一、需求分析:
- 编写小学四则运算程序,自动生成小学四则运算题目。
- 能完成简单的加,减,乘,除运算,可以通过输入参数来控制随机生成的题目数量。
- 由于小学没有接触负数,,所以应去掉随机计算结果为负的。
- 练习题随机生成完成后,将生成的n到随机计算题及其答案输入名为“result。txt”的文件中。
二、设计思路:
- 使用java中的Random类,随机生成0-100的数,并与随机产生的运算符号结合,生成随机的四则运算表达式。
- 由于小学没有接触负数,故将随机运算结果为负的去掉。
- 当产生符合题目要求的随机时,计算正确答案并输入到“result.txt”文件中。
三、设计实现图:

四、核心代码:
- 随机生成四则运算表达式:
-
int[] number_temp = new int[rand.nextInt(2)+3]; String[] str_temp = new String[number_temp.length-1]; for(int i=0;i<number_temp.length;i++) { if(i<number_temp.length-1) { number_temp[i]=rand.nextInt(100); list_temp.add(String.valueOf(number_temp[i])); str_temp[i]=operator[rand.nextInt(4)]; list_temp.add(str_temp[i]); } else { number_temp[i]=rand.nextInt(100); list_temp.add(String.valueOf(number_temp[i])); } }
- 用调度场算法产生逆波兰式:
-
public static ArrayList<String> produce_RPN(ArrayList<String> list_temp) { int t=0,i=0; String tmp; Tack mytack = new Tack(20); ArrayList<String> lt_temp = new ArrayList<String>(); while(true) { tmp = list_temp.get(i++); if(isInteger(tmp)) { lt_temp.add(tmp); } else{ if(mytack.myisempty()) { mytack.mypush(tmp); } else{ if(isCPriority(tmp, mytack.mypeek())) mytack.mypush(tmp); else{ lt_temp.add(mytack.mypop()); mytack.mypush(tmp); } } } if(i>=list_temp.size()) { while(!mytack.myisempty()) lt_temp.add(mytack.mypop()); System.out.println(transform_string(list_temp)); list_temp = lt_temp; System.out.println(list_temp); return list_temp; } } }
- 用逆波兰式计算表达式的结果:
-
public static int calculate_RPN(ArrayList<String> list_temp) { int i=0,t; double a=0,b=0; String l_temp; Stack sk=new Stack(20); for(t=0;t<list_temp.size();t++) { l_temp = list_temp.get(i++); if(!isInteger(l_temp)) { b = sk.mypop(); a = sk.mypop(); switch(l_temp) { case "+":sk.mypush(a+b);break; case "-":sk.mypush(a-b);break; case "*":sk.mypush(a*b);break; case "/": if(b==0) return -1; sk.mypush(a/b);break; } System.out.println("st.mytop: "+sk.mypeek()); } else{ sk.mypush((double)Integer.parseInt(l_temp)); } } if(!sk.myisempty()) { a = sk.mypop(); b = a-(int)a; System.out.println("a: "+a); if(a>0 && b==0 ) { return (int)a; } else return -1; } else return -1; }
- 当计算结果为正数时,添加到数组list,反之,重复上述步骤:
-
count=calculate_RPN(produce_RPN(list_temp)); if(count !=-1) { list_temp.add(" = "+count); list.add(transform_string(list_temp)); number_n--; list_temp.clear(); } else list_temp.clear();
- 当产生符合要求的表达式时,将产生的表达式写入“result.txt”中:
-
try { outSTr = new FileOutputStream(file1); Buff = new BufferedOutputStream(outSTr); try { Buff.write(" ".getBytes()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { try { Buff.write(" ".getBytes()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); i--; } } Buff.flush(); Buff.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } //Buff.close(); try { outSTr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { System.out.print(list.get(i)); System.out.println(); } System.out.print("计算完毕!");
- 其他必要的小函数:
- 1、判断字符串是否为正数:
-
public static boolean isInteger(String str) { for (int i = str.length();--i>=0;){ if (!Character.isDigit(str.charAt(i))){ return false; } } return true; }
2、判断运算符号的优先顺序:
-
public static boolean isCPriority(String str,String s) { if((str+s).equals("*+") || (str+s).equals("*-") || (str+s).equals("/+") || (str+s).equals("/-")) return true; else return false; }
3、将动态数组转换为字符串类型:
-
public static String transform_string(ArrayList<String> list_temp) { String s=""; for(int i=0;i<list_temp.size();i++) { s+=list_temp.get(i); } return s; }
4、栈的应用:
-
static class Stack { int mytop; double stk[]; public Stack(int num) { mytop=-1; stk=new double[num]; } /*出栈*/ double mypop() { double peek=stk[mytop]; mytop--; return peek; } /*入栈*/ void mypush(double x) { mytop++; stk[mytop]=x; } /*判空*/ Boolean myisempty() { if(mytop==-1) return true; else return false; } /*取栈顶元素*/ double mypeek() { double peek=stk[mytop]; return peek; } /*栈大小*/ int mysize() { return mytop+1; } } static class Tack { int mytop; String tk[]; public Tack(int num) { mytop=-1; tk=new String[num]; } /*出栈*/ String mypop() { String peek=tk[mytop]; mytop--; return peek; } /*入栈*/ void mypush(String x) { mytop++; tk[mytop]=x; } /*判空*/ Boolean myisempty() { if(mytop==-1) return true; else return false; } /*取栈顶元素*/ String mypeek() { String peek=tk[mytop]; return peek; } /*栈大小*/ int mysize() { return mytop+1; } }
运行成功截图:
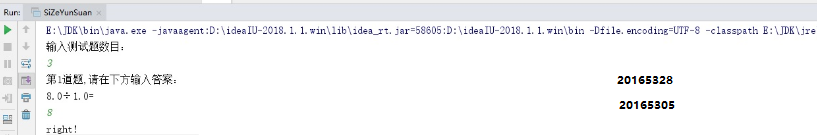
五、实验中遇到的难题及扩展需求:
- 在扩展需求中有要求支持多语言,但我和苏振龙同学没有找出太好的解决方法,于是我们就放弃了,但在星期天也就是今天,我们突然想到了一个简单的解决方法,就是将文字直接设置成变量,再再选用不同的语言时直接赋不同的值就可以了,初步代码如下:
-
System.out.print("请选择语言:简体中文(1)繁體中文(2)English(3):"); int choice = scan2.nextInt(); if (choice == 1) { n = "请输入算式个数:"; } else if (choice == 2) { n = "請輸入算式個數:"; } else if (choice == 3) { n = "Please enter the number of the expression: "; } else { System.out.println("没有那种语言!默认语言为简体中文,祝您愉快"); }
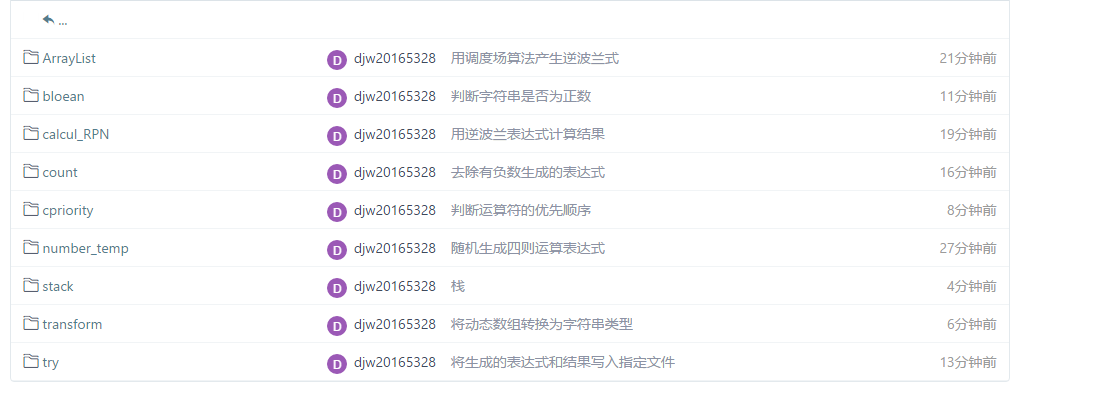
六、码云链接与代码提交截图:
- 码云
- 截图:

七、对结对小伙伴的评价:
- 苏振龙同学和我在这次的结对编程练习相互帮助,相互启迪,很好的达到了互补共进的作用,他在编程过程中提出了许多有建设性的意见,也将这些意见通过代码实现了出来,极大的推进了我们编译的速度,如果硬要评分的话,我大概给出75分左右。