题意是有n个箱子, 每个箱子上最多承放Xi个箱子。 问最少搭成多少堆。
这道题显然是贪心。。但是比赛的时候脑残了。。做了一个多小时的二分, 都不知道为什么100 的数据量自己要去做二分。。。
早上起来发现二分错在判断条件少加了个1.。orz。。。
贪心策略就是从小到大排序,然后把每个箱子放在他能放的最大堆下。。。
题目:
Fox Ciel has n boxes in her room. They have the same size and weight, but they might have different strength. The i-th box can hold at most xi boxes on its top (we'll call xi the strength of the box).
Since all the boxes have the same size, Ciel cannot put more than one box directly on the top of some box. For example, imagine Ciel has three boxes: the first has strength 2, the second has strength 1 and the third has strength 1. She cannot put the second and the third box simultaneously directly on the top of the first one. But she can put the second box directly on the top of the first one, and then the third box directly on the top of the second one. We will call such a construction of boxes a pile.
Fox Ciel wants to construct piles from all the boxes. Each pile will contain some boxes from top to bottom, and there cannot be more than xi boxes on the top of i-th box. What is the minimal number of piles she needs to construct?
The first line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100). The next line contains n integers x1, x2, ..., xn (0 ≤ xi ≤ 100).
Output a single integer — the minimal possible number of piles.
3
0 0 10
2
5
0 1 2 3 4
1
4
0 0 0 0
4
9
0 1 0 2 0 1 1 2 10
3
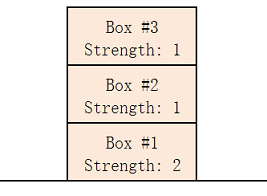
In example 1, one optimal way is to build 2 piles: the first pile contains boxes 1 and 3 (from top to bottom), the second pile contains only box 2.
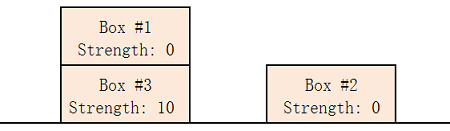
In example 2, we can build only 1 pile that contains boxes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 (from top to bottom).
代码:1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int n; 7 int num[105]; 8 int pile[105]; 9 int pp=0; 10 int main() 11 { 12 13 cin>>n; 14 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 15 { 16 cin>>num[i]; 17 } 18 sort(num,num+n); 19 20 int rec =-1, m = 0; 21 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 22 { 23 rec = -1 ; m=0; 24 for(int j=0;j<pp;j++) 25 { 26 if( num[i] >= pile[j] && pile[j]>m) 27 { 28 rec = j; 29 m = pile[j]; 30 } 31 } 32 if( rec ==-1) 33 { 34 pile[pp++] = 1; 35 } 36 else 37 pile[rec] ++ ; 38 } 39 cout<<pp<<endl; 40 41 return 0; 42 }
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <cstdio> 4 #include <vector> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <stack> 7 #include <cmath> 8 #include <cstring> 9 #include <string> 10 #include <cstdlib> 11 using namespace std; 12 #define LL lolng long 13 int n; 14 int num[105]; 15 int ans[105]; 16 17 bool cmp(int x,int y) 18 { 19 return x>y; 20 } 21 bool C(int x) 22 { 23 int vis[105]; 24 memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); 25 if( x>=n )return true; 26 int cnt; 27 int p; 28 for(int i=0;i<x;i++) 29 { 30 cnt =0; 31 p=n-1; 32 while(p>=x) 33 { 34 if( num[i]>=cnt+1 && (num[p] >=cnt) && !vis[p]) 35 { 36 cnt++; 37 vis[p] =1; 38 } 39 p--; 40 } 41 // cout<<x<<endl; 42 // for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 43 // { 44 // cout<<vis[i]<<" "; 45 // } 46 // cout<<endl; 47 } 48 p = 0; 49 for(int i=n-1;i>=x;i--) 50 { 51 if(!vis[i]) 52 { 53 p++; 54 } 55 } 56 if( p==0)return true; 57 else 58 return false; 59 } 60 int main() 61 { 62 scanf("%d",&n); 63 64 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 65 { 66 cin>>num[i]; 67 } 68 sort(num,num+n,cmp); 69 70 int l = 0, r = 200; 71 int mid; 72 int ans =0; 73 while(l<=r) 74 { 75 //cout<<l<<" "<<r<<endl; 76 mid = (l+r)/2; 77 //cout<<l<<" "<<r<<endl; 78 if( C(mid) ) 79 { 80 ans = mid; 81 r= mid-1; 82 } 83 else 84 l = mid+1; 85 } 86 cout<<ans<<endl; 87 return 0; 88 }