概述
- 属于行为型模式
- 将集合的遍历行为抽取为单独的迭代器对象
- 所有迭代器实现相同的接口,只要有合适的迭代器,客户端代码就能兼容任何类型的集合或遍历算法,如需采用特殊方法遍历集合,创建一个新的迭代器即可,而无需对集合或客户端进行修改
- 集合对象内部结构常常变化各异,但对于这些集合对象,我们希望在不暴露其内部结构的同时,也可以让外部客户代码透明地访问其中包含的元素;同时这种“透明遍历”也为“同一种算法在多种集合对象上进行操作”提供了可能
- 使用面向对象技术将这种遍历机制抽象为“迭代器模式”为“因对变化中的集合对象”提供了一种优雅的方式
- 提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中的各个元素,而不暴露(稳定)该对象内部的表示
- 通过迭代器接口,隔离算法和容器之间的变化
- 面向对象(虚函数)实现迭代器,虚函数调用存在性能问题(运行时多态),在迭代器循环中会造成较大损失(绕虚函数表指针找函数地址的运算),故在c++在98年后改用STL泛型编程模板实现迭代器(编译时多态)
- Java、C#类库中依然使用面向对象实现迭代器
- 迭代抽象:访问一个聚合对象的内容而无需暴露它的内部表示
- 迭代多样:为遍历不同的集合提供一个统一的接口,从而支持同样的算法在不同集合结构上进行操作
- 健壮性:迭代的同时更改迭代器所在的集合结构,会导致问题
- ConcreteAggregate是具体聚合类(容器,如列表(List)或集合(Set)等),ConcreteIterator是容器对应的迭代器类
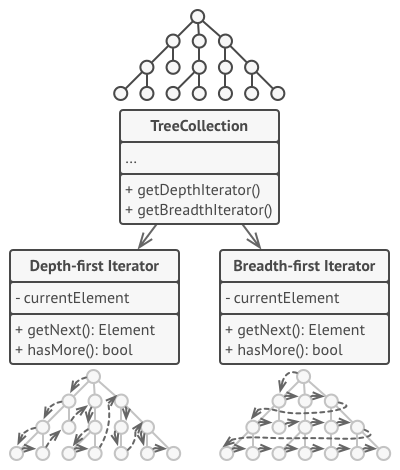
场景
- 采用自由行,手机导航,跟团等方式游览一个城市,城市的景点是一个集合,每个游览方式是一个迭代器
结构
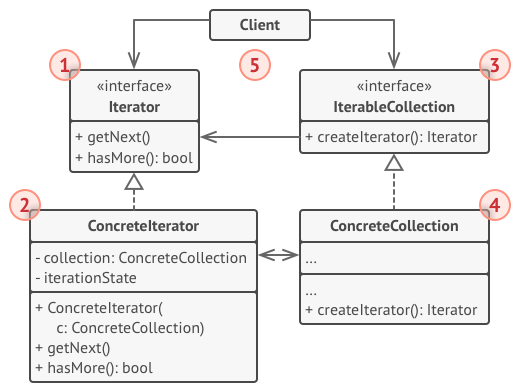
- 迭代器接口:声明了遍历集合所需的操作
- 具体迭代器类:实现遍历集合的一种特定算法
- 集合接口:声明一个或多个方法获取与集合兼容的迭代器,返回迭代器接口
- 具体集合类:客户端请求迭代器时返回一个特定的具体迭代器类实体
- 客户端类:通过集合和迭代器接口与两者进行交互
示例1
Iterator.cpp

1 template<typename T> 2 class Iterator 3 { 4 public: 5 virtual void first() = 0; 6 virtual void next() = 0; 7 virtual bool isDone() const = 0; 8 virtual T& current() = 0; 9 }; 10 11 template<typename T> 12 class MyCollection{ 13 14 public: 15 16 Iterator<T> GetIterator(){ 17 //... 18 } 19 20 }; 21 22 template<typename T> 23 class CollectionIterator : public Iterator<T>{ 24 MyCollection<T> mc; 25 public: 26 27 CollectionIterator(const MyCollection<T> & c): mc(c){ } 28 29 void first() override { 30 31 } 32 void next() override { 33 34 } 35 bool isDone() const override{ 36 37 } 38 T& current() override{ 39 40 } 41 }; 42 43 void MyAlgorithm() 44 { 45 MyCollection<int> mc; 46 47 Iterator<int> iter= mc.GetIterator(); 48 49 for (iter.first(); !iter.isDone(); iter.next()){ 50 cout << iter.current() << endl; 51 } 52 53 }
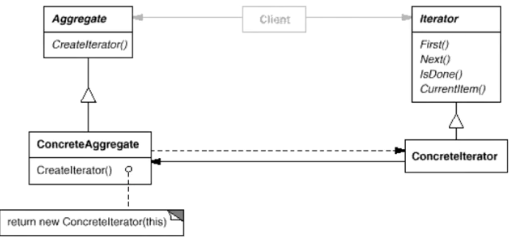
示例2

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <vector> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 template <typename T, typename U> 7 class Iterator{ 8 public: 9 typedef typename vector<T>::iterator iter_type; 10 Iterator(U *p_data, bool reverse = false):m_p_data_(p_data){ 11 m_it_ = m_p_data_->m_data_.begin(); 12 } 13 14 void First(){ 15 m_it_ = m_p_data_ -> m_data_.begin(); 16 } 17 18 void Next(){ 19 m_it_++; 20 } 21 22 bool IsDone(){ 23 return(m_it_ == m_p_data_ -> m_data_.end()); 24 } 25 26 iter_type Current(){ 27 return m_it_; 28 } 29 30 private: 31 U *m_p_data_; 32 iter_type m_it_; 33 }; 34 35 template <class T> 36 class Container{ 37 friend class Iterator<T, Container>; 38 public: 39 void Add(T a){ 40 m_data_.push_back(a); 41 } 42 43 Iterator<T,Container> *CreateIterator(){ 44 return new Iterator<T, Container>(this); 45 } 46 47 private: 48 vector<T> m_data_; 49 }; 50 51 class Data{ 52 public: 53 Data(int a = 0): m_data_(a){} 54 55 void set_data(int a){ 56 m_data_ = a; 57 } 58 59 int data(){ 60 return m_data_; 61 } 62 63 private: 64 int m_data_; 65 }; 66 67 void ClientCode(){ 68 cout<<"________________Iterator with int______________________________________"<<endl; 69 Container<int> cont; 70 71 for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++){ 72 cont.Add(i); 73 } 74 75 Iterator<int, Container<int>> *it = cont.CreateIterator(); 76 for(it->First(); !it->IsDone(); it->Next()){ 77 cout << *it->Current() << endl; 78 } 79 80 Container<Data> cont2; 81 Data a(100),b(1000),c(10000); 82 cont2.Add(a); 83 cont2.Add(b); 84 cont2.Add(c); 85 86 cout<< "________________Iterator with custom Class______________________________"<<endl; 87 Iterator<Data, Container<Data>> *it2 = cont2.CreateIterator(); 88 for(it2->First();!it2->IsDone();it2->Next()){ 89 cout << it2->Current()->data() << endl; 90 } 91 } 92 93 int main(){ 94 ClientCode(); 95 return 0; 96 }
________________Iterator with int______________________________________ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ________________Iterator with custom Class______________________________ 100 1000 10000
示例3
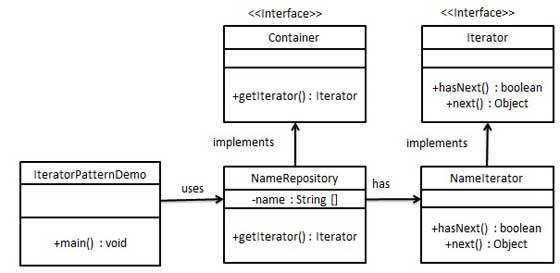

1 public interface Iterator { 2 public boolean hasNext(); 3 public Object next(); 4 } 5 6 public interface Container { 7 public Iterator getIterator(); 8 } 9 10 public class NameRepository implements Container{ 11 public String names[] = {"Robert" , "John" ,"Julie" , "Lora"}; 12 13 @Override 14 public Iterator getIterator() { 15 return new NameIterator(); 16 } 17 18 private class NameIterator implements Iterator{ 19 int index; 20 21 @Override 22 public boolean hasNext() { 23 if(index < names.length) { 24 return true; 25 } 26 return false; 27 } 28 29 @Override 30 public Object next() { 31 if(this.hasNext()) { 32 return names[index++]; 33 } 34 return null; 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 39 public class IteratorPatternDemo { 40 public static void main(String[] args) { 41 NameRepository namesRepository = new NameRepository(); 42 43 for(Iterator iter = namesRepository.getIterator();iter.hasNext();) { 44 String name = (String)iter.next(); 45 System.out.println("Name : " + name); 46 } 47 } 48 }
Name : Robert
Name : John
Name : Julie
Name : Lora
参考
迭代器模式c++实现
https://blog.csdn.net/u012611878/article/details/78010435
CSDN:MachineChen
