一、二叉树
1.满二叉树
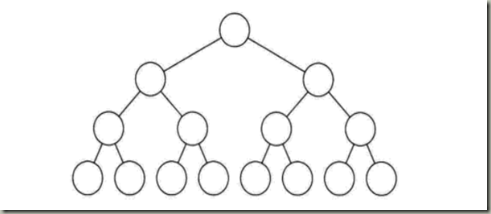
2.完全二叉树
对一棵具有n个结点的二叉树按层序排号,如果编号为 i 的结点与同样深度的 满二叉树 编号为 i 结点在二叉树中位置完全相同,就是完全二叉树。
满二叉树必须是完全二叉树,反过来不一定成立。
其中关键点是按层序编号,然后对应查找。
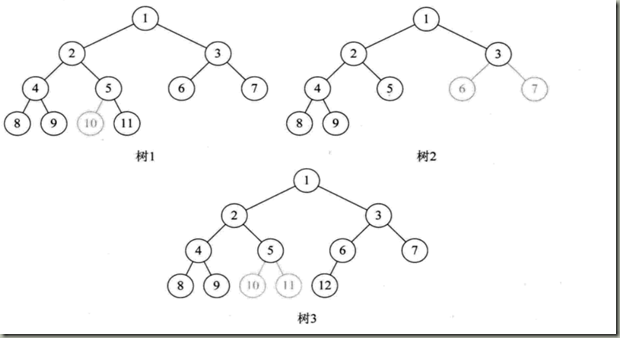
在上图中,
树1,按层次编号5结点没有左子树,有右子树,10结点缺失。
树2由于3结点没有子树,是的6,7位置空挡了。
树3中结点5没有子树。
上图就是一个完全二叉树。
结合完全二叉树定义得到其特点:
- 叶子结点只能出现在最下一层(满二叉树继承而来)
- 最下层叶子结点一定集中在左 部连续位置。
- 倒数第二层,如有叶子节点,一定出现在右部连续位置。
- 同样结点树的二叉树,完全二叉树的深度最小(满二叉树也是对的)。
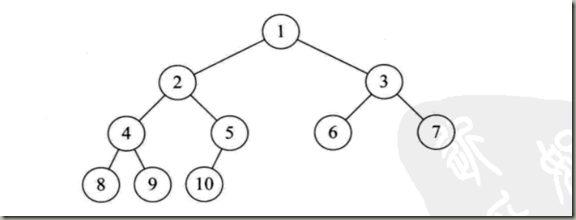
根据下图加深理解,什么时候是完全二叉树。
二、二叉树性质
①一般二叉树性质
1、在非空二叉树的i层上,至多有2i-1个节点(i>=1)。通过归纳法论证。
2、在深度为K的二叉树上最多有2k-1个结点(k>=1)。通过归纳法论证。
3、对于任何一棵非空的二叉树,如果叶节点个数为n0,度数为2的节点个数为n2,则有: n0 = n2 + 1
在一棵二叉树中,除了叶子结点(度为0)之外,就剩下度为2(n2)和1(n1)的结点了。则树的结点总数为T = n0+n1+n2;
在二叉树中结点总数为T,而连线数为T-1.所以有:n0+n1+n2-1 = 2*n2 +n1;最后得到n0 = n2+1;
上图中结点总数是10,n2为4,n1为1,n0为5。
② 完全二叉树性质
1、具有n的结点的完全二叉树的深度为log2n+1.
满二叉树是完全二叉树,对于深度为k的满二叉树中结点数量是2k-1 = n,完全二叉树结点数量肯定最多2k-1,同时完全二叉树倒数第二层肯定是满的(倒数第一层有结点,那么倒是第二层序号和满二叉树相同),所以完全二叉树的结点数最少大于少一层的满二叉树,为2k-1-1。
根据上面推断得出: 2k-1-1< n=<2k-1,因为结点数Nn为整数那么n<=2k-1可以推出n<=2k ,n>2k-1-1可以推出 n>=2k-1,所以2k-1<n<=2k 。即可得k-1<=log2n<k 而k作为整数因此k=[log2n]+1。
2、如果有一颗有n个节点的完全二叉树的节点按层次序编号,对任一层的节点i(1<=i<=n)有
1.如果i=1,则节点是二叉树的根,无双亲,如果i>1,则其双亲节点为[i/2],向下取整
2.如果2i>n那么节点i没有左孩子,否则其左孩子为2i
3.如果2i+1>n那么节点没有右孩子,否则右孩子为2i+1
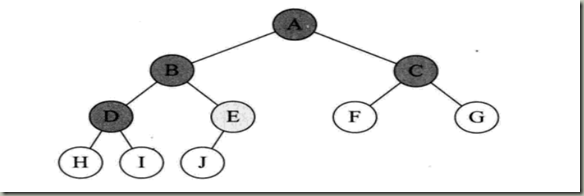
在上图中验证
第一条:
当i=1时,为根节点。当i>1时,比如结点为7,他的双亲就是7/2= 3;结点9双亲为4.
第二条:
结点6,6*2 = 12>10,所以结点6无左孩子,是叶子结点。结点5,5*2 = 10,左孩子是10,结点4,为8.
第三条:
结点5,2*5+1>10,没有右孩子,结点4,则有右孩子。
三、二叉树遍历(先序,中序,后序)
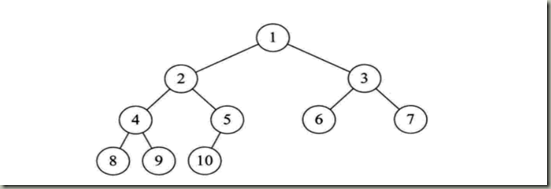
以下是我要解析的一个二叉树的模型形状
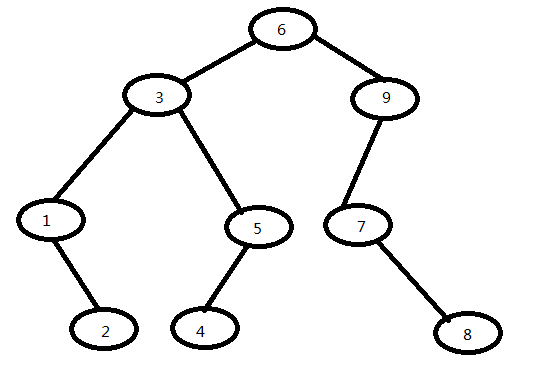
先序遍历
631254978
中序遍历
123456789
后序遍历
214538796
接下来废话不多直接上代码
一种是用递归的方法,另一种是用堆栈的方法:
首先创建一棵树:
public class Node {
private int data;
private Node leftNode;
private Node rightNode;
public Node(int data, Node leftNode, Node rightNode){
this.data = data;
this.leftNode = leftNode;
this.rightNode = rightNode;
}
public int getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node getLeftNode() {
return leftNode;
}
public void setLeftNode(Node leftNode) {
this.leftNode = leftNode;
}
public Node getRightNode() {
return rightNode;
}
public void setRightNode(Node rightNode) {
this.rightNode = rightNode;
}
}
递归:
public class BinaryTree {
/**
* @author yaobo
* 二叉树的先序中序后序排序
*/
public Node init() {//注意必须逆序建立,先建立子节点,再逆序往上建立,因为非叶子结点会使用到下面的节点,而初始化是按顺序初始化的,不逆序建立会报错
Node J = new Node(8, null, null);
Node H = new Node(4, null, null);
Node G = new Node(2, null, null);
Node F = new Node(7, null, J);
Node E = new Node(5, H, null);
Node D = new Node(1, null, G);
Node C = new Node(9, F, null);
Node B = new Node(3, D, E);
Node A = new Node(6, B, C);
return A; //返回根节点
}
public void printNode(Node node){
System.out.print(node.getData());
}
public void theFirstTraversal(Node root) { //先序遍历
printNode(root);
if (root.getLeftNode() != null) { //使用递归进行遍历左孩子
theFirstTraversal(root.getLeftNode());
}
if (root.getRightNode() != null) { //递归遍历右孩子
theFirstTraversal(root.getRightNode());
}
}
public void theInOrderTraversal(Node root) { //中序遍历
if (root.getLeftNode() != null) {
theInOrderTraversal(root.getLeftNode());
}
printNode(root);
if (root.getRightNode() != null) {
theInOrderTraversal(root.getRightNode());
}
}
public void thePostOrderTraversal(Node root) { //后序遍历
if (root.getLeftNode() != null) {
thePostOrderTraversal(root.getLeftNode());
}
if(root.getRightNode() != null) {
thePostOrderTraversal(root.getRightNode());
}
printNode(root);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
Node root = tree.init();
System.out.println("先序遍历");
tree.theFirstTraversal(root);
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("中序遍历");
tree.theInOrderTraversal(root);
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("后序遍历");
tree.thePostOrderTraversal(root);
System.out.println("");
}
}
堆栈:
public class BinaryTree1 {
public Node init() {//注意必须逆序建立,先建立子节点,再逆序往上建立,因为非叶子结点会使用到下面的节点,而初始化是按顺序初始化的,不逆序建立会报错
Node J = new Node(8, null, null);
Node H = new Node(4, null, null);
Node G = new Node(2, null, null);
Node F = new Node(7, null, J);
Node E = new Node(5, H, null);
Node D = new Node(1, null, G);
Node C = new Node(9, F, null);
Node B = new Node(3, D, E);
Node A = new Node(6, B, C);
return A; //返回根节点
}
public void printNode(Node node){
System.out.print(node.getData());
}
public void theFirstTraversal_Stack(Node root) { //先序遍历
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
Node node = root;
while (node != null || stack.size() > 0) { //将所有左孩子压栈
if (node != null) { //压栈之前先访问
printNode(node);
stack.push(node);
node = node.getLeftNode();
} else {
node = stack.pop();
node = node.getRightNode();
}
}
}
public void theInOrderTraversal_Stack(Node root) { //中序遍历
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
Node node = root;
while (node != null || stack.size() > 0) {
if (node != null) {
stack.push(node); //直接压栈
node = node.getLeftNode();
} else {
node = stack.pop(); //出栈并访问
printNode(node);
node = node.getRightNode();
}
}
}
public void thePostOrderTraversal_Stack(Node root) { //后序遍历
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
Stack<Node> output = new Stack<Node>();//构造一个中间栈来存储逆后序遍历的结果
Node node = root;
while (node != null || stack.size() > 0) {
if (node != null) {
output.push(node);
stack.push(node);
node = node.getRightNode();
} else {
node = stack.pop();
node = node.getLeftNode();
}
}
System.out.println(output.size());
while (output.size() > 0) {
printNode(output.pop());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree1 tree = new BinaryTree1();
Node root = tree.init();
System.out.println("先序遍历");
tree.theFirstTraversal_Stack(root);
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("中序遍历");
tree.theInOrderTraversal_Stack(root);
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("后序遍历");
tree.thePostOrderTraversal_Stack(root);
System.out.println("");
}
}
参考出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/polly333/p/4740355.html, http://www.cnblogs.com/yaobolove/p/6213936.html