多元函数的二阶导数又称为Laplacian算子:
[ riangledown f(x, y) = frac {partial^2 f}{partial x^2} + frac {partial^2 f}{partial y^2}
]
对于图像上的离散(f(x, y)):
[ riangledown f(x, y) = f(x + 1, y) + f(x - 1,y) - 2 f(x,y) + f(x, y + 1) + f(x, y -1) - 2 f(x, y) \= f(x + 1, y) + f(x - 1,y) + f(x, y + 1) + f(x, y -1) - 4 f(x, y)
]
它对应的3阶mask为:
[left [
egin{matrix}
0 & 1 & 0\
1 & -4 & 1\
0 & 1 & 0
end{matrix}
ight ]
]
若考虑两个对角线方向的偏导数, 则为:
[left [
egin{matrix}
1 & 1 & 1\
1 & -8 & 1\
1 & 1 & 1
end{matrix}
ight ]
]
应用
孤立点检测(Isolated Point Detection)
如之前所说, 二阶mask对细节更敏感, 所以Laplacian算子的一个常见应用是孤立点检测.
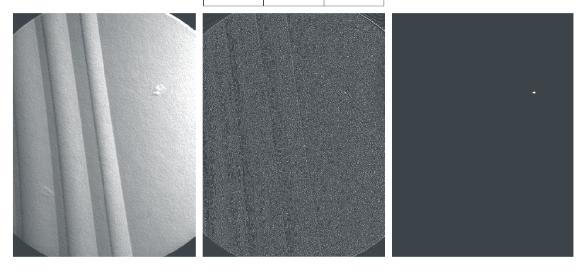
线条检测(Line detection)
一个像素宽的是线条, 两个像素宽的是线条, 三个, 四个, ..., (n)个呢? 所以先得区分线条和region. 不比mask宽的才是线条, 比mask宽的就是region了. (DIP 10.2.3).
用于line detection的mask可以是方向不特异的(检测所有方向的线条, 如上面已列出的.), 也可以方向特异的(只检测某个方向的线条). 这种检测还是有thresholding过程: response大于threshold的才认为是属于检测目标的像素点.

应用(+45^circ)的mask:
