namedargs.pop(argspec.keywords, {}))
func_wrapper.__namedargs__ = namedargs
func_wrapper.__unnamedargs__ = unnamedargs
func_wrapper.__annotations__ = annotations
func(*args, **kwargs)
return func_wrapper
return func_decorator
annotation的的用法仿照Python 3的Function Annotation,可以对参数做标记等,这里所有的标记都会存放在function.__annotations__中:
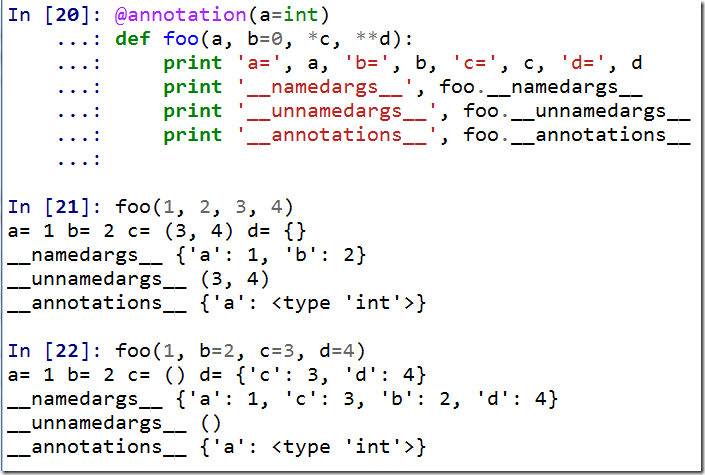
如果只要annotation,那么可以这样做避免额外调用开销:
def annotation(**anno):
"""
A decorator to update decorator's args to function.__annotations__.
"""
def func_decorator(func):
"""
Static check annotation.
"""
argspec = inspect.getargspec(func)
callargs = set(argspec.args)
callargs.add(argspec.varargs)
callargs.add(argspec.keywords)
invalid_keys = anno.viewkeys() - callargs
if invalid_keys:
raise TypeError('Invalid annotation keys = %s' % (invalid_keys))
else:
func.__annotations__ = anno
return func
return func_decorator