常用方法1
//文件长度
System.out.println("获取文件的长度:"+f.length());
//文件最后修改时间
long time = f.lastModified();
Date d = new Date(time);
System.out.println("获取文件的最后修改时间:"+d);
//设置文件修改时间为1970.1.1 08:00:00
f.setLastModified(0);
//文件重命名
File f2 =new File("d:/LOLFolder/DOTA.exe");
f.renameTo(f2);
System.out.println("把LOL.exe改名成了DOTA.exe");
文件常用方法2

新特性
遍历文件夹
一般说来操作系统都会安装在C盘,所以会有一个 C:WINDOWS目录。
遍历这个目录下所有的文件(不用遍历子目录)
找出这些文件里,最大的和最小(非0)的那个文件,打印出他们的文件名
注: 最小的文件不能是0长度
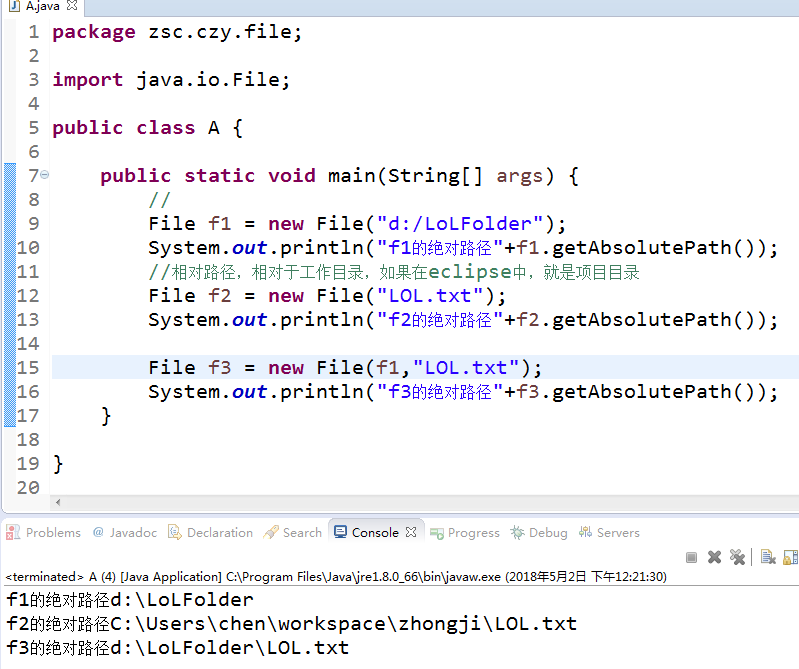
package zsc.czy.file;
import java.io.File;
public class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//
File f1 = new File("c://WINDOWS");
System.out.println("f1的绝对路径" + f1.getAbsolutePath());
// 相对路径,相对于工作目录,如果在eclipse中,就是项目目录
File[] fs = f1.listFiles();
long MINSiZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
long MAXSIZE = 0;
File minFile = null;
File maxFile = null;
System.out.println(MINSiZE);
for (File f : fs) {
if (f.length() >= MAXSIZE) {
MAXSIZE = f.length();
maxFile = f;
}
if (f.length() != 0 && f.length() < MINSiZE) {
MINSiZE = f.length();
minFile = f;
}
}
System.out.printf("最大的文件是%s,其大小是%,d字节%n", maxFile.getAbsoluteFile(),
maxFile.length());
System.out.printf("最小的文件是%s,其大小是%,d字节%n", minFile.getAbsoluteFile(),
minFile.length());
}
}
笔记:最大值先给它0初始,最小值 先给它Intger的r最大值初始
假如:File f = new File("d:/xyz/abc/def/lol2.txt");
System.out.println(f.getParent()); 则是输出 d:xyzabcdef
题目2-遍历子文件夹
同上的练习,要求遍历子文件夹
InputStream字节输入流
OutputStream字节输出流
用于以字节的形式读取和写入数据
题目3--写入数据到文件
以字节流的形式向文件写入数据 中的例子,当lol2.txt不存在的时候,是会自动创建lol2.txt文件的。
但是,如果是写入数据到d:/xyz/lol2.txt,而目录xyz又不存在的话,就会抛出异常。
那么怎么自动创建xyz目录?
如果是多层目录 d:/xyz/abc/def/lol2.txt 呢?
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
File f = new File("d:/xyz/abc/def/lol2.txt");
//因为默认情况下,文件系统中不存在 d:xyzabcdef,所以输出会失败
//首先获取文件所在的目录
File dir = f.getParentFile();
//如果该目录不存在,则创建该目录
if(!dir.exists()){
// dir.mkdir(); //使用mkdir会抛出异常,因为该目录的父目录也不存在
dir.mkdirs(); //使用mkdirs则会把不存在的目录都创建好
}
byte data[] = { 88, 89 };
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(f);
fos.write(data);
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f = new File("d:/xyz/abc/def/lol2.txt");
File dir = f.getParentFile();
if(!dir.exists()){
// dir.mkdir(); //使用mkdir会抛出异常,因为该目录的父目录也不存在
dir.mkdirs(); //这一步执行完,我的电脑就有了 D:xyzabcdef ,不过还不存在lol2.txt
}
}
笔记: dir.mkdirs() 和mkdir()最大的区别是 前者能连没有的父目录都创建出来。
题目4--拆分文件
找到一个大于100k的文件,按照100k为单位,拆分成多个子文件,并且以编号作为文件名结束。
比如文件 eclipse.exe,大小是309k。
拆分之后,成为
eclipse.exe-0
eclipse.exe-1
eclipse.exe-2
eclipse.exe-3
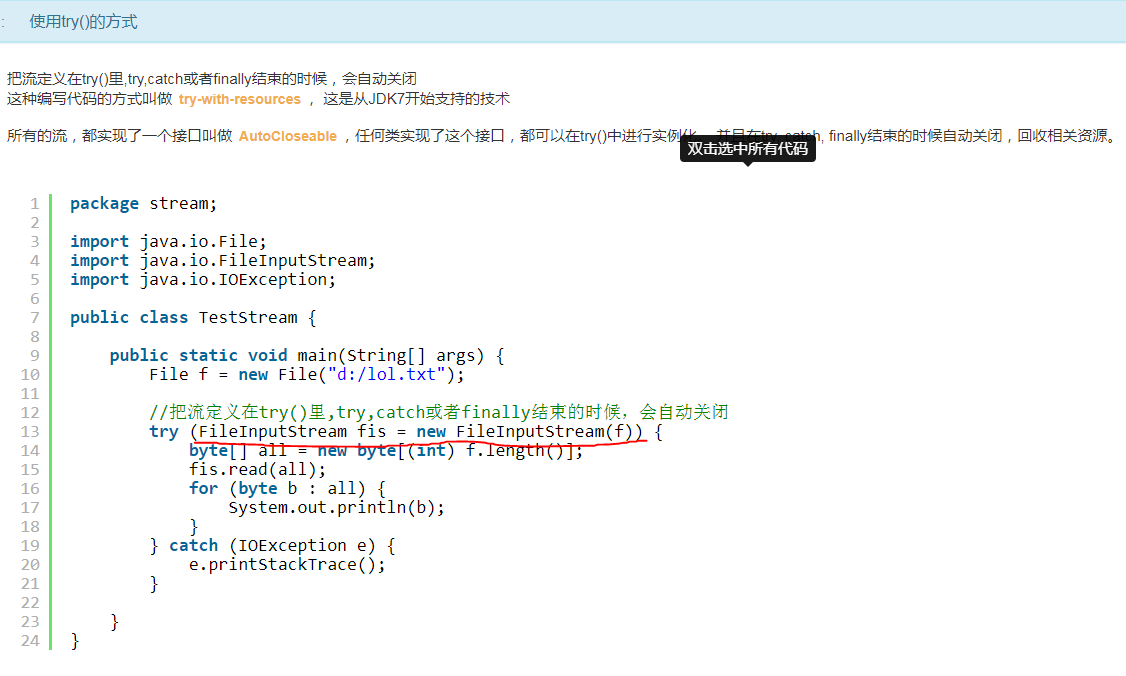
package stream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class TestStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int eachSize = 100 * 1024; // 100k
File srcFile = new File("d:/eclipse.exe");
splitFile(srcFile, eachSize);
}
/**
* 拆分的思路,先把源文件的所有内容读取到内存中,然后从内存中挨个分到子文件里
* @param srcFile 要拆分的源文件
* @param eachSize 按照这个大小,拆分
*/
private static void splitFile(File srcFile, int eachSize) {
if (0 == srcFile.length())
throw new RuntimeException("文件长度为0,不可拆分");
byte[] fileContent = new byte[(int) srcFile.length()];
// 先把文件读取到数组中
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
fis.read(fileContent);
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 计算需要被划分成多少份子文件
int fileNumber;
// 文件是否能被整除得到的子文件个数是不一样的
// (假设文件长度是25,每份的大小是5,那么就应该是5个)
// (假设文件长度是26,每份的大小是5,那么就应该是6个)
if (0 == fileContent.length % eachSize)
fileNumber = (int) (fileContent.length / eachSize);
else
fileNumber = (int) (fileContent.length / eachSize) + 1;
for (int i = 0; i < fileNumber; i++) {
String eachFileName = srcFile.getName() + "-" + i;
File eachFile = new File(srcFile.getParent(), eachFileName);
byte[] eachContent;
// 从源文件的内容里,复制部分数据到子文件
// 除开最后一个文件,其他文件大小都是100k
// 最后一个文件的大小是剩余的
if (i != fileNumber - 1) // 不是最后一个
eachContent = Arrays.copyOfRange(fileContent, eachSize * i, eachSize * (i + 1));
else // 最后一个
eachContent = Arrays.copyOfRange(fileContent, eachSize * i, fileContent.length);
try {
// 写出去
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(eachFile);
fos.write(eachContent);
// 记得关闭
fos.close();
System.out.printf("输出子文件%s,其大小是 %d字节%n", eachFile.getAbsoluteFile(), eachFile.length());
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
题目5--合并文件
把上述拆分出来的文件,合并成一个原文件。
思路:
拆分文件不同(先把所有数据读取到内存中),合并文件采用另一种思路。
这种思路,不需要把所有的子文件都先读取到内存中,而是一边读取子文件的内容,一边写出到目标文件
即从eclipse.exe-0开始,读取到一个文件,就开始写出到 eclipse.exe中,然后处理eclipse.exe-1eclipse.exe-2 eclipse.exe-3 ... 直到没有文件可以读
package stream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.security.auth.DestroyFailedException;
public class TestStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
murgeFile("d:/", "eclipse.exe");
}
/**
* 合并的思路,就是从eclipse.exe-0开始,读取到一个文件,就开始写出到 eclipse.exe中,直到没有文件可以读
* @param folder
* 需要合并的文件所处于的目录
* @param fileName
* 需要合并的文件的名称
* @throws FileNotFoundException
*/
private static void murgeFile(String folder, String fileName) {
try {
// 合并的目标文件
File destFile = new File(folder, fileName);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
int index = 0;
while (true) {
//子文件
File eachFile = new File(folder, fileName + "-" + index++);
//如果子文件不存在了就结束
if (!eachFile.exists())
break;
//读取子文件的内容
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(eachFile);
byte[] eachContent = new byte[(int) eachFile.length()];
fis.read(eachContent);
fis.close();
//把子文件的内容写出去
fos.write(eachContent);
fos.flush();
System.out.printf("把子文件 %s写出到目标文件中%n",eachFile);
}
fos.close();
System.out.printf("最后目标文件的大小:%,d字节" , destFile.length());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
所有的流,无论是输入流还是输出流,使用完毕之后,都应该关闭。 如果不关闭,会产生对资源占用的浪费。 当量比较大的时候,会影响到业务的正常开展。
Reader字符输入流
Writer字符输出流
专门用于字符的形式读取和写入数据
笔记:
inputStream 和outputStream 这些都是用byte[] 来 读入 写出的
Reader Writer 这些都是用char[] 来 读入 写出的
题目6-文件加密
准备一个文本文件(非二进制),其中包含ASCII码的字符和中文字符。
设计一个方法
public static void encodeFile(File encodingFile, File encodedFile);
在这个方法中把encodingFile的内容进行加密,然后保存到encodedFile文件中。
加密算法:
数字:
如果不是9的数字,在原来的基础上加1,比如5变成6, 3变成4
如果是9的数字,变成0
字母字符:
如果是非z字符,向右移动一个,比如d变成e, G变成H
如果是z,z->a, Z-A。
字符需要保留大小写
非字母字符
比如',&^ 保留不变,中文也保留不变
奇怪现象-原来字符数组 始终打印不出
//有bug的
package zsc.czy.file;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class E {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File encodingFile = new File("d:/Test1.txt");
System.out.println(encodingFile.length());
File encodedFile = new File("d:/Test2.txt");
encodeFile(encodingFile, encodedFile);
}
public static void encodeFile(File encodingFile, File encoudeFile) {
try {
System.out.println("长度"+encodingFile.length()); //长度5
FileReader fr = new FileReader(encodingFile);
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(encoudeFile);
char[] fileContent = new char[(int) encoudeFile.length()];
System.out.println("数组长度"+fileContent.length); //数组长度0
fr.read(fileContent);
System.out.println("数组长度2"+fileContent.length); //数组长度20
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(fileContent));//[]
System.out.println(new String(fileContent)); //空白
// 进行加密
encode(fileContent);
System.out.println("加密后的内容:");
System.out.println(new String(fileContent));
fw.write(fileContent);
fw.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
private static void encode(char[] fileContent) {
for (int i = 0; i < fileContent.length; i++) {
char c = fileContent[i];
if (isLetterOrDigit(c)) {
switch (c) {
case '9':
c = '0';
break;
case 'z':
c = 'a';
break;
case 'Z':
c = 'A';
break;
default:
c++;
break;
}
}
fileContent[i] = c;
}
}
private static boolean isLetterOrDigit(char c) {
// 不使用Character类的isLetterOrDigit方法是因为,中文也会被判断为字母
String letterOrDigital = "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz";
return -1 == letterOrDigital.indexOf(c) ? false : true;
}
}
正确的:
package zsc.czy.file;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class F {
/**
*
* @param encodingFile
* 被加密的文件
* @param encodedFile
* 加密后保存的位置
*/
public static void encodeFile(File encodingFile, File encodedFile) {
try (FileReader fr = new FileReader(encodingFile); FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(encodedFile)) {
// 读取源文件
char[] fileContent = new char[(int) encodingFile.length()];
fr.read(fileContent);
System.out.println("加密前的内容:");
System.out.println(new String(fileContent));
// 进行加密
encode(fileContent);
// 把加密后的内容保存到目标文件
System.out.println("加密后的内容:");
System.out.println(new String(fileContent));
fw.write(fileContent);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void encode(char[] fileContent) {
for (int i = 0; i < fileContent.length; i++) {
char c = fileContent[i];
if (isLetterOrDigit(c)) {
switch (c) {
case '9':
c = '0';
break;
case 'z':
c = 'a';
break;
case 'Z':
c = 'A';
break;
default:
c++;
break;
}
}
fileContent[i] = c;
}
}
public static boolean isLetterOrDigit(char c) {
// 不使用Character类的isLetterOrDigit方法是因为,中文也会被判断为字母
String letterOrDigital = "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz";
return -1 == letterOrDigital.indexOf(c) ? false : true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
File encodingFile = new File("d:/Test3.txt");
File encodedFile = new File("d:/Test4.txt");
encodeFile(encodingFile, encodedFile);
}
}
题目7--文件解密
解密在文件加密中生成的文件。
设计一个方法
public static void decodeFile(File decodingFile, File decodedFile);
在这个方法中把decodingFile的内容进行解密,然后保存到decodedFile文件中。
解密算法:
数字:
如果不是0的数字,在原来的基础上减1,比如6变成5, 4变成3
如果是0的数字,变成9
字母字符:
如果是非a字符,向左移动一个,比如e变成d, H变成G
如果是a,a->z, A-Z。
字符需要保留大小写
非字母字符:
比如',&^ 保留不变,中文也保留不变
···
package stream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class TestStream {
/**
*
* @param decodingFile
* 被解密的文件
* @param decodedFile
* 解密后保存的位置
*/
public static void decodeFile(File decodingFile, File decodedFile) {
try (FileReader fr = new FileReader(decodingFile); FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(decodedFile)) {
// 读取源文件
char[] fileContent = new char[(int) decodingFile.length()];
fr.read(fileContent);
System.out.println("源文件的内容:");
System.out.println(new String(fileContent));
// 进行解密
decode(fileContent);
System.out.println("解密后的内容:");
System.out.println(new String(fileContent));
// 把解密后的内容保存到目标文件
fw.write(fileContent);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void decode(char[] fileContent) {
for (int i = 0; i < fileContent.length; i++) {
char c = fileContent[i];
if (isLetterOrDigit(c)) {
switch (c) {
case '0':
c = '9';
break;
case 'a':
c = 'z';
break;
case 'A':
c = 'Z';
break;
default:
c--;
break;
}
}
fileContent[i] = c;
}
}
public static boolean isLetterOrDigit(char c) {
// 不使用Character类的isLetterOrDigit方法是因为,中文也会被判断为字母
String letterOrDigital ="0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz";
return -1 == letterOrDigital.indexOf(c) ? false : true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
File decodingFile = new File("E:/project/j2se/src/Test2.txt");
File decodedFile = new File("E:/project/j2se/src/Test1.txt");
decodeFile(decodingFile, decodedFile);
}
}
···
题目8-数字对应的中文
找出 E5 B1 8C 这3个十六进制对应UTF-8编码的汉字
package zsc.czy.zhongwen;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
public class C {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
byte[] bs =new byte[3];
bs[0] = (byte) 0xE5;
bs[1] = (byte) 0xB1;
bs[2] = (byte) 0x8C;
String str =new String(bs,"UTF-8");
System.out.println("E5 B1 8C 对应的字符是:"+str);
}
}
题目9--移除BOM
package stream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class TestStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f = new File("E:\project\j2se\src\test.txt");
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f);) {
byte[] all = new byte[(int) f.length()];
fis.read(all);
System.out.println("首先确认按照UTF-8识别出来有?");
String str = new String(all,"UTF-8");
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println("根据前面的所学,知道'中'字对应的UTF-8编码是:e4 b8 ad");
System.out.println("打印出文件里所有的数据的16进制是:");
for (byte b : all) {
int i = b&0xff;
System.out.print(Integer.toHexString(i)+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("通过观察法得出 UTF-8的 BOM 是 ef bb bf");
byte[] bom = new byte[3];
bom[0] = (byte) 0xef;
bom[1] = (byte) 0xbb;
bom[2] = (byte) 0xbf;
byte[] fileContentWithoutBOM= removeBom(all,bom);
System.out.println("去掉了BOM之后的数据的16进制是:");
for (byte b : fileContentWithoutBOM) {
int i = b&0xff;
System.out.print(Integer.toHexString(i)+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("对应的字符串就没有问号了:");
String strWithoutBOM=new String(fileContentWithoutBOM,"UTF-8");
System.out.println(strWithoutBOM);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static byte[] removeBom(byte[] all, byte[] bom) {
return Arrays.copyOfRange(all, bom.length, all.length);
}
}
题目10-移除注释
设计一个方法,用于移除Java文件中的注释
public void removeComments(File javaFile)
比如,移出以//开头的注释行
File f = new File("d:/LOLFolder/LOL.exe");
System.out.println("当前文件是:" +f);
//文件是否存在
System.out.println("判断是否存在:"+f.exists());
//是否是文件夹
System.out.println("判断是否是文件夹:"+f.isDirectory());
答案
注意:要在通过BuffedReader 读取完数据后,才能建立Printwriter,因为创建输出流的时候,会把目标文件内容清空
package stream;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class TestStream {
public static void removeComments(File javaFile) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
//读取内容
try (FileReader fr = new FileReader(javaFile); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);) {
while (true) {
String line = br.readLine();
if (null == line)
break;
//如果不是以//开头,就保存在StringBuffer中
if (!line.trim().startsWith("//"))
sb.append(line).append("
");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try (
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(javaFile);
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(fw);
) {
//写出内容
pw.write(sb.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
File javaFile = new File("E:\project\j2se\src\character\MyStringBuffer2.java");
System.out.println(javaFile.exists());
System.out.println(javaFile.length());
removeComments(javaFile);
}
}
==========================
DataInputStream 数据输入流
DataOutputStream 数据输出流
题目11--向文件中写入两个数字,然后把这两个数字分别读取出来
要求
第一种方式: 使用缓存流把两个数字以字符串的形式写到文件里,再用缓存流以字符串的形式读取出来,然后转换为两个数字。
注: 两个数字之间要有分隔符用于区分这两个数字。 比如数字是31和15,如果不使用分隔符,那么就是3115,读取出来就无法识别到底是哪两个数字。 使用分隔符31@15能解决这个问题。
第二种方式: 使用数据流DataOutputStream向文件连续写入两个数字,然后用DataInpuStream连续读取两个数字
package stream;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class TestStream {
static File f =new File("d:/data.txt");
static int x = 31;
static int y = 15;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//缓存流方式
method1();
//数据流方式
method2();
}
private static void method2() {
try (
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f);
DataInputStream dis =new DataInputStream(fis);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(f);
DataOutputStream dos =new DataOutputStream(fos);
){
dos.writeInt(x);
dos.writeInt(y);
int x = dis.readInt();
int y = dis.readInt();
System.out.printf("使用数据流读取出的x是 %d y是 %d%n",x,y);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void method1() {
try (
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(f);
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(fw);
FileReader fr = new FileReader(f);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
) {
pw.print(x+"@"+y);
pw.flush();
String str = br.readLine();
String[] ss =str.split("@");
int x = Integer.parseInt(ss[0]);
int y = Integer.parseInt(ss[1]);
System.out.printf("使用缓存流读取出的x是 %d y是 %d%n",x,y);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void read() {
File f =new File("d:/data.txt");
try (
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f);
DataInputStream dis =new DataInputStream(fis);
){
boolean b= dis.readBoolean();
int i = dis.readInt();
String str = dis.readUTF();
System.out.println("读取到布尔值:"+b);
System.out.println("读取到整数:"+i);
System.out.println("读取到字符串:"+str);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void write() {
File f =new File("d:/data.txt");
try (
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(f);
DataOutputStream dos =new DataOutputStream(fos);
){
dos.writeBoolean(true);
dos.writeInt(300);
dos.writeUTF("123 this is gareen");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
额外知识点:



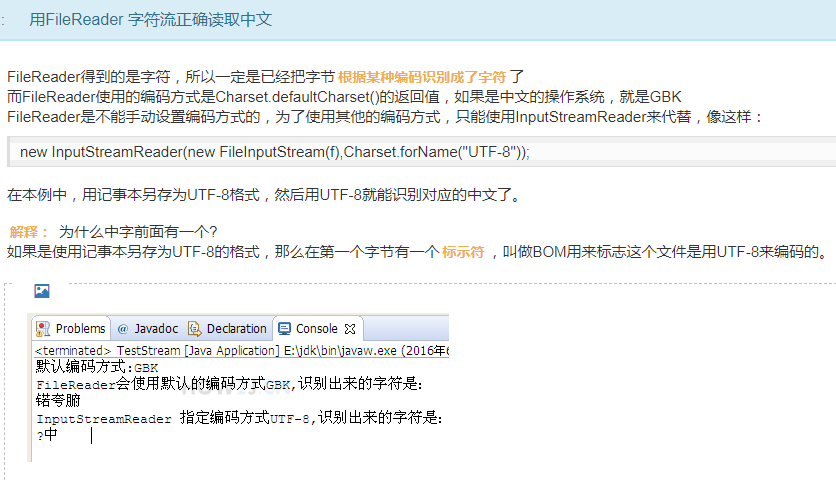
笔记:使用字节流读取了文本后,再使用对应的编码方式去识别这些数字,得到正确的字符
(字节流就是数字)

==============================
以介质是硬盘为例,字节流和字符流的弊端:
在每一次读写的时候,都会访问硬盘。 如果读写的频率比较高的时候,其性能表现不佳。
为了解决以上弊端,采用缓存流。
缓存流在读取的时候,会一次性读较多的数据到缓存中,以后每一次的读取,都是在缓存中访问,直到缓存中的数据读取完毕,再到硬盘中读取。
File f = new File("d:/lol.txt");
// 创建文件字符流
// 缓存流必须建立在一个存在的流的基础上
try (
FileReader fr = new FileReader(f);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
)

笔记
缓存流必须建立在一个存在的流的基础上
缓存字符输入流 BufferedReader 可以一次读取一行数据
PrintWriter 缓存字符输出流, 可以一次写出一行数据