深挖Openstack Nova - Scheduler调度策略
一. Scheduler的作用就是在创建实例(instance)时,为实例选择出合适的主机(host)。这个过程分两步:过滤(Fliter)和计算权值(Weight)
1. 过滤:
过滤掉不符合我们的要求,或镜像要求(比如物理节点不支持64bit,物理节点不支持Vmware EXi等)的主机,留下符合过滤算法的主机集合。
2. 计算权值
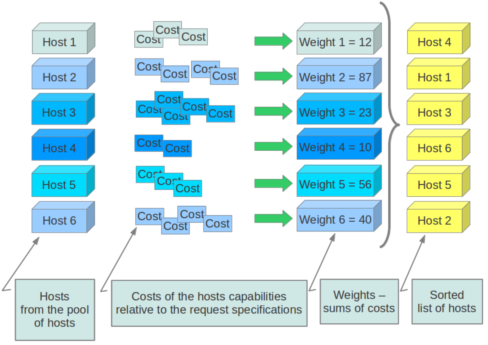
通过指定的权值计算算法,计算在某物理节点上申请这个虚机所必须的消耗cost。物理节点越不适合这个虚机,消耗cost就越大,权值Weight就越大,调度算法会选择权值最小的主机。
二. 过滤策略
Filter算法在nova-scheduler中是通过oslo.config.cfg模块从nova.conf配置文件中动态获取的,应用了Python的反射机制,在运行时刻决定初始化所选择的filter算法。
OpenStack支持多种过滤策略,均在/nova/scheduler/filters包下:
1. CoreFilter:根据CPU数过滤主机
2. RamFilter:根据指定的RAM值选择资源足够的主机
3. AvailabilityZoneFilter:返回创建虚拟机参数指定的集群内的主机
4. JsonFilter:根据JSON串指定的规则选择主机
三. 目录结构
1. /nova/scheduler/filter_scheduler.py:继承于类Scheduler,实现基于主机过滤器选取主机节点方式的调度器
2. /nova/scheduler/host_manager.py: 描述了跟调度器操作相关的主机的实现,其中,HostState类描述了从主机获取相关数据和状态的一些实现,HostManager类描述了跟调度器操作相关的一些主机管理实现
3. /nova/weights.py:实现了跟计算权值相关的方法
四. 分析调度_schedule方法
该方法对应在/nova/scheduler/filter_scheduler.py中
-
# 调度方法,返回一系列满足要求的主机(host)
-
def _schedule(self, context, request_spec, filter_properties)
1. 信息初始化
-
# 返回带有admin标志设置的context的版本
-
elevated = context.elevated()
-
# 获取实例信息
-
instance_properties = request_spec['instance_properties']
2. 更新过滤器属性信息
-
filter_properties.update({'context': context,
-
'request_spec': request_spec,
-
'config_options': config_options,
-
'instance_type': instance_type})
3. 过滤不可用的host
-
# 过滤掉不可用的主机节点
-
hosts = self._get_all_host_states(elevated)
深入_get_all_host_states方法,对应的是/nova/scheduler/host_manager.py。
(1)获取可用的计算节点
-
# 获取可用计算节点的资源使用情况
-
# 获取所有compute_node(计算节点)
-
compute_nodes = objects.ComputeNodeList.get_all(context)
(2)设置基本信息
-
# 获取主机host
-
host = compute.host
-
# 获取hypervisor_hostname作为节点名
-
node = compute.hypervisor_hostname
-
state_key = (host, node)
-
# 从host_state_map获取并更新host状态
-
host_state = self.host_state_map.get(state_key)
-
if host_state:
-
host_state.update_from_compute_node(compute)
-
else:
-
host_state = self.host_state_cls(host, node, compute=compute)
-
self.host_state_map[state_key] = host_state
(3)更新host状态
-
# 每次请求到来都要更新host状态
-
host_state.aggregates = [self.aggs_by_id[agg_id] for agg_id in
-
self.host_aggregates_map[
-
host_state.host]]
-
host_state.update_service(dict(service))
-
self._add_instance_info(context, compute, host_state)
-
seen_nodes.add(state_key)
(4)删除不活跃的计算节点
-
# 从host_state_map中删除不活跃的计算节点
-
dead_nodes = set(self.host_state_map.keys()) - seen_nodes
-
for state_key in dead_nodes:
-
host, node = state_key
-
LOG.info(_LI("Removing dead compute node %(host)s:%(node)s "
-
"from scheduler"), {'host':host, 'node': node})
-
del self.host_state_map[state_key]
4.循环遍历实例,获取符合过滤要求的host
-
for num in range(num_instances):
-
# 基于具体要求过滤本地主机
-
hosts = self.host_manager.get_filtered_hosts(hosts,
-
filter_properties, index=num)
-
# 一个符合要求的host都没有
-
if not hosts:
-
break
深入get_filtered_hosts方法,对应的是/nova/scheduler/host_manager.py。
(1)定义所要使用的过滤器
-
# 如果没有设置过滤器,则使用默认的过滤器
-
if filter_class_names is None:
-
filters = self.default_filters
-
else:
-
# 获取过滤器方法
-
filters = self._choose_host_filters(filter_class_names)
(2)然后处理三种类型的host
1》忽略的host
ignore_hosts = filter_properties.get('ignore_hosts', [])-
# 除去忽略的host
-
def _strip_ignore_hosts(host_map, hosts_to_ignore):
2》强制使用的host
force_hosts = filter_properties.get('force_hosts', [])-
# 匹配强制使用的host
-
def _match_forced_hosts(host_map, hosts_to_force):
3》强制使用的nodes
force_nodes = filter_properties.get('force_nodes', [])-
# 匹配强制使用的nodes
-
def _match_forced_nodes(host_map, nodes_to_force):
-
# 执行过滤操作,返回满足所有过滤条件的host对象
-
return self.filter_handler.get_filtered_objects(filters,
-
hosts, filter_properties, index)
5. 对主机进行称重
-
# 获取并返回一个WeightedObjects的主机排序列表(最高分排在第一)
-
weighted_hosts = self.host_manager.get_weighted_hosts(hosts,
-
filter_properties)
深入get_weighted_hosts方法,最终对应的是/nova/weights.py。
(1)用相乘累加的方式计算host主机的权重
-
# 根据多方面参数来判定权值,比如主机剩余内存、剩余磁盘空间、vcpu的使用情况
-
# 每个参数乘于一个weight,累加得到host主机的权值
-
for i, weight in enumerate(weights):
-
obj = weighted_objs[i]
-
obj.weight += weigher.weight_multiplier() * weight
(2)将获取权值的host主机排序后返回
-
# 对WeighedObjects列表进行排序返回
-
return sorted(weighed_objs, key=lambda x: x.weight, reverse=True)
开发者也可以实现自己的权值计算函数,对于OpenStack采用的方法来说,主机拥有的剩余内存越多,权值越小,被选择在其上创建虚拟机的可能性就越大。
6. 设置调度使用的主机数目
-
# scheduler_host_subset_size:定义了新的实例将会被调度到一个主机上
-
# 这个主机是随机从最好的(分数最高的)N个主机组成的子集中选择出来
-
scheduler_host_subset_size = CONF.scheduler_host_subset_size
-
if scheduler_host_subset_size > len(weighed_hosts):
-
scheduler_host_subset_size = len(weighed_hosts)
-
if scheduler_host_subset_size < 1:
-
scheduler_host_subset_size = 1
7. 获取随机选择出来的主机
-
# 从分数最高的若干主机组成的子集中,随机选择一个主机
-
# 新的实例将会调度到这个主机上
-
chosen_host = random.choice(
-
weighed_hosts[0:scheduler_host_subset_size])
-
LOG.debug("Selected host: %(host)s", {'host': chosen_host})
-
# 把选好的主机增加到selected_hosts列表中
-
selected_hosts.append(chosen_host)
8. 为下一次实例选择主机做好准备
-
# 此次选择了一个主机后,在下一个实例选择主机前,更新主机资源信息
-
chosen_host.obj.consume_from_instance(instance_properties)
-
if update_group_hosts is True:
-
if isinstance(filter_properties['group_hosts'], list):
-
filter_properties['group_hosts'] = set(
-
filter_properties['group_hosts'])
-
filter_properties['group_hosts'].add(chosen_host.obj.host)
9. 返回所有实例选择的主机列表
-
# 循环为每一个实例获取合适的主机后,返回选择的主机列表
-
return selected_hosts