NumPy库
NumPy数组对象
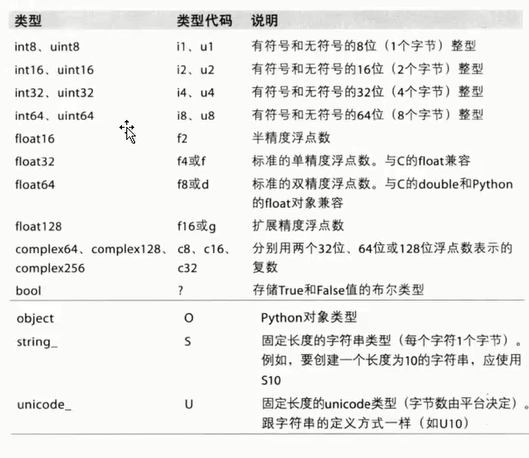
NumPy数据类型
数组的索引
数组的切片
数组的组合
数组的分割
数组的属性
NumPy数组对象
NumPy数据类型

#numpy数据类型 print "In: float64(42)" print np.float64(42) print "In: int8(42.0)" print np.int8(42.0) print "In: bool(42)" print np.bool(42) print np.bool(0) print "In: bool(42.0)" print np.bool(42.0) print "In: float(True)" print np.float(True) print np.float(False) print "In: arange(7, dtype=uint16)" print np.arange(7, dtype=np.uint16) print "In: int(42.0 + 1.j)"

# 数据类型转换 arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) arr.dtype float_arr = arr.astype(np.float64) float_arr.dtype arr = np.array([3.7, -1.2, -2.6, 0.5, 12.9, 10.1]) arr arr.astype(np.int32) numeric_strings = np.array(['1.25', '-9.6', '42'], dtype=np.string_) numeric_strings.astype(float)

import numpy as np a = np.array([[1,2],[3,4]]) print(a.dtype.byteorder) #= print(a.dtype.itemsize) #4

print np.arange(7, dtype='f') print np.arange(7, dtype='D') print np.dtype(float) print np.dtype('f') print np.dtype('d') print np.dtype('f8') print np.dtype('Float64')

#dtype类的属性 t = np.dtype('Float64') print t.char print t.type print t.str #创建自定义数据类型 t = np.dtype([('name', np.str_, 40), ('numitems', np.int32), ('price', np.float32)]) print t print t['name'] itemz = np.array([('Meaning of life DVD', 42, 3.14), ('Butter', 13, 2.72)], dtype=t) print itemz[1]
数组操作
数组与标量之间的运算
#创建多维数组 m=np.array([np.arange(2),np.arange(2)]) print(m) print(m.shape) print(m.dtype)
#数组与标量的运算 arr = np.array([[1., 2., 3.], [4., 5., 6.]]) arr arr * arr
结果: array([[ 1., 4., 9.],
[16., 25., 36.]])
arr - arr 1 / arr arr ** 0.5
数组的索引

#布尔型索引 names = np.array(['Bob', 'Joe', 'Will', 'Bob', 'Will', 'Joe', 'Joe']) data = randn(7, 4) names data names == 'Bob' data[names == 'Bob'] data[names == 'Bob', 2:] data[names == 'Bob', 3] names != 'Bob' data[-(names == 'Bob')] mask = (names == 'Bob') | (names == 'Will') mask data[mask] data[data < 0] = 0 data data[names != 'Joe'] = 7 data

#花式索引 arr = np.empty((8, 4)) for i in range(8): arr[i] = i arr arr[[4, 3, 0, 6]] arr[[-3, -5, -7]] arr = np.arange(32).reshape((8, 4)) arr arr[[1, 5, 7, 2], [0, 3, 1, 2]] arr[[1, 5, 7, 2]][:, [0, 3, 1, 2]] arr[np.ix_([1, 5, 7, 2], [0, 3, 1, 2])]
数组的切片
#多维数组的切片与索引 b = np.arange(24).reshape(2,3,4) #生成二维数组,三行四列 print b.shape print b #array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7], [ 8, 9, 10, 11]], [[12, 13, 14, 15], [16, 17, 18, 19], [20, 21, 22, 23]]]) print b[0,0,0] print b[:,0,0] print b[0] print b[0, :, :] print b[0, ...] print b[0,1] print b[0,1,::2] print b[...,1] print b[:,1] print b[0,:,1] print b[0,:,-1] print b[0,::-1, -1] print b[0,::2,-1] print b[::-1] s = slice(None, None, -1) print b[(s, s, s)]
数组的组合

#数组转置 arr = np.arange(15).reshape((3, 5)) arr arr.T #改变数组的维度 b = np.arange(24).reshape(2,3,4) print b print b.ravel() print b.flatten() b.shape = (6,4) print b print b.transpose() b.resize((2,12)) print b

#组合数组 a = np.arange(9).reshape(3,3) print a b = 2 * a print b print np.hstack((a, b)) 水平组合 print np.concatenate((a, b), axis=1) print np.vstack((a, b)) 垂直组合 print np.concatenate((a, b), axis=0) print np.dstack((a, b)) 深度组合 oned = np.arange(2) print oned twice_oned = 2 * oned print twice_oned print np.column_stack((oned, twice_oned)) 列组合 print np.column_stack((a, b)) print np.column_stack((a, b)) == np.hstack((a, b)) print np.row_stack((oned, twice_oned)) print np.row_stack((a, b)) print np.row_stack((a,b)) == np.vstack((a, b))
数组的分割

#数组的分割 a = np.arange(9).reshape(3, 3) print a print np.hsplit(a, 3) 水平分割 print np.split(a, 3, axis=1) print np.vsplit(a, 3) 垂直分割 print np.split(a, 3, axis=0) c = np.arange(27).reshape(3, 3, 3) print c print np.dsplit(c, 3)
数组的属性

#数组的属性 b=np.arange(24).reshape(2,12) b.ndim 维度 b.size 数组元素总个数 b.itemsize 元素占的字节数 b.nbytes b = np.array([ 1.+1.j, 3.+2.j]) b.real 实部 b.imag 虚部 b=np.arange(4).reshape(2,2) b.flat b.flat[2] #数组的转换 b = np.array([ 1.+1.j, 3.+2.j]) print b print b.tolist() 转化成python中的列表 print b.tostring() print np.fromstring('x00x00x00x00x00x00xf0?x00x00x00x00x00x00xf0?x00x00x00x00x00x00x08@x00x00x00x00x00x00x00@', dtype=complex) print np.fromstring('20:42:52',sep=':', dtype=int) print b print b.astype(int) print b.astype('complex')