系统分析与设计结对项目 ——WordCount
合作者:201631105117(同学一),201631062607(同学二)
码云上的项目地址:https://gitee.com/SenLinJ/wc
本次作业的链接地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/cpp-cpp/p/9762389.html
结对的另一个同学的作业地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/silvercv/p/9799229.html
一、结对的PSP表格
PSP2.1表格
|
PSP2.1 |
PSP阶段 |
预估耗时 (分钟) |
实际耗时 (分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
20 |
30 |
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
20 |
30 |
|
Development |
开发 |
670 |
1155 |
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
120 |
100 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
0 |
0 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
0 |
0 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
20 |
30 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
50 |
115 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
300 |
660 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
60 |
100 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
120 |
150 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
120 |
200 |
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
60 |
90 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
30 |
50 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
30 |
60 |
|
合计 |
810 |
1385 |
二、互审代码情况
第一次的两个WordCount项目的地址:同学一: https://www.cnblogs.com/silvercv/p/9692483.html
同学二: https://www.cnblogs.com/cpp-cpp/p/9695903.html
审查的模块名称、发现的问题等:
同学一:同学二的代码没有采用模块化的形式,逻辑比较严谨,代码风格不错,这点值得学习。
同学二:同学的代码采用了工程式的思想完成,思路清晰,结构完整,注释和命名方面也做的很好。反观自己,就像写个小程序的样子,小惭愧。而且通过看同学的代码,发现了自己代码之前不够严谨的地方。
三、设计过程
这次编程我们决定采用java,我们两个人第一次WordCount都是使用C语言编写的。起初合并时还是使用C语言编写,虽然已经实现那些基本和扩展功能,但是过程太过复杂。虽然我们前期花了一定时间去编写并且大部分功能已经实现,但是高级功能实现不太现实,所以改变了使用的语言,这是我们浪费了许多时间,是我们的失误。
使用结构设计,比如有几个类或几个函数,他们之间关系如何:
我们分类编写,每个类实现一个小功能。比如:
AbstractBaseCount、BaseCount、ExternCount等,类与类之间大多是继承关系。
关键函数的算法设计(流程图):
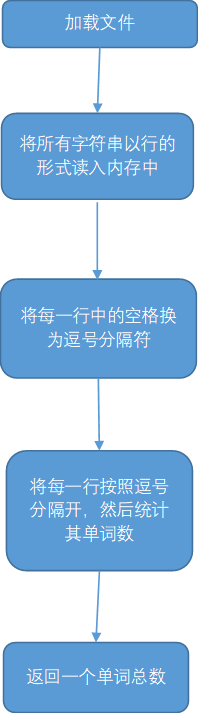
字符统计:

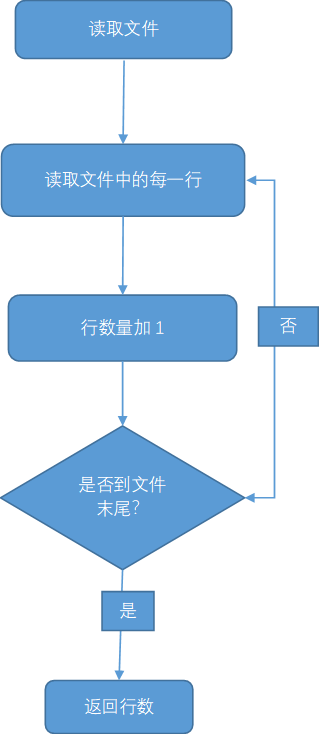
行数统计:
如果有停用词,按照获取单词的流程可以获取一个停用词的Vector,然后通过循环,来遍历停用词和从要处理的文件中或取的单词列表,
记录单词列表中出现停用词的次数,然后用总的单词次数减去停用次的次数,那么就可得到去除停用词之后的单词数量。
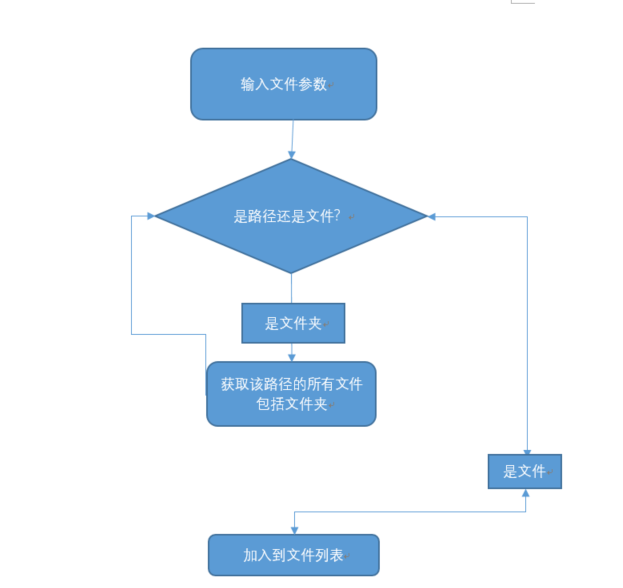
以尾递归的形式将所有文件放入到一个文件列表中,对于这个文件列表遍历执行所需要进行的操作。
四、代码说明
关键代码及注释说明:
protected BufferedReader bufferedReader;
protected BufferedWriter bufferedWriter;
public AbstractBaseCount(){
}
public AbstractBaseCount(File fileName){
getBufferedInputStream(fileName);
}
public AbstractBaseCount(File input_file, String output_file){
getBufferedInputStream(input_file);
this.output = output_file;
}
try{
File file = new File(filePath);
bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file,flag));
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
}
private void getBufferedInputStream(File file){
try{
if(!file.exists()){
Util.Tips();
}
bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
}
public void Write(List<String> buff){
/*
buff 为写入文件的字符
flag 表示其模式
*/
getBufferedWriter(output,false);
boolean flag = false;
if(buff.size() >= 2){
flag = true;
}
getBufferedWriter(output,flag);
try{
for(String str: buff) {
bufferedWriter.write(str);
}
}catch (IOException e){
System.out.println(e.toString());
}finally {
try{
bufferedWriter.close();
}catch (IOException e){
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
}
}
protected String filename;
protected List<String> buff = new ArrayList<>(); //将读取的东西保存在内存中,不用反复读取
private void GetBUff(){
String buf;
try {
while ((buf = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
buff.add(buf);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try{
bufferedReader.close();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public BaseCount(){
super();
GetBUff(); //读取数据到文件中
}
public BaseCount(File file){
super(file);
this.filename = file.getName();
GetBUff();
}
public BaseCount(File inputFile, String output_file){
super(inputFile,output_file);
this.filename = inputFile.getName(); //输出文件
GetBUff();
}
protected int getCharNum(){ //获取字符的数量
int CharNum = 0;
for(String str : buff){
CharNum += str.length() ; //获取每一行字符的数量
}
return CharNum;
}
int WordNum = 0;
for(String str:buff){
WordNum += str.replace(" ",",").split(",").length;//获取单词的数量
}
return WordNum;
}
int LineNum = 0;
LineNum = buff.size() ;//行数
return LineNum;
}
/*这个类是用来实现扩展功能 * */ public class ExternCount extends BaseCount { public ExternCount(){ super(); } public ExternCount(File fileName){ super(fileName); } public ExternCount(File inputFile, String output_file){ super(inputFile,output_file); } protected String OtherLines(){ int CodeLine = 0; //代码行 int NoteLine = 0; //注释行 int SpacLine = 0; //空行 int size = buff.size(); for (int i=0; i<size;i++){ if (buff.get(i).length() <= 1 || buff.get(i).trim().length() <=1){ SpacLine++; //当整行中只有少于一个可显示字符的时候 }else{ if (buff.get(i).contains("/*")){ while(!buff.get(i).contains("*/")){ i++; NoteLine++; //用来判断块注释 } i++; NoteLine++; }else{ String[] sp = buff.get(i).split("//"); //用注释符分开 if(sp.length <= 1 && buff.get(i).contains("//")){ //本行含有注释符 NoteLine++; }else if (sp[0].length() <=1){ //在注释符前含有一个字符 NoteLine++; }else { CodeLine++; //其余情况为代码行 } } } } //最终返回一个字符串 String buf = filename + ", 代码行/注释行/空行:"+CodeLine+"/"+NoteLine+"/"+SpacLine+" "; return buf; } protected int StopSize(String StopWordsFile){ int Stopsize = 0; try { List<String> StopWords = getStopWords(StopWordsFile);//加载停用词 List<String> Words = getWords(); for(String stop : StopWords){ if(Words.remove(stop)){ Stopsize++; } } }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println(e.toString()); } return Stopsize; } //从文件中读取停用词 private List<String> getStopWords(String StopWordsFile){ List<String> StopWords = new ArrayList<>(); try{ String buf = null; File file = new File(StopWordsFile); if(!file.exists()){ Util.Tips(); }else { BufferedReader buffered = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(StopWordsFile)); //包含停用词的文件 while ((buf = buffered.readLine()) != null) { //停用词以空格分开 for (String s : buf.split(" ")) { StopWords.add(s); } } } }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println(e.toString()); } return StopWords; } private List<String> getWords(){ //获取所有的单词 List<String> Words = new ArrayList<>(); try{ for(String buf:buff){ for(String s : buf.replace(' ',',').split(",")){ Words.add(s); } } }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println(e.toString()); } return Words; } }
//解析命令行参数 public class ParseArgs { private static String ext = "."; //从命令行中获取文件和参数 public static Map<String,String> getOptions(String[] args) { if (args.length < 1){ Util.Tips(); } HashMap<String, String> options = new HashMap<>(); int size = args.length; //判断当只有一个参数的时候 if (size == 1 && !args[size-1].equals("-x")){ Util.Tips(); }else if(args[size-1].equals("-x")) { options.put("-x","-x"); } if(size >= 2) { // -o或者-e后没有文件 if (args[size - 1].equals("-o") || args[size - 1].equals("-e")) { Util.Tips(); } if (args[size - 2].equals("-o") && !args[size - 1].equals("-o")) { options.put(args[size - 2], args[size - 1]); size -= 2; } else if (args[size - 3].contains("-")) { Util.Tips(); } for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { //停用词必须在-e之后 if (args[i].equals("-e") && args[i + 1].endsWith(".txt")) { options.put(args[i], args[++i]); } else if (args[i].equals("-e") && !args[i + 1].endsWith(".txt")) { Util.Tips(); } else if (args[i].equals("-e") && args[i - 1].contains("-")) { Util.Tips(); } else { options.put(args[i], args[i]); //将参数放入哈希表中 } } } return options; //返回一个哈希map } private static String getDir(String FileName){ String dir = null; String[] exts = FileName.split("\."); if(!exts[0].endsWith("*") ){ //如果只是一个文件 或者是一个文件夹 return FileName; } else { if(exts[0].endsWith("*") && exts[0].equals("*")) { dir = new File("").getAbsolutePath(); //获取绝对路径 }else{ dir = exts[0].split("\*")[0]; } } return dir; } private static void getAllFiles(String FileName,List<File> Files){ try{ String dir = getDir(FileName); //获取文件路径 File file = new File(dir); //获取当前文件路径下的所有文件或者路径 if (file != null &&file.isFile()){ Files.add(file); }else { File[] files = file.listFiles(); if (files != null && files.length !=0 ){ for (File f : files) { if (f.isDirectory()) { getAllFiles(f.getAbsolutePath(), Files); } else if(f.isFile()){ if(ext == null){ Files.add(f); }else{ if(f.getName().endsWith(ext)){ Files.add(f); } } } } } } }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println(e.toString()); } } public static List<File> getAllFiles(String FileName){ String[] exts = FileName.split("\."); //如果没有扩展名 if (exts.length == 1){ ext = null; }else{ ext += exts[exts.length-1]; } List<File> files = new ArrayList<>(); getAllFiles(FileName,files); if (files == null || files.size() == 0){ Util.Tips(); } return files; } public static void Start(String[] args) { Map<String,String> options = getOptions(args); //如果参数中含有-x if (options.containsKey("-x")){ WordsUI.main(args); }else{ String fileName = null; //找到文件位置 for(String key : options.keySet()){ if (!key.contains("-")){ fileName = options.get(key); //处理读入文件 break; } } if (fileName == null){ Util.Tips(); } String output = null; List<String> buf = new ArrayList<>(); List<File> files = new ArrayList<>(); //有-s参数 if (options.containsKey("-s")) { files = getAllFiles(fileName); }else{ //无递归调用条件 try{ files.add(new File(fileName)); }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println(e.toString()); } } if (options.containsKey("-o")){ output = options.get("-o"); //获取输出文件的位置 }else{ output = null; } WordCount wc; for (File f: files){ if (null != output){ wc = new WordCount(f,output); }else { wc = new WordCount(f); } if (options.containsKey("-c")){ buf.add(wc.CharSize()); } if (options.containsKey("-w") && !options.containsKey("-e")){ buf.add(wc.WordSize()); } if (options.containsKey("-l")){ buf.add(wc.LineSize()); } if (options.containsKey("-a")){ buf.add(wc.OtherLine()); } if (options.containsKey("-w") && options.containsKey("-e")){ buf.add(wc.WordSize(options.get("-e"))); } wc.Write(buf); } } } }
五、总结
结合在构建之法中学习到的相关内容与结对项目的实践经历,描述结对的感受,是否1+1>2?
同学一:见他的博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/silvercv/p/9799229.html
同学二:我感受到了1+1>2 。我们分别都充当了驾驶员和领航员的角色。对于模块,我们一起讨论,得出解决方案,然后我在编程时,同学在一旁指导,指出错误。
同学在编程时,我也可以观看他平时的一些写代码的习惯,借鉴一些值得学习的地方。比如会在代码开头给一个注释,解释一些关键变量和关键函数等。
所以,我认为结对编程使代码的质量都提升了,也让大家相互学习,得到了发展。
这次项目虽然完成了,但是时间远远超过了预期时间,中途更换编程语言是一个方面,另一个方面是处理.c文件那部分,对功能的分析花费的时间太长了。好在还是做出来啦。
最后,当然是感谢我的小伙伴啦~在他的帮助下,我们一起完成了这个小项目。从他那里学到了很多东西。