你是否再为配置文件web.xml容易出错而烦恼?是否为web.xml文件存放位置而不知所措?是否为web.xml为什么要这样配?怎么才能更好的配置web.xml而烦恼?那么一种新的方式出现了:
spring提供了支持servlet 3+以上的编程方式,它可以替换或者和web.xml共存的方式工作。其相关类如下:
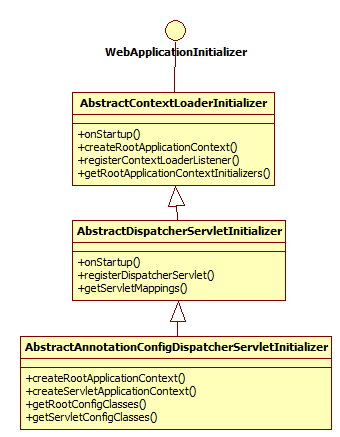
WebApplicationInitializer
传统上,我们基于web.xml这种方式来配置web应用,而WebApplicationInitializer的实现支持在servlet 3.0以上的环境里通过编程的方式来配置ServletContext,这种方式既可以替换web.xml这种方式,也可以和web.xml这种方式共存。
这种SPI的实现通常由SpringServletContainerInitializer来自动发现,SpringServletContainerInitializer可以被servlet 3.0以上的容器自动启动。详细请参考下面的章节。示例如下:
传统基于xml的方式
绝大多数spring开发者构建web应用时需要注册spring DispatcherServlet到WEB/web.xml如下方式:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/dispatcher-config.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
基于编程方式的WebApplicationInitializer
下面基于WebApplicationInitializer样式的代码等同于DispatcherServlet的注册逻辑:
public class MyWebAppInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer { @Override public void onStartup(ServletContext container) { XmlWebApplicationContext appContext = new XmlWebApplicationContext(); appContext.setConfigLocation("/WEB-INF/spring/dispatcher-config.xml"); ServletRegistration.Dynamic dispatcher = container.addServlet("dispatcher", new DispatcherServlet(appContext)); dispatcher.setLoadOnStartup(1); dispatcher.addMapping("/"); } }
上面的实现,还可以通过扩展org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer实现。
如上所示,归功于servlet3.0的ServletContext#addServlet方法,我们注册一个DispatcherServlet的实例,这意味着DispatcherServlet可以如其他Object一样,接受在应用上下文中通过构造器进行注入。
这种方式不但简单还很明了。不需要关注init-param的处理等等,仅有通常的javaBean样式的属性和构造参数。可以在DispatcherServlet注入之前,尽可能的自由的创建spring context、使用spring context。
绝大部分spring web组件已经更新来支持这种注册方式,你会发现DispatcherServlet、FrameworkServlet、ContextLoaderListener和DelegatingFilterProxy现在都支持构造参数。
尽管个别组件(非spring的,其他第三方的)没有更新到支持WebApplicationInitializer的使用,它们仍然可以使用。servlet 3.0的ServletContext api支持编码式设置init-params,context-param等的属性。
基于编码式的配置
上例中,WEB/web.xml可以通过WebApplicationInitializer样式的代码完全替换掉,但真正的dispatcher-config.xml spring配置文件仍然是基于xml方式的。WebApplicationInitializer也是一个很棒的方式来进行spring的基于编程方式的配置类,详情参考org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration。
下面的例子中,将使用spring的
org.springframework.web.context.support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext
类来替代XmlWebApplicationContext,用户自定义的@Configuration配置类AppConfig和DispatcherConfig来替换spring的xml文件来重构上面的例子。这个示例也有一些超出部分,用来展示root application context的的通用配置和ContextLoaderListener的注册:
public class MyWebAppInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer { @Override public void onStartup(ServletContext container) { // Create the 'root' Spring application context AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext rootContext = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext(); rootContext.register(AppConfig.class); // Manage the lifecycle of the root application context container.addListener(new ContextLoaderListener(rootContext)); // Create the dispatcher servlet's Spring application context AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext dispatcherContext = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext(); dispatcherContext.register(DispatcherConfig.class); // Register and map the dispatcher servlet ServletRegistration.Dynamic dispatcher = container.addServlet("dispatcher", new DispatcherServlet(dispatcherContext)); dispatcher.setLoadOnStartup(1); dispatcher.addMapping("/"); } }
上面的示例的另一种实现方式,可以通过扩展org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer来实现。
注意,WebApplicationInitializer的实现是自动发现的,因此无需在你的应用中打包。
WebApplicationInitializer执行顺序
WebApplicationInitializer的实现可以通过@order来注解也可以通过实现spring的org.springframework.core.Ordered接口,如果这样,就根据优先级去触发。spring为用户提供了一种在servlet container初始化时保证执行顺序的机制。使用这种特性的应用场景比较罕见,因为典型的应用通常在一个单独的WebApplicationInitializer中集中所有的容器初始化。
附加说明
web.xml版本信息
WEB/web.xml和WebApplicationInitializer不是相斥的。例如web.xml可以注册一个servlet,WebApplicationInitializer可以注册另外一个servlet。一个WebApplicationInitializer甚至可以通过方法如ServletContext#getServletRegistration(String)来修改web.xml中的注册信息。然而,若应用中出现web.xml,它的version属性必须设置成3.0或者以上,否则ServletContainerInitializer将会在servlet容器启动时被忽略启动。
tomcat下映射到"/"
apache tomcat映射它内部的DefaultServlet到"/",并且当tomcat版本小于7.0.14时,这个映射属性不能通过编码重写。7.0.15解决了这个问题。重写"/"映射已经在glassFish3.1中进行了验证确认。
public interface WebApplicationInitializer { /** * Configure the given {@link ServletContext} with any servlets, filters, listeners * context-params and attributes necessary for initializing this web application. See * examples {@linkplain WebApplicationInitializer above}. * @param servletContext the {@code ServletContext} to initialize * @throws ServletException if any call against the given {@code ServletContext} * throws a {@code ServletException} */ void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException; }
1 SpringServletContainerInitializer
和传统基于web.xml的方式不同,servlet 3.0 ServletContainerInitializer 使用spring的WebApplicationInitializer来支持对servlet container的基于编程的配置支持。
工作机制
假定spring-web模块的jar都出现在classpath上,在容器启动时,servlet 3.0兼容的容器将会加载类,并初始化,然后触发它的onStartup方法。Jar服务Api 方法ServiceLoader#load(class)发现spring-web模块的META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer服务提供配置文件,详情参考http://docs.oracle.com/javase/6/docs/technotes/guides/jar/jar.html#Service%20Provider
和web.xml共用
一个web应用在启动阶段选择限制classpath 扫描的servlet container的数量的方式有两种,一种通过web.xml的属性metadata-complete,它控制server注解的扫描。另一种是通过web.xml中的absolute-ordering属性,它控制哪些web片段(例如jar文件)允许servletContainerInitializer扫描。当使用这些特色,springServletContainerInitializer通过增加spring_web到web.xml的命名片段中来启用这些,如下所示:
<absolute-ordering>
<name>some_web_fragment</name>
<name>spring_web</name>
</absolute-ordering>
与spring的WebApplicationInitializer的关系
spring的WebApplicationInitializer spi仅仅包含了一个方法WebApplicationInitializer#onStartup(ServletContext),类似于ServletContainerInitializer#onStartup(Set, ServletContext)。SpringServletContainerInitializer负责初始化并对用户定义的WebApplicationInitializer代理servletContext。然后负责让每个WebApplicationInitializer去做servletContext初始化的具体工作。代理的精确过程描述在下文的onStartup方法。
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class) public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer { /** * Delegate the {@code ServletContext} to any {@link WebApplicationInitializer} * implementations present on the application classpath. * <p>Because this class declares @{@code HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)}, * Servlet 3.0+ containers will automatically scan the classpath for implementations * of Spring's {@code WebApplicationInitializer} interface and provide the set of all * such types to the {@code webAppInitializerClasses} parameter of this method. * <p>If no {@code WebApplicationInitializer} implementations are found on the classpath, * this method is effectively a no-op. An INFO-level log message will be issued notifying * the user that the {@code ServletContainerInitializer} has indeed been invoked but that * no {@code WebApplicationInitializer} implementations were found. * <p>Assuming that one or more {@code WebApplicationInitializer} types are detected, * they will be instantiated (and <em>sorted</em> if the @{@link * org.springframework.core.annotation.Order @Order} annotation is present or * the {@link org.springframework.core.Ordered Ordered} interface has been * implemented). Then the {@link WebApplicationInitializer#onStartup(ServletContext)} * method will be invoked on each instance, delegating the {@code ServletContext} such * that each instance may register and configure servlets such as Spring's * {@code DispatcherServlet}, listeners such as Spring's {@code ContextLoaderListener}, * or any other Servlet API componentry such as filters. * @param webAppInitializerClasses all implementations of * {@link WebApplicationInitializer} found on the application classpath * @param servletContext the servlet context to be initialized * @see WebApplicationInitializer#onStartup(ServletContext) * @see AnnotationAwareOrderComparator */ @Override public void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException { List<WebApplicationInitializer> initializers = new LinkedList<>(); if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) { for (Class<?> waiClass : webAppInitializerClasses) { // Be defensive: Some servlet containers provide us with invalid classes, // no matter what @HandlesTypes says... if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) && WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) { try { initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer) ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(waiClass).newInstance()); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", ex); } } } } if (initializers.isEmpty()) { servletContext.log("No Spring WebApplicationInitializer types detected on classpath"); return; } servletContext.log(initializers.size() + " Spring WebApplicationInitializers detected on classpath"); AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers); for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) { initializer.onStartup(servletContext); } } }