概述
详细
一、概述:
在日常的app使用中,我们会在android 的app中看见 热门标签等自动换行的流式布局,今天,我们就来看看如何
自定义一个类似热门标签那样的流式布局吧
类似的自定义换行流式布局控件。下面我们就来详细介绍流式布局的应用特点以及用的的技术点:
1.流式布局的特点以及应用场景
特点:当上面一行的空间不够容纳新的TextView时候,
才开辟下一行的空间
原理图:
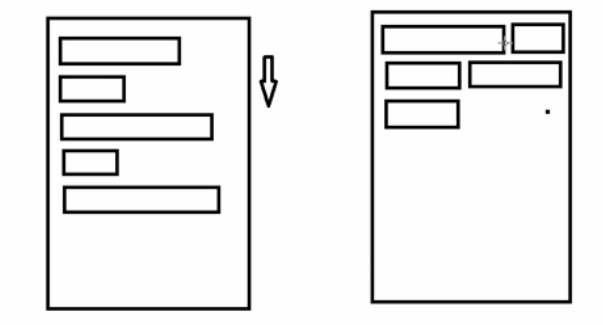
场景:主要用于关键词搜索或者热门标签等场景
2.自定义ViewGroup,重点重写下面两个方法
1、onMeasure:测量子view的宽高,设置自己的宽和高
2、onLayout:设置子view的位置
onMeasure:根据子view的布局文件中属性,来为子view设置测量模式和测量值
测量=测量模式+测量值;
测量模式有3种:
EXACTLY:表示设置了精确的值,一般当childView设置其宽、高为精确值、match_parent时,ViewGroup会将其设置为EXACTLY;
AT_MOST:表示子布局被限制在一个最大值内,一般当childView设置其宽、高为wrap_content时,ViewGroup会将其设置为AT_MOST;
UNSPECIFIED:表示子布局想要多大就多大,一般出现在AadapterView的item的heightMode中、ScrollView的childView的heightMode中;此种模式比较少见。
3.LayoutParams
ViewGroup LayoutParams :每个 ViewGroup 对应一个 LayoutParams; 即 ViewGroup -> LayoutParams
getLayoutParams 不知道转为哪个对应的LayoutParams ,其实很简单,就是如下:
子View.getLayoutParams 得到的LayoutParams对应的就是 子View所在的父控件的LayoutParams;
例如,LinearLayout 里面的子view.getLayoutParams ->LinearLayout.LayoutParams
所以 咱们的FlowLayout 也需要一个LayoutParams,由于上面的效果图是子View的 margin,
所以应该使用MarginLayoutParams。即FlowLayout->MarginLayoutParams
4.最后来看看实现的最终效果图:
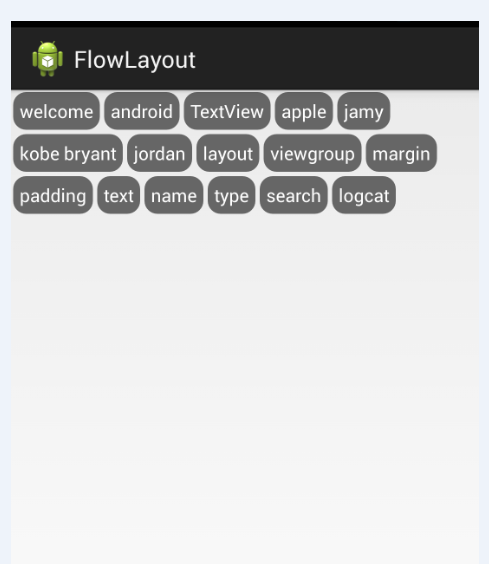
二、热门标签的流式布局的实现:
1. 自定义热门标签的ViewGroup实现
根据上面的技术分析,自定义类继承于ViewGroup,并重写 onMeasure和onLayout等方法。具体核心实现代码如下:
package com.czm.flowlayout;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
/**
*
* @author caizhiming
*
*/
public class XCFlowLayout extends ViewGroup{
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//父控件传进来的宽度和高度以及对应的测量模式
int sizeWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int modeWidth = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int sizeHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int modeHeight = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
//如果当前ViewGroup的宽高为wrap_content的情况
int width = 0;//自己测量的 宽度
int height = 0;//自己测量的高度
//记录每一行的宽度和高度
int lineWidth = 0;
int lineHeight = 0;
//获取子view的个数
int childCount = getChildCount();
for(int i = 0;i < childCount; i ++){
View child = getChildAt(i);
//测量子View的宽和高
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//得到LayoutParams
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
//子View占据的宽度
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
//子View占据的高度
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
//换行时候
if(lineWidth + childWidth > sizeWidth){
//对比得到最大的宽度
width = Math.max(width, lineWidth);
//重置lineWidth
lineWidth = childWidth;
//记录行高
height += lineHeight;
lineHeight = childHeight;
}else{//不换行情况
//叠加行宽
lineWidth += childWidth;
//得到最大行高
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight);
}
//处理最后一个子View的情况
if(i == childCount -1){
width = Math.max(width, lineWidth);
height += lineHeight;
}
}
//wrap_content
setMeasuredDimension(modeWidth == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? sizeWidth : width,
modeHeight == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? sizeHeight : height);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
mAllChildViews.clear();
mLineHeight.clear();
//获取当前ViewGroup的宽度
int width = getWidth();
int lineWidth = 0;
int lineHeight = 0;
//记录当前行的view
List<View> lineViews = new ArrayList<View>();
int childCount = getChildCount();
for(int i = 0;i < childCount; i ++){
View child = getChildAt(i);
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
//如果需要换行
if(childWidth + lineWidth + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin > width){
//记录LineHeight
mLineHeight.add(lineHeight);
//记录当前行的Views
mAllChildViews.add(lineViews);
//重置行的宽高
lineWidth = 0;
lineHeight = childHeight + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
//重置view的集合
lineViews = new ArrayList();
}
lineWidth += childWidth + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
lineViews.add(child);
}
//处理最后一行
mLineHeight.add(lineHeight);
mAllChildViews.add(lineViews);
//设置子View的位置
int left = 0;
int top = 0;
//获取行数
int lineCount = mAllChildViews.size();
for(int i = 0; i < lineCount; i ++){
//当前行的views和高度
lineViews = mAllChildViews.get(i);
lineHeight = mLineHeight.get(i);
for(int j = 0; j < lineViews.size(); j ++){
View child = lineViews.get(j);
//判断是否显示
if(child.getVisibility() == View.GONE){
continue;
}
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int cLeft = left + lp.leftMargin;
int cTop = top + lp.topMargin;
int cRight = cLeft + child.getMeasuredWidth();
int cBottom = cTop + child.getMeasuredHeight();
//进行子View进行布局
child.layout(cLeft, cTop, cRight, cBottom);
left += child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
}
left = 0;
top += lineHeight;
}
}
}
2.相关的布局文件:
引用自定义控件:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/container"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<com.czm.flowlayout.XCFlowLayout
android:id="@+id/flowlayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
</com.czm.flowlayout.XCFlowLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
三、使用该自定义布局控件类
最后,如何使用该自定义的热门标签控件类呢?很简单,请看下面实例代码:
package com.czm.flowlayout;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams;
import android.view.ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams;
import android.widget.TextView;
/**
*
* @author caizhiming
*
*/
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private String mNames[] = {
"welcome","android","TextView",
"apple","jamy","kobe bryant",
"jordan","layout","viewgroup",
"margin","padding","text",
"name","type","search","logcat"
};
private XCFlowLayout mFlowLayout;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initChildViews();
}
private void initChildViews() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
mFlowLayout = (XCFlowLayout) findViewById(R.id.flowlayout);
MarginLayoutParams lp = new MarginLayoutParams(
LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
lp.leftMargin = 5;
lp.rightMargin = 5;
lp.topMargin = 5;
lp.bottomMargin = 5;
for(int i = 0; i < mNames.length; i ++){
TextView view = new TextView(this);
view.setText(mNames[i]);
view.setTextColor(Color.WHITE);
view.setBackgroundDrawable(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.textview_bg));
mFlowLayout.addView(view,lp);
}
}
}
四、项目代码目录结构图