1. 集合部分
1.1 HashMap排序
package cn.Douzi.hashMap01; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.LinkedHashMap; import java.util.Map.Entry; import java.util.Set; import javax.jws.soap.SOAPBinding.Use; public class hashMap_demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { HashMap<Integer, User> hashMap = new HashMap<Integer, User>(); User user = new User(); user.setName("张三"); user.setAge(23); hashMap.put(1, user); User user2 = new User(); user2.setName("李四"); user2.setAge(24); hashMap.put(2, user2); User user3 = new User(); user3.setAge(21); user3.setName("王五"); hashMap.put(3, user3); System.out.println("排序前HashMap:" + hashMap); HashMap<Integer, User> sortedHashMap = sortHashMap(hashMap); System.out.println("排序后:" + sortedHashMap); } private static HashMap<Integer, User> sortHashMap( HashMap<Integer, User> hashMap) { /** * 创建一个有序的HashMap数据结构,LinkedHashMap */ LinkedHashMap<Integer, User> newHashMap = new LinkedHashMap<Integer, User>(); //凡是要对集合排序,首先想到的就是集合的工具类 //把Map结构转换为list结构 //把Map转换为Set集合 Set<Entry<Integer, User>> entrySet = hashMap.entrySet(); //把Set集合转换为List ArrayList<Entry<Integer, User>> list = new ArrayList<>(entrySet); Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Entry<Integer, User>>() { @Override public int compare(Entry<Integer, User> o1, Entry<Integer, User> o2) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub // -1:正序排序; 前面-后面:正序;后面-前面:倒序 return o2.getValue().getAge() - o1.getValue().getAge(); } }); //将排好顺序的list转换为LinkedHashMap for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { Entry<Integer, User> entry = list.get(i); newHashMap.put(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); } return newHashMap; } }
2.java中的引用类型
- 强引用
- 软引用:SoftReference
- 弱引用:WeakReference
- 虚引用:PhantomReference
对象的可及性:
- 强可及对象,永远不会被GC回收
- 软可及对象:当系统内存不足的时候,被GC回收。
- 弱可及对象:当系统GC发现这个对象,就被回收
package cn.Douzi.Reference; import java.lang.ref.PhantomReference; import java.lang.ref.SoftReference; import java.lang.ref.WeakReference; public class ReferenceTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //强引用 // String str = "abc"; //常量池 //1. 在堆内存中创建了String对象 2.在常量池中创建了abc对象 String str = new String("abc"); //创建一个软引用,引用到str SoftReference<String> sfr = new SoftReference<String>(str); //创建一个弱引用,引用到str WeakReference<String> wrf = new WeakReference<String>(str); //虚引用:检测对象是否被虚拟机回收掉 // PhantomReference //相当于去掉了强引用链 str = null; //清楚软引用的引用链 sfr.clear(); System.gc(); //回收了堆内存, 无法回收常量池的内存 String srfString = sfr.get(); String wrfString = wrf.get(); System.out.println("软引用获取到的对象:" + srfString); System.out.println("弱引用获取到的对象:" + wrfString); } }

3. 多线程线程池部分
- 需求:控制一个方法的并发量,比如 同时只能有5个线程进来
- 注意:不要用 synchronized,用synchronized关键字的两个线程1和线程2,如果当前线程1获得锁,线程2线程等待。如果线程1阻塞,线程2则会一直等待下去。
3.1 使用 Semaphore
package cn.Douzi.Thread_Pool; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore; public class ThreadPoolTest { //信号量 private static Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(5); //允许个数, 相当于放了5把锁 public static void main(String[] args) { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub try { method(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }).start(); } } //同时最多只运行5个进程过来 public static void method() throws InterruptedException { semaphore.acquire(); //获取一把锁 System.out.println("ThreadName" + Thread.currentThread().getName()+"进来了"); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("ThreadName="+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"出去了"); semaphore.release(); //释放一把锁 } }
3.2 线程池
线程池的启动策略
系统自带的线程池
//网络访问框架,都要用线程池 private static Executor executors = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //缓存线程池 private static Executor executor2 = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); //固定线程个数的线程 private static Executor executor3 = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5); //计划任务线程池 private static Executor executor4 = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); //单个线程的线程池
手写线程池
/*
* 参数1:corePoolSize:核心池大小
* 参数2:maximumPoolSize:最大线程池上限个数
* 参数3:keepAliveTime:保存最长时间,任务执行完之后,要裁员的延时
* 参数4:unit:时间单位
* 参数5:workQueue:用于存储任务的工作队列(即将被执行的任务)(BlockingQueue)
* 参数6:ThreadFactory: 线程工厂, 用来创建线程的
*
*/
ThreadPoolExecutor poolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS, blockingQueue, threadFactlory);
创建一个线程工厂
ThreadFactory threadFactlory = new ThreadFactory() {
//线程安全的int的包装类
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
//创建一个线程,然后把r赋值给该线程
Thread thread = new Thread(r);
thread.setName("MyThread=" + atomicInteger.getAndIncrement());
return thread;
}
};
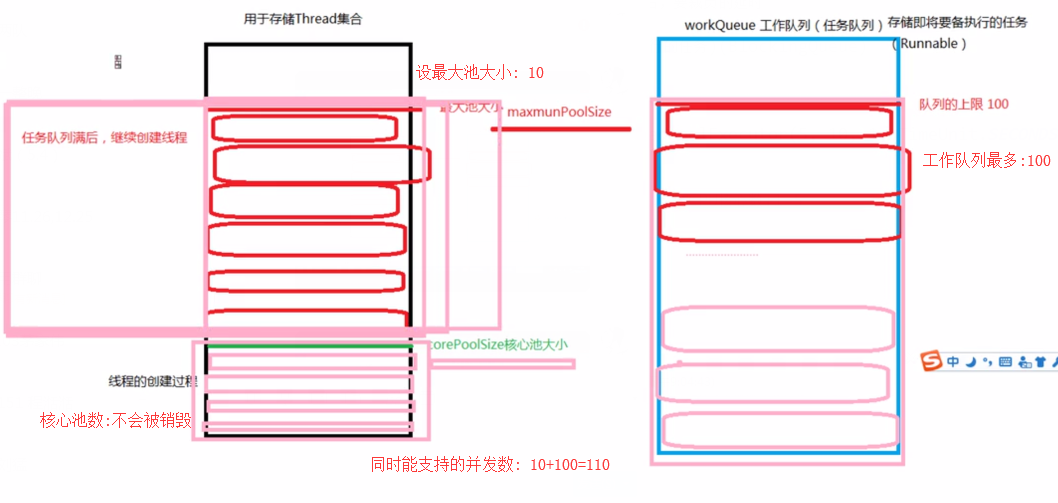
完整创建核心池
package cn.Douzi.Thread_Pool;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class ThreadPoolTest02 {
//网络访问框架,都要用线程池
private static Executor executors = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //缓存线程池
private static Executor executor2 = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); //固定线程个数的线程
private static Executor executor3 = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5); //计划任务线程池
private static Executor executor4 = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); //单个线程的线程池
public static void main(String[] args) {
// BlockingQueue<E> //单端队列
// BlockingDQueue //双端队列
LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable> blockingQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(100); //该容器的最大上限
//创建一个线程工厂
ThreadFactory threadFactlory = new ThreadFactory() {
//线程安全的int的包装类
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
//创建一个线程,然后把r赋值给该线程
Thread thread = new Thread(r);
thread.setName("MyThread=" + atomicInteger.getAndIncrement());
return thread;
}
};
/*
* 参数1:corePoolSize:核心池大小
* 参数2:maximumPoolSize:最大线程池上限个数
* 参数3:keepAliveTime:保存最长时间,任务执行完之后,要裁员的延时
* 参数4:unit:时间单位
* 参数5:workQueue:用于存储任务的工作队列(即将被执行的任务)(BlockingQueue)
* 参数6:ThreadFactory: 线程工厂, 用来创建线程的
*
*/
ThreadPoolExecutor poolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS, blockingQueue, threadFactlory);
/**
* 线程不是越多越好,Google工程给了一个推荐值:线程的个数=CPU核心数+1=5
*/
//用自己打造的线程池
for (int i = 0; i < 110; i++) {
poolExecutor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
method();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
//用系统自带的线程池
// for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
// executor2.execute(new Runnable() {
//
// @Override
// public void run() {
// // TODO Auto-generated method stub
// try {
// method();
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// // TODO Auto-generated catch block
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// }
// });
// }
}
//同时最多只运行5个进程过来
public static void method() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("ThreadName= " + Thread.currentThread().getName()+"进来了");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("ThreadName= "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"出去了");
}
}
注意:核心池为0,执行完会自动退出;核心池 > 0不会被退出。