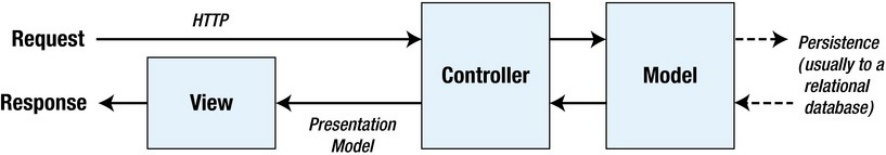
正如ASP.NET MVC名字所揭示的一样,是以模型-视图-控制设计模式构建在ASP.NET基础之上的WEB应用程序,我们需要创建相应的程序类来协调处理,完成从客户端请求到结果相应的整个过程:
VS2012中一个典型的MVC工程结构是这样的:

Controllers文件夹下存放控制类,Models文件下是业务数据模型类,Views文件下则是类似于aspx的视图文件。在传统ASP.NET form的应用程序中,客户端的请求最后都映射到磁盘上对应路径的一个aspx的页面文件,而MVC程序中所有的网络请求映射到控制类的某一个方法,我们就从控制类说起,而在讲控制类前,必须要讲的是URL路由。
注册URL路由
我们在浏览器中请求链接 http://mysite.com/Home/Index,MVC认为是这样的URL模式(默认路径映射):
{controller}/{action}
也就是说上面的请求会被映射到Home控制类的Index方法,MVC命名规则中控制类必须以Controller结尾,所以Home控制类应该是HomeController:
public class HomeController : Controller { public ActionResult Index() { return View(); } }
MVC是根据什么将上面的请求映射到控制类的相应方法的呢?答案就是路由表,Global.asax在应用程序启动时会调用路由配置类来注册路径映射:
public class MvcApplication : System.Web.HttpApplication { protected void Application_Start() { AreaRegistration.RegisterAllAreas(); WebApiConfig.Register(GlobalConfiguration.Configuration); FilterConfig.RegisterGlobalFilters(GlobalFilters.Filters); RouteConfig.RegisterRoutes(RouteTable.Routes); BundleConfig.RegisterBundles(BundleTable.Bundles); } }
路径映射的配置类则在App_Start目录下:
public class RouteConfig { public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes) { routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.axd/{*pathInfo}"); routes.MapRoute( name: "Default", url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}", defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional } ); } }
routes.MapRoute()添加了一个URL路由到路由表中,URL的映射模式是"{controller}/{action}/{id}",controller和action我们已经清楚,id则是请求中额外的参数,比如我们的请求可以是 http://mysite.com/Home/Index/3,对应的action方法可以是:
public ActionResult Index(int id=1) { return View(); }
在传递到Index方法时参数id会被赋值3(保存在RouteData.Values["id"]),MVC足够智能来解析参数并转化为需要的类型,MVC称之为模型绑定(后续具体来看)。上面注册路由时使用了默认参数:defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional },如果我们在请求URL没有指定某些参数,defaults参数会被用作默认值,比如:
mydomain.com = mydomain.com/home/index mydomain.com/home = mydomain/home/index mydomain.com/customer = mydomain/customer/index
id为可选参数,可以不包括在URL请求中,所以上面注册的路径可以映射的URL有:
mydomain.com mydomain.com/home mydomain.com/home/list mydomain.com/customer/list/4
除此之外不能映射的请求都会得到404错误,比如mydomain.com/customer/list/4/5,这里参数过多不能被映射。
RouteCollection.MapRoute()等同于:
Route myRoute = new Route("{controller}/{action}", new MvcRouteHandler()); routes.Add("MyRoute", myRoute);
这里直接向Routes表添加一个Route对象。
其他一些URL映射的例子:
routes.MapRoute("", "Public/{controller}/{action}",new { controller = "Home", action = "Index" }); //URL可以包含静态的部分,这里的public routes.MapRoute("", "X{controller}/{action}"); //所有以X开头的控制器路径,比如mydomain.com/xhome/index映射到home控制器 routes.MapRoute("ShopSchema", "Shop/{action}",new { controller = "Home" }); //URL可以不包含控制器部分,使用这里的默认Home控制器 routes.MapRoute("ShopSchema2", "Shop/OldAction",new { controller = "Home", action = "Index" }); //URL可以是全静态的,这里mydomain.com/shop/oldaction传递到home控制器的index方法
一个比较特殊的例子:
routes.MapRoute("MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}", new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional });
这可以映射任意多的URL分段,id后的所有内容都被赋值到cathall参数,比如/Customer/List/All/Delete/Perm,catchall = Delete/Perm。
需要注意的是路径表的注册是有先后顺序的,按照注册路径的先后顺序在搜索到匹配的映射后搜索将停止。
命名空间优先级
MVC根据{controller}在应用程序集中搜索同名控制类,如果在不同命名空间下有同名的控制类,MVC会给出多个同名控制类的异常,我们可以在注册路由的时候指定搜索的命令空间:
routes.MapRoute("MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}", new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional , new[] { "URLsAndRoutes.AdditionalControllers" });
这里表示我们将在"URLsAndRoutes.AdditionalControllers"命名空间搜索控制类,可以添加多个命名空间,比如:
routes.MapRoute("MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}", new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }, new[] { "URLsAndRoutes.AdditionalControllers", "UrlsAndRoutes.Controllers"});
"URLsAndRoutes.AdditionalControllers", "UrlsAndRoutes.Controllers"两个命名空间是等同处理没有优先级的区分,如果这两个空间里有重名的控制类一样导致错误,这种情况可以分开注册多条映射:
routes.MapRoute("AddContollerRoute", "Home/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}", new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }, new[] { "URLsAndRoutes.AdditionalControllers" }); routes.MapRoute("MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}", new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }, new[] { "URLsAndRoutes.Controllers" });
路由限制
除了在注册路由映射时可以指定控制器搜索命名空间,还可以使用正则表达式限制路由的应用范围,比如:
routes.MapRoute("MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}", new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }, new { controller = "^H.*", action = "^Index$|^About$", httpMethod = new HttpMethodConstraint("GET")}, new[] { "URLsAndRoutes.Controllers" });
这里限制MyRoute路由仅用于映射所有H开头的控制类、且action为Index或者About、且HTTP请求方法为GET的客户端请求。
如果标准的路由限制不能满足要求,可以从IRouteConstraint接口扩展自己的路由限制类:
public class UserAgentConstraint : IRouteConstraint { private string requiredUserAgent; public UserAgentConstraint(string agentParam) { requiredUserAgent = agentParam; } public bool Match(HttpContextBase httpContext, Route route, string parameterName, RouteValueDictionary values, RouteDirection routeDirection) { return httpContext.Request.UserAgent != null &&httpContext.Request.UserAgent.Contains(requiredUserAgent); } }
在注册路由时这样使用:
routes.MapRoute("ChromeRoute", "{*catchall}", new { controller = "Home", action = "Index" }, new { customConstraint = new UserAgentConstraint("Chrome")}, new[] { "UrlsAndRoutes.AdditionalControllers" });
这表示我们限制路由仅为浏览器Agent为Chrome的请求时使用。
路由到磁盘文件
除了控制器方法,我们也需要返回一些静态内容比如HTML、图片、脚本到客户端,默认情况下路由系统优先检查是否有和请求路径一致的磁盘文件存在,如果有则不再从路由表中匹配路径。我们可以通过配置颠倒这个顺序:
public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes) { routes.RouteExistingFiles = true; ... ....
还需要修改web配置文件:
<add name="UrlRoutingModule-4.0" type="System.Web.Routing.UrlRoutingModule" preCondition=""/>
这里设置preCondition为空。如果我们再请求一些静态内容比如~/Content/StaticContent.html时会优先从路径表中匹配。
而如果我们又需要忽略某些路径的路由匹配,可以:
... public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes) { routes.RouteExistingFiles = true; routes.IgnoreRoute("Content/{filename}.html");
...
它会在RouteCollection中添加一个route handler为StopRoutingHandler的路由对象,在匹配到content路径下的后缀为html的文件时停止继续搜索路径表,转而匹配磁盘文件。
生成对外路径
路径表注册不仅影响到来自于客户端的URL映射,也影响到我们在视图中使用HTML帮助函数生成对外路径,比如我们注册了这样的映射
public class RouteConfig { public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes) { routes.MapRoute("MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}/{id}", new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }); } ...
在视图中调用Html.ActionLink生成一个对外路径:
<div> @Html.ActionLink("This is an outgoing URL", "CustomVariable") </div>
根据我们当前的请求链接,http://localhost:5081/home,生成的outgoing链接为:
<a href="/Home/CustomVariable">This is an outgoing URL</a>
而如果我们调整路径表为:
... public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes) { routes.MapRoute("NewRoute", "App/Do{action}", new { controller = "Home" }); routes.MapRoute("MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}/{id}", new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }); } ...
“@Html.ActionLink("This is an outgoing URL", "CustomVariable") ”得到的结果是:
<a href="/App/DoCustomVariable">This is an outgoing URL</a>
它将使用在路径表中找到的第一条匹配的记录来生成相应的链接路径。
Html.ActionLink()有多个重载,可以多中方式生成URL链接:
@Html.ActionLink("This targets another controller", "Index", "Admin") //生成到Admin控制器Index方法的链接 @Html.ActionLink("This is an outgoing URL", "CustomVariable", new { id = "Hello" }) //生成额外参数的链接,比如上面的路径配置下结果为“href="/App/DoCustomVariable?id=Hello"”;如果路径映射为 "{controller}/{action}/{id}",结果为href="/Home/CustomVariable/Hello" @Html.ActionLink("This is an outgoing URL", "Index", "Home", null, new {id = "myAnchorID", @class = "myCSSClass"}) //设定生成A标签的属性,结果类似“<a class="myCSSClass"href="/" id="myAnchorID">This is an outgoing URL</a> ”
参数最多的调用方式是:
@Html.ActionLink("This is an outgoing URL", "Index", "Home", "https", "myserver.mydomain.com", " myFragmentName", new { id = "MyId"}, new { id = "myAnchorID", @class = "myCSSClass"})
得到的结果是:
<a class="myCSSClass" href="https://myserver.mydomain.com/Home/Index/MyId#myFragmentName" id="myAnchorID">This is an outgoing URL</a>
Html.ActionLink方法生成的结果中带有HTML的<a>标签,而如果只是需要URL,可以使用Html.Action(),比如:
@Url.Action("Index", "Home", new { id = "MyId" }) //结果为单纯的/home/index/myid
如果需要在生成URL指定所用的路径记录,可以:
@Html.RouteLink("Click me", "MyOtherRoute","Index", "Customer") //指定使用路径注册表中的MyOtherRoute记录
上面讲的都是在Razor引擎视图中生成对外URL,如果是在控制器类中我们可以:
string myActionUrl = Url.Action("Index", new { id = "MyID" }); string myRouteUrl = Url.RouteUrl(new { controller = "Home", action = "Index" });
更多的情况是在控制类方法中需要转到其他的Action,我们可以:
... public RedirectToRouteResultMyActionMethod() { return RedirectToAction("Index"); } ... public RedirectToRouteResult MyActionMethod() { return RedirectToRoute(new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = "MyID" }); } ...
创建自定义ROUTE类
除了使用MVC自带的Route类,我们可以从RouteBase扩展自己的Route类来实现自定义的路径映射:
public class LegacyRoute : RouteBase { private string[] urls; public LegacyRoute(params string[] targetUrls) { urls = targetUrls; } public override RouteData GetRouteData(HttpContextBase httpContext) { RouteData result = null; string requestedURL = httpContext.Request.AppRelativeCurrentExecutionFilePath; if (urls.Contains(requestedURL, StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase)) { result = new RouteData(this, new MvcRouteHandler()); result.Values.Add("controller", "Legacy"); result.Values.Add("action", "GetLegacyURL"); result.Values.Add("legacyURL", requestedURL); } return result; } public override VirtualPathData GetVirtualPath(RequestContext requestContext, RouteValueDictionary values) { VirtualPathData result = null; if (values.ContainsKey("legacyURL") && urls.Contains((string)values["legacyURL"], StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase)) { result = new VirtualPathData(this, new UrlHelper(requestContext) .Content((string)values["legacyURL"]).Substring(1)); } return result; } }
GetRouteData()函数用于处理URL请求映射,我们可以这样注册路径映射:
routes.Add(new LegacyRoute( "~/articles/Windows_3.1_Overview.html", "~/old/.NET_1.0_Class_Library"));
上面的例子中如果我们请求"~/articles/Windows_3.1_Overview.html"将被映射到Legacy控制器的GetLegacyURL方法。
GetVirtualPath()方法则是用于生成对外链接,在视图中使用:
@Html.ActionLink("Click me", "GetLegacyURL", new { legacyURL = "~/articles/Windows_3.1_Overview.html" })
生成对外链接时得到的结果是:
<a href="/articles/Windows_3.1_Overview.html">Click me</a>
创建自定义ROUTE Handler
除了可以创建自定义的Route类,还可以创建自定义的Route handler类:
public class CustomRouteHandler : IRouteHandler { public IHttpHandler GetHttpHandler(RequestContext requestContext) { return new CustomHttpHandler(); } } public class CustomHttpHandler : IHttpHandler { public bool IsReusable { get { return false; } } public void ProcessRequest(HttpContext context) { context.Response.Write("Hello"); } }
注册路径时使用自定义的Route handler:
routes.Add(new Route("SayHello", new CustomRouteHandler()));
其效果就是针对链接 /SayHello的访问得到的结果就是“Hello”。
使用Area
大型的Web应用可能分为不同的子系统(比如销售、采购、管理等)以方便管理,可以在MVC中创建不同的Area来划分这些子系统,在VS中右键点击Solution exploer->Add->Area可以添加我们想要的区域,在Solution exploer会生成Areas/<区域名称>的文件夹,其下包含Models、Views、Controllers三个目录,同时生成一个AreaRegistration的子类,比如我们创建一个名为Admin的区域,会自动生成名为AdminAreaRegistration的类:
namespace UrlsAndRoutes.Areas.Admin { public class AdminAreaRegistration : AreaRegistration { public override string AreaName { get { return "Admin"; } } public override void RegisterArea(AreaRegistrationContext context) { context.MapRoute( "Admin_default", "Admin/{controller}/{action}/{id}", new { action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional } ); } } }
它的主要作用是注册一个到Admin/{controller}/{action}/{id}路径映射,在global.asax中会通过AreaRegistration.RegisterAllAreas()来调用到这里的RegisterArea()来注册区域自己的路径映射。
在Area下创建Controller、视图同整个工程下创建是相同的,需要注意的是可能遇到控制器重名的问题,具体解决参见命名空间优先级一节。
如果在视图中我们需要生成到特定Area的链接,可以在参数中指定Area:
@Html.ActionLink("Click me to go to another area", "Index", new { area = "Support" })
如果需要得到顶级控制器的链接area=""留空即可。
以上为对《Apress Pro ASP.NET MVC 4》第四版相关内容的总结,不详之处参见原版 http://www.apress.com/9781430242369。