任务:构建字符级语言模型来生成新的名称
1.数据集与预处理
读取恐龙名称的数据集,创建一个唯一字符列表(a-z和 ), 充当EOS名称结束的作用。
1 import numpy as np 2 import random 3 import time 4 import cllm_utils 5 6 data = open("datasets/dinos.txt", 'r').read() 7 data= data.lower() 8 chars = list(set(data)) # 转化为无序且不重复的元素列表 9 print(sorted(chars)) 10 data_size, vocab_size = len(data), len(chars) 11 print('There are %d total characters and %d unique characters in your data.' % (data_size, vocab_size))
[' ', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z']
There are 19909 total characters and 27 unique characters in your data.
创建两个字典,一个是{元素:索引},一个是{索引:元素},它会帮助我们找出softmax层的概率分布输出中的字符。
1 char_to_ix = { ch:i for i,ch in enumerate(sorted(chars)) } 2 ix_to_char = { i:ch for i,ch in enumerate(sorted(chars)) } 3 print(char_to_ix) 4 print(ix_to_char)
{'
': 0, 'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3, 'd': 4, 'e': 5, 'f': 6, 'g': 7, 'h': 8, 'i': 9, 'j': 10, 'k': 11, 'l': 12, 'm': 13, 'n': 14, 'o': 15, 'p': 16, 'q': 17, 'r': 18, 's': 19, 't': 20, 'u': 21, 'v': 22, 'w': 23, 'x': 24, 'y': 25, 'z': 26}
{0: '
', 1: 'a', 2: 'b', 3: 'c', 4: 'd', 5: 'e', 6: 'f', 7: 'g', 8: 'h', 9: 'i', 10: 'j', 11: 'k', 12: 'l', 13: 'm', 14: 'n', 15: 'o', 16: 'p', 17: 'q', 18: 'r', 19: 's', 20: 't', 21: 'u', 22: 'v', 23: 'w', 24: 'x', 25: 'y', 26: 'z'}
2.构建模型中的模块
整个循环结构通常包括前向传播、成本计算、反向传播和参数更新。在更新参数之前,我们将在需要时执行梯度修剪,以确保我们的梯度不是“爆炸”的。
2.1梯度修剪

np.clip(a, a_min, a_max, out=None)
将数组a中的所有数限定到范围a_min和a_max中,即az中所有比a_min小的数都会强制变为a_min,a中所有比a_max大的数都会强制变为a_max。
- 其中a_min和a_max可以为一个和a一样大小的数组(列表也可以,只要是类似数组的结构就是可行的),则
数组中相应位置的元素进行比较。 - out是可选项,表示把强制截取后的结果放到这个数组中,但是out中的数组必须和a形状一样
1 def clip(gradients, maxValue): 2 ''' 3 Clips the gradients' values between minimum and maximum. 4 5 Arguments: 6 gradients -- a dictionary containing the gradients "dWaa", "dWax", "dWya", "db", "dby" 7 maxValue -- everything above this number is set to this number, and everything less than -maxValue is set to -maxValue 8 9 Returns: 10 gradients -- a dictionary with the clipped gradients. 11 ''' 12 dWaa, dWax, dWya, db, dby = gradients['dWaa'], gradients['dWax'], gradients['dWya'], gradients['db'], gradients['dby'] 13 14 ### START CODE HERE ### 15 # clip to mitigate exploding gradients, loop over [dWax, dWaa, dWya, db, dby]. (≈2 lines) 16 for gradient in [dWaa, dWax, dWya, db, dby]: 17 np.clip(gradient, -maxValue, maxValue, out=gradient) 18 ### END CODE HERE ### 19 20 gradients = {"dWaa": dWaa, "dWax": dWax, "dWya": dWya, "db": db, "dby": dby} 21 return gradients
2.2采样
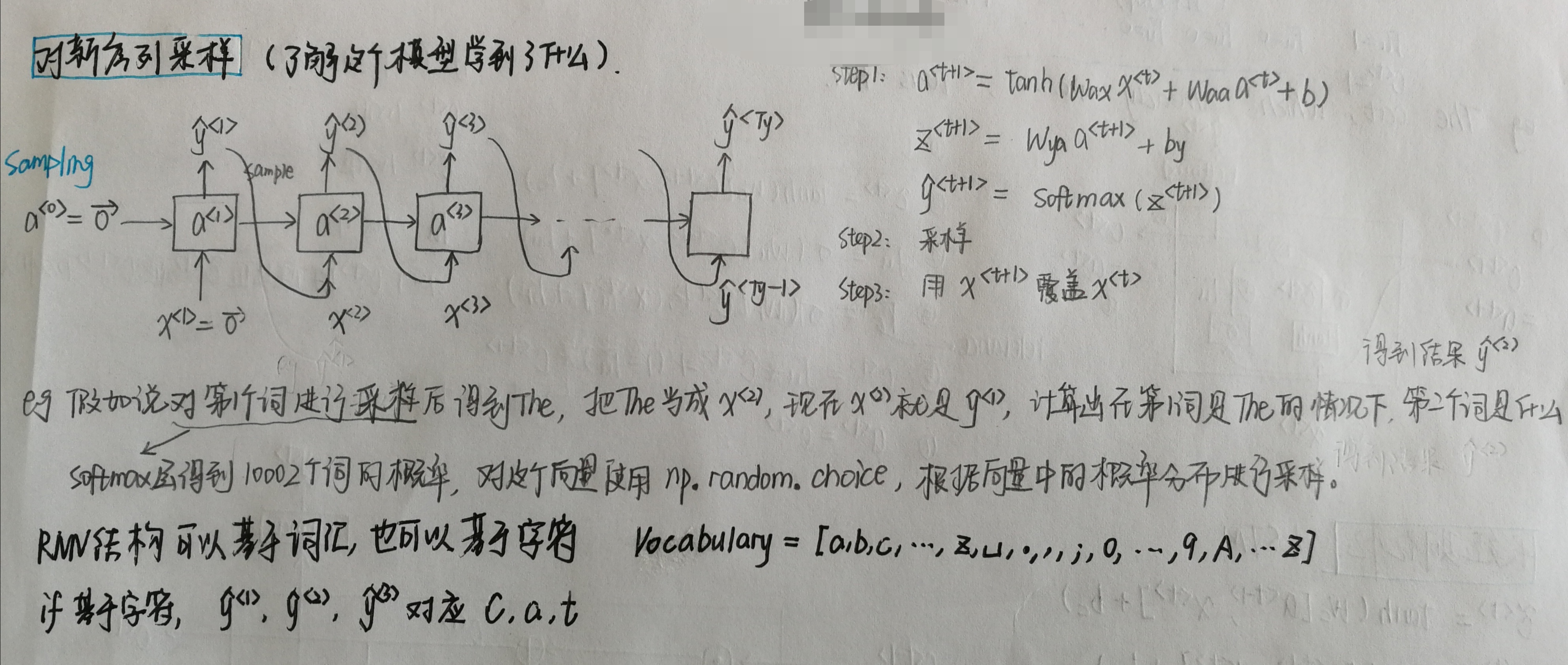
1 def sample(parameters, char_to_ix, seed): 2 """ 3 Sample a sequence of characters according to a sequence of probability distributions output of the RNN 4 5 Arguments: 6 parameters -- python dictionary containing the parameters Waa, Wax, Wya, by, and b. 7 char_to_ix -- python dictionary mapping each character to an index. 8 seed -- used for grading purposes. Do not worry about it. 9 10 Returns: 11 indices -- a list of length n containing the indices of the sampled characters. 12 """ 13 14 # Retrieve parameters and relevant shapes from "parameters" dictionary 15 Waa, Wax, Wya, by, b = parameters['Waa'], parameters['Wax'], parameters['Wya'], parameters['by'], parameters['b'] 16 vocab_size = by.shape[0] 17 n_a = Waa.shape[1] 18 19 ### START CODE HERE ### 20 # Step 1: Create the one-hot vector x for the first character (initializing the sequence generation). (≈1 line) 21 x = np.zeros((vocab_size, 1)) 22 # Step 1': Initialize a_prev as zeros (≈1 line) 23 a_prev = np.zeros((n_a, 1)) 24 25 # Create an empty list of indices, this is the list which will contain the list of indices of the characters to generate (≈1 line) 26 indices = [] 27 28 # Idx is a flag to detect a newline character, we initialize it to -1 29 idx=-1 30 31 # Loop over time-steps t. At each time-step, sample a character from a probability distribution and append 32 # its index to "indices". We'll stop if we reach 50 characters (which should be very unlikely with a well 33 # trained model), which helps debugging and prevents entering an infinite loop. 34 counter = 0 35 newline_character = char_to_ix[' '] 36 37 while (idx != newline_character and counter != 50): 38 39 # Step 2: Forward propagate x using the equations (1), (2) and (3) 40 a = np.tanh(np.dot(Wax, x) + np.dot(Waa, a_prev) + b) 41 z = np.dot(Wya, a) +by 42 y = softmax(z) 43 # for grading purposes 44 np.random.seed(counter + seed) 45 46 # Step 3: Sample the index of a character within the vocabulary from the probability distribution y 47 idx = np.random.choice(list(range(vocab_size)), p=y.ravel()) 48 # Append the index to "indices" 49 indices.append(idx) 50 51 # Step 4: Overwrite the input character as the one corresponding to the sampled index. 52 x = np.zeros((vocab_size, 1)) 53 x[idx]=1 54 55 # Update "a_prev" to be "a" 56 a_prev = a 57 58 # for grading purpose 59 seed += 1 60 counter += 1 61 ### END CODE HERE ### 62 63 if (counter == 50): 64 indices.append(char_to_ix[' ']) 65 return indices
3.构建语言模型
3.1梯度下降
RNN的优化循环步骤:前向传播计算损失、反向传播计算关于参数的梯度损失、修剪梯度、使用梯度下降更新参数,使用单步随机梯度下降优化这一过程。
1 def optimize(X, Y, a_prev, parameters, learning_rate = 0.01): 2 """ 3 Execute one step of the optimization to train the model. 4 5 Arguments: 6 X -- list of integers, where each integer is a number that maps to a character in the vocabulary. 7 Y -- list of integers, exactly the same as X but shifted one index to the left. 8 a_prev -- previous hidden state. 9 parameters -- python dictionary containing: 10 Wax -- Weight matrix multiplying the input, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_x) 11 Waa -- Weight matrix multiplying the hidden state, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a) 12 Wya -- Weight matrix relating the hidden-state to the output, numpy array of shape (n_y, n_a) 13 b -- Bias, numpy array of shape (n_a, 1) 14 by -- Bias relating the hidden-state to the output, numpy array of shape (n_y, 1) 15 learning_rate -- learning rate for the model. 16 17 Returns: 18 loss -- value of the loss function (cross-entropy) 19 gradients -- python dictionary containing: 20 dWax -- Gradients of input-to-hidden weights, of shape (n_a, n_x) 21 dWaa -- Gradients of hidden-to-hidden weights, of shape (n_a, n_a) 22 dWya -- Gradients of hidden-to-output weights, of shape (n_y, n_a) 23 db -- Gradients of bias vector, of shape (n_a, 1) 24 dby -- Gradients of output bias vector, of shape (n_y, 1) 25 a[len(X)-1] -- the last hidden state, of shape (n_a, 1) 26 """ 27 ### START CODE HERE ### 28 # Forward propagate through time (≈1 line) 29 loss, cache = rnn_forward(X, Y, a_prev, parameters) 30 31 # Backpropagate through time (≈1 line) 32 gradients, a = rnn_backward(X, Y, parameters, cache) 33 34 # Clip your gradients between -5 (min) and 5 (max) (≈1 line) 35 gradients = clip(gradients, maxValue=5) 36 37 # Update parameters (≈1 line) 38 parameters = update_parameters(parameters, gradients, learning_rate) 39 ### END CODE HERE ### 40 41 return loss, gradients, a[len(X)-1]
3.2训练模型
给定恐龙名称的数据集,我们使用数据集的每一行(一个名称)作为一个训练样本。每100步随机梯度下降,你将抽样10个随机选择的名字,看看算法是怎么做的。记住要打乱数据集,以便随机梯度下降以随机顺序访问样本。
当examples[index]包含一个恐龙名称(String)时,为了创建一个样本(X,Y),你可以使用这个:
1 index = j % len(examples) 2 X = [None] + [char_to_ix[ch] for ch in examples[index]] 3 Y = X[1:] + [char_to_ix[" "]]
需要注意的是我们使用了index= j % len(examples),其中= 1....num_iterations,为了确保examples[index]总是有效的(index小于len(examples)),rnn_forward()会将X的第一个值None解释为x<0>=0向量。此外,为了确保Y等于X,会向左移动一步,并添加一个附加的“ ”以表示恐龙名称的结束。
1 def model(data, ix_to_char, char_to_ix, num_iterations = 35000, n_a = 50, dino_names = 7, vocab_size = 27): 2 """ 3 Trains the model and generates dinosaur names. 4 5 Arguments: 6 data -- text corpus 7 ix_to_char -- dictionary that maps the index to a character 8 char_to_ix -- dictionary that maps a character to an index 9 num_iterations -- number of iterations to train the model for 10 n_a -- number of units of the RNN cell 11 dino_names -- number of dinosaur names you want to sample at each iteration. 12 vocab_size -- number of unique characters found in the text, size of the vocabulary 13 14 Returns: 15 parameters -- learned parameters 16 """ 17 # Retrieve n_x and n_y from vocab_size 18 n_x, n_y = vocab_size, vocab_size 19 20 # Initialize parameters 21 parameters = initialize_parameters(n_a, n_x, n_y) 22 23 # Initialize loss (this is required because we want to smooth our loss, don't worry about it) 24 loss = get_initial_loss(vocab_size, dino_names) 25 26 # Build list of all dinosaur names (training examples). 27 with open("datasets/dinos.txt") as f: 28 examples = f.readlines() 29 examples = [x.lower().strip() for x in examples] 30 31 # Shuffle list of all dinosaur names 32 np.random.seed(0) 33 np.random.shuffle(examples) 34 35 # Initialize the hidden state of your LSTM 36 a_prev = np.zeros((n_a, 1)) 37 38 # Optimization loop 39 for j in range(num_iterations): 40 41 ### START CODE HERE ### 42 # Use the hint above to define one training example (X,Y) (≈ 2 lines) 43 index = j % len(examples) 44 X = [None] + [char_to_ix[ch] for ch in examples[index]] 45 Y = X[1:] + [char_to_ix[" "]] 46 47 # Perform one optimization step: Forward-prop -> Backward-prop -> Clip -> Update parameters 48 # Choose a learning rate of 0.01 49 curr_loss, gradients, a_prev = optimize(X, Y, a_prev, parameters, learning_rate = 0.01) 50 ### END CODE HERE ### 51 52 # Use a latency trick to keep the loss smooth. It happens here to accelerate the training. 53 loss = smooth(loss, curr_loss) 54 55 # Every 2000 Iteration, generate "n" characters thanks to sample() to check if the model is learning properly 56 if j % 2000 == 0: 57 58 print('Iteration: %d, Loss: %f' % (j, loss) + ' ') 59 60 # The number of dinosaur names to print 61 seed = 0 62 for name in range(dino_names): 63 64 # Sample indices and print them 65 sampled_indices = sample(parameters, char_to_ix, seed) 66 print_sample(sampled_indices, ix_to_char) 67 68 seed += 1 # To get the same result for grading purposed, increment the seed by one. 69 70 print(' ') 71 72 return parameters
运行:
parameters = model(data, ix_to_char, char_to_ix)
执行结果:

1 Iteration: 0, Loss: 23.087336 2 3 Nkzxwtdmfqoeyhsqwasjkjvu 4 Kneb 5 Kzxwtdmfqoeyhsqwasjkjvu 6 Neb 7 Zxwtdmfqoeyhsqwasjkjvu 8 Eb 9 Xwtdmfqoeyhsqwasjkjvu 10 11 12 Iteration: 2000, Loss: 27.884160 13 14 Liusskeomnolxeros 15 Hmdaairus 16 Hytroligoraurus 17 Lecalosapaus 18 Xusicikoraurus 19 Abalpsamantisaurus 20 Tpraneronxeros 21 22 23 Iteration: 4000, Loss: 25.901815 24 25 Mivrosaurus 26 Inee 27 Ivtroplisaurus 28 Mbaaisaurus 29 Wusichisaurus 30 Cabaselachus 31 Toraperlethosdarenitochusthiamamumamaon 32 33 34 Iteration: 6000, Loss: 24.608779 35 36 Onwusceomosaurus 37 Lieeaerosaurus 38 Lxussaurus 39 Oma 40 Xusteonosaurus 41 Eeahosaurus 42 Toreonosaurus 43 44 45 Iteration: 8000, Loss: 24.070350 46 47 Onxusichepriuon 48 Kilabersaurus 49 Lutrodon 50 Omaaerosaurus 51 Xutrcheps 52 Edaksoje 53 Trodiktonus 54 55 56 Iteration: 10000, Loss: 23.844446 57 58 Onyusaurus 59 Klecalosaurus 60 Lustodon 61 Ola 62 Xusodonia 63 Eeaeosaurus 64 Troceosaurus 65 66 67 Iteration: 12000, Loss: 23.291971 68 69 Onyxosaurus 70 Kica 71 Lustrepiosaurus 72 Olaagrraiansaurus 73 Yuspangosaurus 74 Eealosaurus 75 Trognesaurus 76 77 78 Iteration: 14000, Loss: 23.382338 79 80 Meutromodromurus 81 Inda 82 Iutroinatorsaurus 83 Maca 84 Yusteratoptititan 85 Ca 86 Troclosaurus 87 88 89 Iteration: 16000, Loss: 23.268257 90 91 Mbutosaurus 92 Indaa 93 Iustolophulurus 94 Macagosaurus 95 Yusoclichaurus 96 Caahosaurus 97 Trodon 98 99 100 Iteration: 18000, Loss: 22.928870 101 102 Phytrogiaps 103 Mela 104 Mustrha 105 Pegamosaurus 106 Ytromacisaurus 107 Efanshie 108 Troma 109 110 111 Iteration: 20000, Loss: 23.008798 112 113 Onyusperchohychus 114 Lola 115 Lytrranfosaurus 116 Olaa 117 Ytrrcharomulus 118 Ehagosaurus 119 Trrcharonyhus 120 121 122 Iteration: 22000, Loss: 22.794515 123 124 Onyvus 125 Llecakosaurus 126 Mustodonosaurus 127 Ola 128 Yusodon 129 Eiadosaurus 130 Trodontorus 131 132 133 Iteration: 24000, Loss: 22.648635 134 135 Meutosaurus 136 Incaachudachus 137 Itntodon 138 Mecaessan 139 Yurong 140 Daadropachusaurus 141 Troenatheusaurosaurus 142 143 144 Iteration: 26000, Loss: 22.599152 145 146 Nixusehoenomulushapnelspanthuonathitalia 147 Jigaadroncansaurus 148 Kustodonis 149 Nedantrocantiteniupegyankuaeusalomarotimenmpangvin 150 Ytrodongoluctos 151 Eebdssaegoterichus 152 Trodolopiunsitarbilus 153 154 155 Iteration: 28000, Loss: 22.628455 156 157 Pnywrodilosaurus 158 Loca 159 Mustodonanethosaurus 160 Phabesceeatopsaurus 161 Ytrodonnoludosaurus 162 Elaishacaosaurus 163 Trrdilosaurus 164 165 166 Iteration: 30000, Loss: 22.587893 167 168 Piusosaurus 169 Locaadrus 170 Lutosaurus 171 Pacalosaurus 172 Yusochesaurus 173 Eg 174 Trraodon 175 176 177 Iteration: 32000, Loss: 22.314649 178 179 Nivosaurus 180 Jiacamisaurus 181 Kusplasaurus 182 Ncaadosaurus 183 Yusiandon 184 Eeaisilaanus 185 Trokalenator 186 187 188 Iteration: 34000, Loss: 22.445100 189 190 Mewsroengosaurus 191 Ilabafosaurus 192 Justoeomimavesaurus 193 Macaeosaurus 194 Yrosaurus 195 Eiaeosaurus 196 Trodondolus
