具体分工
- 031601131 杨喜源:负责WordCount代码编写。
- 031601232 朱志豪:负责爬虫和附加题编写。
PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 30 | 30 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 60 | 60 |
| Development | 开发 | 300 | 400 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 60 | 60 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 30 | 30 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 | 30 | 30 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 30 | 20 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 60 | 120 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 120 | 150 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 120 | 210 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 180 | 180 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 60 | 80 |
| · Test Repor | · 测试报告 | 20 | 20 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 10 | 10 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 30 | 20 |
| 合计 | 1110 | 1420 |
解题思路描述与设计实现说明
爬虫使用
本次爬虫采用python完成,代码是自己写的
思路:
爬取[CVPR2018网页](http://openaccess.thecvf.com/CVPR2018.py)内容,用正则表达式将网页内容中论文链接提前到字符串数组中。
遍历数组,在每次访问论文网页的过程中将论文标题和摘要爬取出来。
根据题目要求的输出格式,将数据输出到result.txt文件中。
代码:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from urllib.request import urlopen
import re
import random
filename = 'data.txt'
base_url = "http://openaccess.thecvf.com/CVPR2018.py"
b_url="http://openaccess.thecvf.com/"
html = urlopen(base_url).read().decode('utf-8')
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, features='lxml')
sub_urls = soup.find_all("a", { "href": re.compile("content_cvpr_2018/html/(.)+CVPR_2018_paper.html$")})
k=len(sub_urls)
print(k)
with open(filename,'w',encoding='utf-8') as f:
for i in range (5):
his=sub_urls[i]['href']
url= b_url + his
html2 = urlopen(url).read().decode('utf-8')
soup2 = BeautifulSoup(html2, features='lxml')
sub_urls2 = soup2.find_all("div",id="papertitle")
sub_urls3 = soup2.find_all("div",id="abstract")
j=str(i)
f.write(j)
f.write('
')
f.write("Title:"+sub_urls2[0].text.lstrip('
'))
f.write('
')
f.write("Abstract:"+sub_urls3[0].text.lstrip('
'))
f.write('
')
f.write("
")`
代码组织与内部实现设计(类图)
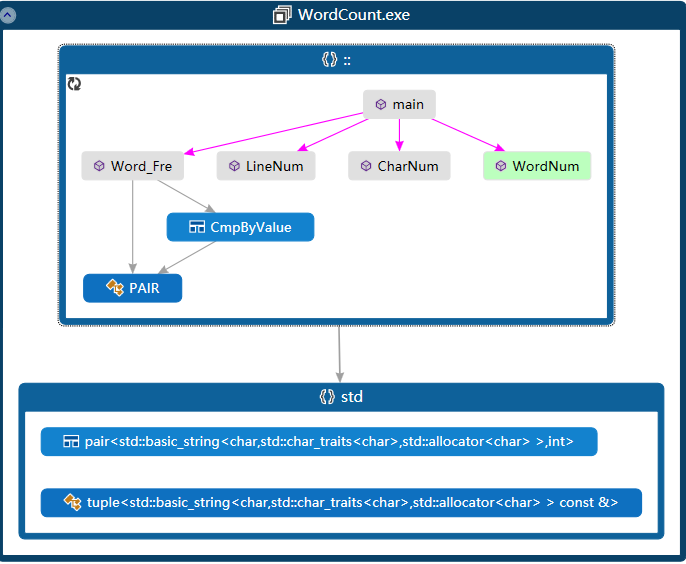
- main():处理命令行输入的字符串,把处理后参数传递给其他函数。
- CharNum():统计字符数量。
- LineNum():统计行数量。
- WordNum():统计单词数量。
- Word_Fre():通过主函数传递的-m,-n,-w参数来输出词频前n的词组。
说明算法的关键与关键实现部分流程图
由于本次作业与个人作业2的代码部分相同,如判断单词等。这里就不赘述了。
处理命令行输入的字符串
- 命令行输入的内容传递到 char *argv[]的二维数组中,通过查找其中的"-i","-o","-m","-w","-n"等字符串的下一个字符串即为要传入的参数
- 由于"-i","-o"所传递的本身为字符串,所以无需做特殊处理,记录其下标即可。
- 而"-m","-w","-n"所要传递的参数为int型,所以要用atoi()函数将string转换为int
- 由于"-i","-o","-w"必须传入,所以对未传入这个三个参数的命令行应该报错
部分代码如下:
int topn = 10;
int word_m = 1;
int word_w = 1;
int i = 1;
int infile=-1, outfile=-1;
string in = "-i",o="-o",w="-w",m="-m",n="-n";
while (argv[i])
{
if (argv[i] == in) infile = i + 1;
if (argv[i] == o) outfile = i + 1;
if (argv[i] == w) word_w= atoi(argv[i+1]);
if (argv[i] == m) word_m = atoi(argv[i + 1]);
if (argv[i] == n) topn = atoi(argv[i + 1]);
i++;
}
权重的设置和改变 -w
根据论文的爬取结果格式,可以很明显的看出,一篇论文共占用5行,其中第二行为"Title: "行,第三行为"Abstract: "行
- 对回车数(int huiche)进行统计,则回车数huiche%5==1为"Title: "行,回车数huiche%5==2为"Abstract: "行。
- 执行完huiche%51和huiche%52,后将光标移动到“:”冒号后,可以消除Abstract: 和Title: 对统计的影响,同时也可以消除论文编号和Title:行和Abstract:行可能出现的空白行 回车符不被记录,保证一遍论文占用5行。
- 判断完此时为Title:行还是Abstract:行就可以改变此次的权重了
代码如下:
if (w == 1) //赋值权重
{
if (ch == '
')
{
huiche++;
if (huiche % 5 == 1)
{
while ((ch = fgetc(file)) != ':');
quanzhong = 10;
}
if (huiche % 5 == 2)
{
while ((ch = fgetc(file)) != ':');
quanzhong = 1;
}
}
}
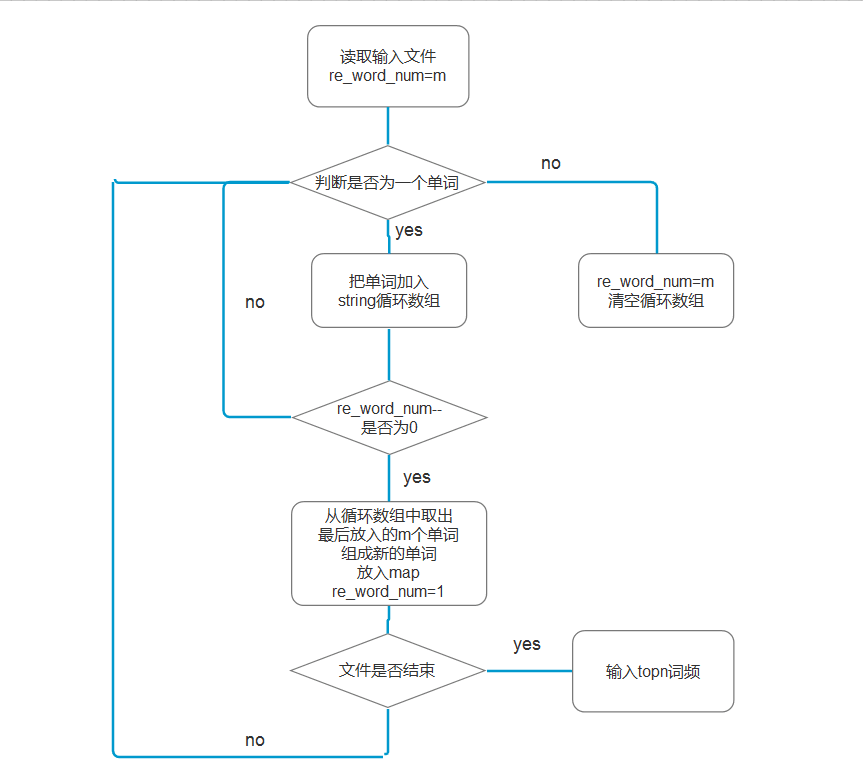
词组统计 -m
如何判断是否为一个单词这里就不重复了,详见这里
本篇重点介绍如何判断一个词组。
- 由于实际情况词组出现频率前几都是以空格为分隔符的词组,所以这里将分隔符不是空格的词组忽略
- 这里使用一个string word_array[20]模拟循环数组来暂时存放单词,用int re_word_num记录一个词组还剩余的单词数
- 当re_word_num==0时,表示此时已经记录了m个单词了,就将循环数组中,最后放入的m的单词取出,中间加空格生成词组,并加入map,同时把re_word_num=1表示在来一个单词就可以生成新的词组了。
- 当遇到一个失败的单词时,re_word_num=m即重新记录单词数量。
- 最后将map转换为vector,用sort进行排序,输出前n个即可。
代码如下:
string word_array[20];
int wn = 0;
int re_word_num = m;
for (; (ch = fgetc(file)) != EOF;) //Determine the word and insert map
{
if ('A' <= ch && ch <= 'Z')
ch = ch + 32;
if (flag == 0) {
if (ch >= 'a'&&ch <= 'z') { flag = 1; word = word + ch; }
else if (ch !=' ') { wn = 0; re_word_num=m; }
}
else if (flag == 1) {
if (ch >= 'a'&&ch <= 'z') { flag = 2; word = word + ch; }
else { flag = 0; word = ""; wn = 0; re_word_num = m;}
}
else if (flag == 2) {
if (ch >= 'a'&&ch <= 'z') { flag = 3; word = word + ch; }
else { flag = 0; word = ""; wn = 0; re_word_num = m;}
}
else if (flag == 3) {
if (ch >= 'a'&&ch <= 'z') { flag = 4; word = word + ch; }
else { flag = 0; word = ""; wn = 0; re_word_num = m;}
}
else if (flag == 4) {
if (ch >= 'a'&&ch <= 'z' || (ch >= '0'&&ch <= '9')) { word = word + ch; }
else {
word_array[wn % 20] = word;
word_num++;
wn++;
re_word_num--;
word = "";
if (re_word_num == 0)
{
for (int j = m; j > 1; j--)
word = word + word_array[(wn - j) % 20]+" ";
word = word + word_array[(wn - 1) % 20];
Word_Num_map[word] = Word_Num_map[word] + quanzhong;
re_word_num = 1;
}
word = "";
flag = 0;
}
}
if (ch == '
')//换行初始化。
{
wn = 0;
re_word_num = m;
}
if (w == 1) //赋值权重
{
if (ch == '
')
{
huiche++;
if (huiche % 5 == 1)
{
while ((ch = fgetc(file)) != ':');
quanzhong = 10;
}
if (huiche % 5 == 2)
{
while ((ch = fgetc(file)) != ':');
quanzhong = 1;
}
}
}
}
if (flag == 4) {
re_word_num--;
word_array[wn % 20] = word;
wn++;
if (re_word_num == 0)
{
word = "";
for (int j = m; j > 1; j--)
word = word + word_array[(wn - j) % 30] + " ";
word = word + word_array[(wn - 1) % 30];
Word_Num_map[word] = Word_Num_map[word] ++;
}
}
vector <PAIR> Word_Num_vec(Word_Num_map.begin(), Word_Num_map.end());
sort(Word_Num_vec.begin(), Word_Num_vec.end(), CmpByValue());
FILE * stream;
freopen_s(&stream, outfile, "a", stderr);
if(Word_Num_vec.size()<n)
for (int i = 0; i != Word_Num_vec.size(); ++i) {
const char *ss = Word_Num_vec[i].first.c_str();
//cout << ss << ":" << Word_Num_vec[i].second << endl;
fprintf(stream, "<%s>: %d
", ss, Word_Num_vec[i].second);
//outfile <<"<"<< ss << ">"<<":" << Word_Num_vec[i].second << endl;);
}
else
for (int i = 0; i != n; ++i) {
const char *ss = Word_Num_vec[i].first.c_str();
fprintf(stream, "<%s>: %d
", ss, Word_Num_vec[i].second);
}
Word_Num_vec.clear();
fclose(file);
算法流程图如下:
附加题设计和展示
附加题及爬虫python代码实现和爬虫数据文本戳这里
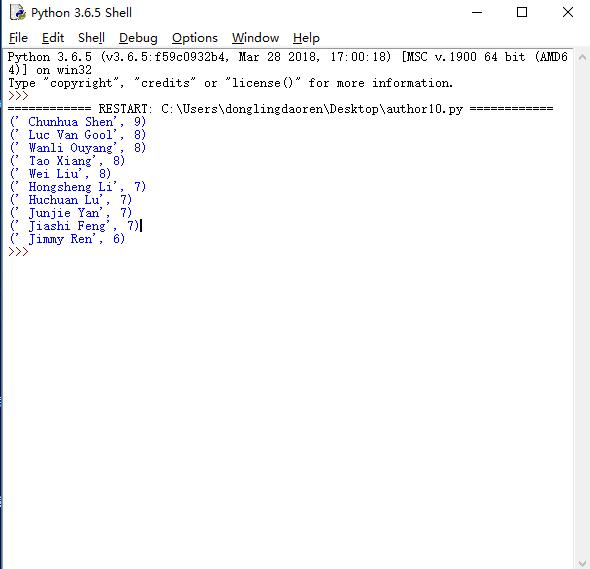
展示发文数量前十的作者:
思路:和前面爬摘要部分一样,用python可以将我们想要的作者名字爬取下来,然后用Count函数返回出现频率最高的十名作者。
结果展示图:(右侧是作者在顶会上发布论文的数量)
代码如下:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from urllib.request import urlopen
import re
import random
filename = 'author.txt'
base_url = "http://openaccess.thecvf.com/CVPR2018.py"
b_url="http://openaccess.thecvf.com/"
html = urlopen(base_url).read().decode('utf-8')
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, features='lxml')
sub_urls = soup.find_all("a", { "href": re.compile("content_cvpr_2018/html/(.)+CVPR_2018_paper.html$")})
k=len(sub_urls)
print(k)
with open(filename,'w',encoding='utf-8') as f:
for i in range (k):
his=sub_urls[i]['href']
url= b_url + his
html2 = urlopen(url).read().decode('utf-8')
soup2 = BeautifulSoup(html2, features='lxml')
sub_urls2 = soup2.find_all("div",id="authors")
ls=sub_urls2[0].text.split(";")
f.write(ls[0].lstrip('
'))
print(i)
print('yes')`
将网站中的作者名字爬出
from collections import Counter
f=open('author.txt','r',encoding="utf-8")
t=f.read()
f.close()
tx=t.strip()
ls=tx.split(",")
def counter(arr):
return Counter(arr).most_common(10) # 返回出现频率最高的十个作家
author=counter(ls)
for i in range(10):
print(author[i])`
将出现频率最高的十个作者打印出
将作者发布论文数量多少用可视化方法来体现
前面已经将论文作者的名字爬下来了,可视化部分用python的wordcloud库可以很轻易地实现这一功能
效果图如下:

代码如下:
import wordcloud
f=open('author.txt','r',encoding="utf-8")
t=f.read()
f.close()
tx=t.replace(' ','')
ls=tx.split(",")
txt=" ".join(ls)
w=wordcloud.WordCloud(width=1000,height=700)
w.generate(txt)
w.to_file("author.png")
filename = 'authorall.txt'
with open(filename,'w',encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(txt)`
将论文下载的pdf链接放到TXT文件中
用户在查看摘要的过程中,如果感兴趣,就可以凭这个链接直接下载论文的pdf或者在线阅读,本功能也可用Excel来存储,更为直观
效果图:

代码如下:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup`
from urllib.request import urlopen`
import re`
import random`
filename = 'data.txt'`
base_url = "http://openaccess.thecvf.com/CVPR2018.py"`
b_url="http://openaccess.thecvf.com/"`
html = urlopen(base_url).read().decode('utf-8')`
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, features='lxml')`
sub_urls = soup.find_all("a", { "href": re.compile("content_cvpr_2018/html/(.)+CVPR_2018_paper.html$")})`
k=len(sub_urls)`
with open(filename,'w',encoding='utf-8') as f:`
for i in range (k):`
his=sub_urls[i]['href']`
url= b_url + his`
html2 = urlopen(url).read().decode('utf-8')`
soup2 = BeautifulSoup(html2, features='lxml')`
sub_urls2 = soup2.find_all("div",id="papertitle")`
sub_urls3 = soup2.find_all("div",id="abstract")`
sub_urls4 = soup2.find_all("a", { "href":re.compile("(.)+CVPR_2018_paper.pdf$")})`
j=str(i)`
f.write(j)`
f.write('
')`
f.write("Title:"+sub_urls2[0].text.lstrip('
'))`
f.write('
')`
f.write("Abstract:"+sub_urls3[0].text.lstrip('
'))`
f.write('
')`
l=sub_urls4[0]['href'][6:-1]`
link=b_url+l`
f.write("Link:"+link)`
f.write("
")`
性能分析与改进
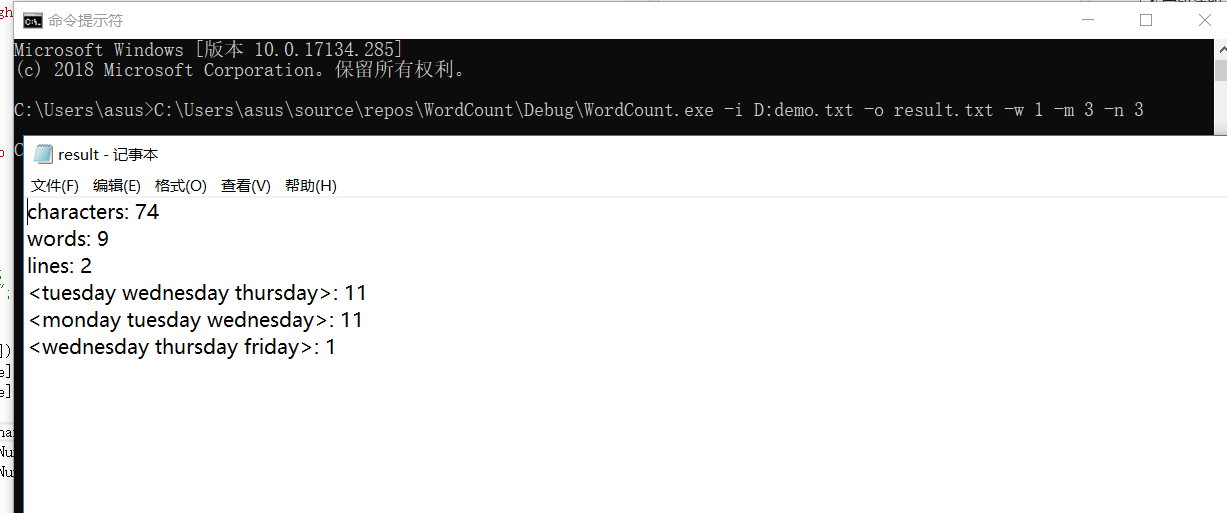
测试使用了977篇论文爬取结果作为输入数,命令行参数为
-i D:\date.txt -o result.txt -w 1 -m 3 -n 10
结果为:
性能报告如下:


显然耗时最大的函数为Word_Fre()进行单词判定和词组输出,所以会比较耗时,可以看出主要耗时在单词判定上,我将map改为unordered_map时间并没有明显提升。
单元测试
设计了十个单元测试样例,被说明测试的函数,构造测试数据见下表:
| 测试名 | 单元测试内容 | 测试模块 | 结果 |
|---|---|---|---|
| UnitTestCharNum | 正常文本输入,统计字符数量 | CharNum.cpp | 通过 |
| UnitTestLineNum | 正常文本输入,统计有效行数量 | LineNum.cpp | 通过 |
| UnitTestWordNum | 正常文本输入,统计单词数量 | WordNum.cpp | 通过 |
| specialfile | Abstract : 行为空的文本,有效行数量 | LIneNum.cpp | 通过 |
| emptya | 传入一个空文件,输出为0 | CharNUm.cpp LIneNum.cpp WordNum.cpp | 通过 |
| twowordnum | 两个单词的词组数量 | Word_Fre.cpp | 通过 |
| emptyinputfile | 没有-i参数的传入,错误报告 | main.cpp | 通过 |
| topntest | top3输出 | Word_Fre.cpp | 通过 |
| weightwordfre | 加入权重的单词频率输出 | Word_Fre.cpp | 通过 |
运行结果如下:
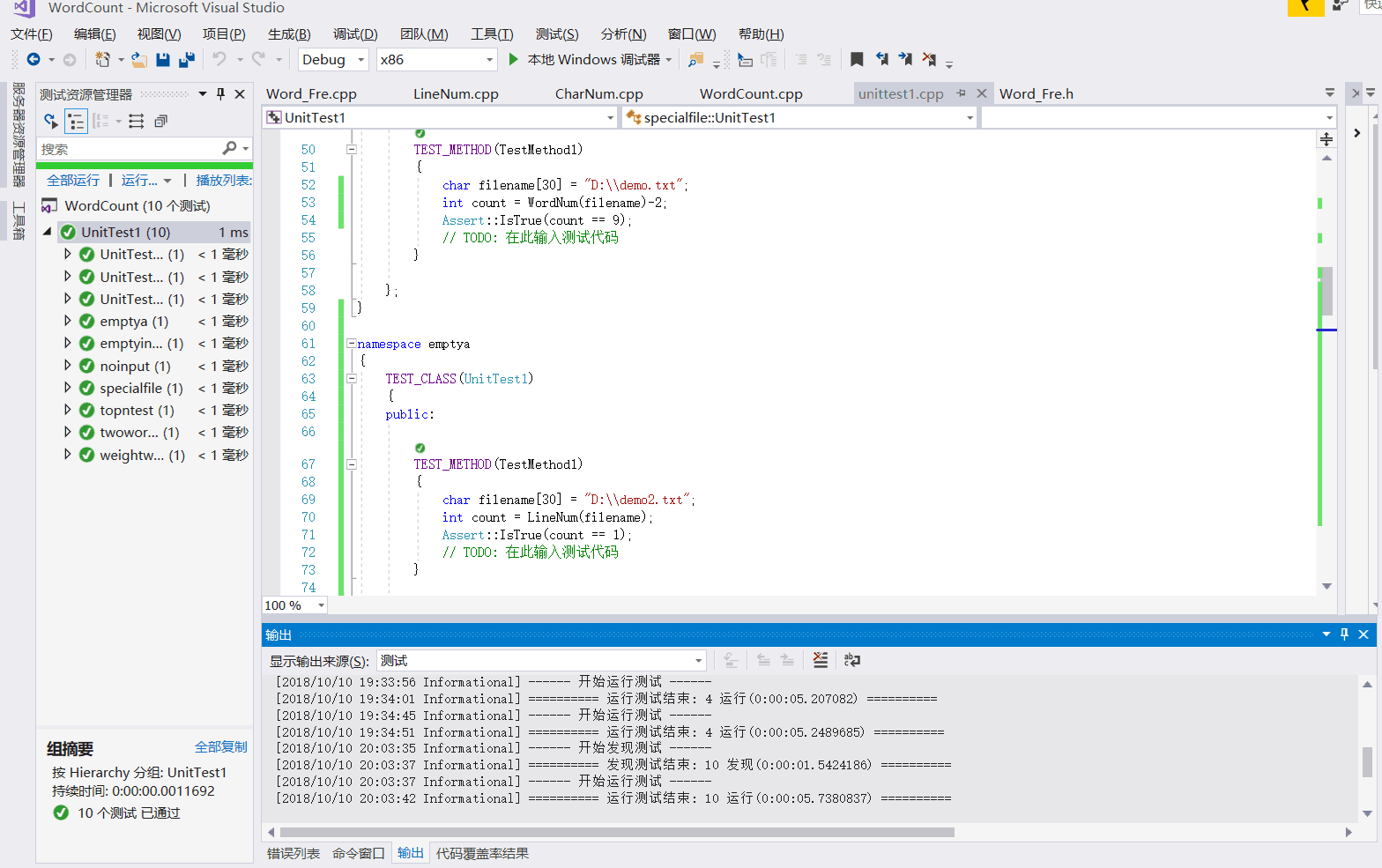
部分代码展示如下:
namespace UnitTestCharNum
{
TEST_CLASS(UnitTest1)
{
public:
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod1)
{
char filename[30] = "D:\demo.txt";
int count = CharNum(filename);
Assert::IsTrue(count == 74);
// TODO: 在此输入测试代码
}
};
}
namespace UnitTestLineNum
{
TEST_CLASS(UnitTest1)
{
public:
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod1)
{
char filename[30] = "D:\demo.txt";
int count = LineNum(filename);
Assert::IsTrue(count == 2);
// TODO: 在此输入测试代码
}
};
}
namespace UnitTestWordNum
{
TEST_CLASS(UnitTest1)
{
public:
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod1)
{
char filename[30] = "D:\demo.txt";
int count = WordNum(filename)-2;
Assert::IsTrue(count == 9);
// TODO: 在此输入测试代码
}
};
}
namespace emptya
{
TEST_CLASS(UnitTest1)
{
public:
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod1)
{
char filename[30] = "D:\demo2.txt";
int count = LineNum(filename);
Assert::IsTrue(count == 1);
// TODO: 在此输入测试代码
}
};
}
贴出Github的代码签入记录
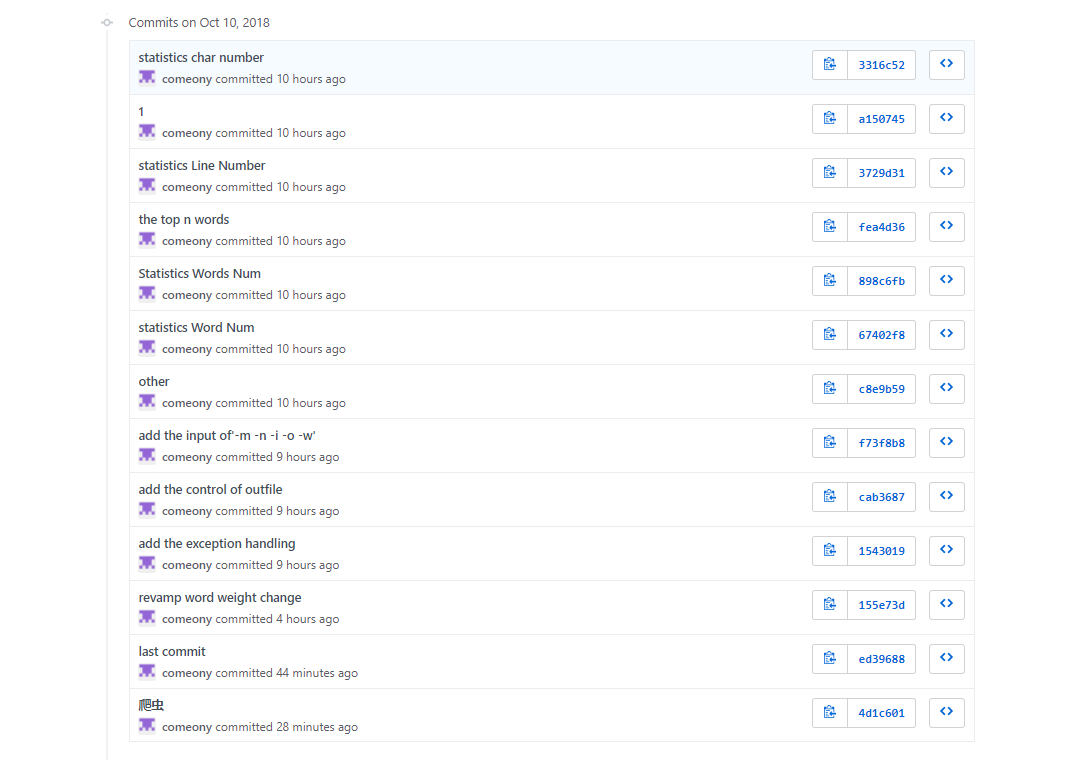
遇到的代码模块异常或结对困难及解决方法
- 问题描述:
主要问题是爬虫和词组的判断
- 做过哪些尝试:
一开始尝试词组打算用个人项目的那个代码,只不过是多循环几次,后来发现单纯的在原来word的基础上增加长度,这样判断词组会有以后,即不能回读。
- 是否解决:
算是圆满地解决了,通过string数组暂时存放单词,这样就可以在光标移到后面,也可以回读前面的单词。
- 有何收获:
有,比如软工实践还是要趁早做,就像前面说的,deadline并不是万能的。
还有学习新知识一定要耐心,如何从浩瀚的网络海洋中学到你想要的,这是一门人生的必修课
评价你的队友
我的队友,高端大气上档次,低调奢华有内涵。
- 值得我学习的地方:做事效率高。
- 需要改进的地方:不够完美。
学习进度条
| 第N周 | 新增代码(行) | 累计代码(行) | 本周学习耗时(小时) | 累计学习耗时(小时) | 重要成长 |
| 1 | 300 | 300 | 15 | 15 | 熟悉了C++语言,了解了单元测试,代码覆盖率和性能分析 |
| 2 | 0 | 300 | 8 | 23 | |
| 3 | 300 | 600 | 14 | 37 | 爬虫,代码能力更上一步 |
| ... |