1、Map集合
Collection集合的特点是每次进行单个对象的保存,若要对一对对象来进行保存就只能用Map集合来保存。即Map集合中一次可以保存两个对象,且这两个对象的关系是key = value结构。这种结构最大的好处就是可以利用已知的key值找到对应的value值。
Map接口的定义:public interface Map<K,V>
常用方法:
向Map中追加元素: V put(K key, V value) 根据指定的key值取得对应的value若没有返回null:V get(Object key) 取得所有key信息,key不能重复:Set<K> keySet() 取得所有value信息,value可重复:Collection<V> values() 将Map集合变为Set集合:Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet() |
Map和Collection一样本身就是一个接口,需要使用子类来进行实例化,Map常用的子类有:HashMap、HashTable、TreeMap、ConcurrentHashMap。
(1)HashMap
HashMap是Map中的常用子类。
HashMap中Key值不允许重复,若重复则会把对应的value值进行更新;Key和value都允许为空,key为空有且只能有一个。
基本操作:
- /*
- * HashMap
- * */
- public class Test{
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Map<Integer,String> map = new HashMap<>();
- map.put(1, "num1");
- map.put(2, "num2");
- map.put(3, "num3");
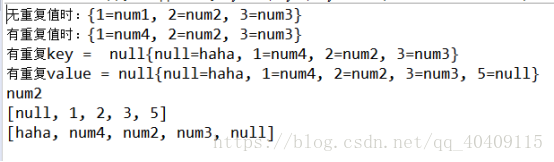
- System.out.println("无重复值时:"+map);
- //重复的key值
- map.put(1, "num4");
- System.out.println("有重复值时:"+map);
- //重复的为null的key值
- map.put(null, null);
- map.put(null, "haha");
- System.out.println("有重复key = null"+map);
- //重复的为null的value值
- map.put(5, null);
- System.out.println("有重复value = null" +map);
- //获得key为2对应的value值
- System.out.println(map.get(2));
- //取得所有的key值
- System.out.println(map.keySet());
- //取得所有的value值
- System.out.println(map.values());
- }
- }
HashMap的原理:在数据量小的时候(jdk1.8后阈值为8)按照HashMap是按照链式存储,当数据量变大时为了快速查找,会将链表变为红黑树(均衡二叉树)来进行数据保存,用hash码作为数据定位。
(2)HashTable(最早实现二次偶对象存储)
在HashTale中key和value均不允许为null。当两者任意一个为null时,会报出如下异常:java.lang.NullPointerException。
- /*
- * HashTable
- * */
- public class Test{
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Map<Integer, String> map = new Hashtable<>();
- map.put(1, "key");
- map.put(2, "value");
- //重复的key值
- map.put(1, "value");
- //key值为null
- //map.put(null,"haha");
- //value值为null
- //map.put(3, null);
- System.out.println(map);
- }
- }
当key值或者value值为空时:
HashMap和HashTable的区别:
1.版本上:HashTable是jdk1.0推出的;而HashMap是jdk1.2推出的。 |
2.性能上:HashTable属于同步处理,性能较低;而HashMap属于异步处理,性能较高 |
3.安全性方面:HashTable是线程安全的;而HashMap是非线程安全的。 |
4.null操作上:在HashTable中key和value都不允许为null,否则有NullPointException异常抛出;而HashMap允许key和value为null,且可key为null有且只有一个。 |
(3)ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrrentHashMap具有HashTable的线程安全性同时也具有HashMap的高性能。且在ConcurrentHashMap中和HashTable一样都不想允许key和value为null。
- /*
- * ConcurrentHashMap
- * */
- public class Test{
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Map<Integer, String> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
- map.put(1, "key");
- //重复key值
- map.put(1, "value");
- map.put(2, "value");
- System.out.println(map);
- }
- }
其使用也和之前的HashTable和HashMap类似,因为他们都是Map的子类。
其高性能主要表现在:
a. 数据更新时,只能对特定的区域进行上锁,而其他区域不受影响。
b. 在锁的区域使用读写锁,读异步而写同步,即便在同一个桶中,数据的读取仍然不受影响。
(4)TreeMap
TreeMap是Map集合中唯一一个可用于排序的集合,是按照key值进行排序的。
- /*
- * TreeMap
- * */
- public class Test{
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Map<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>();
- map.put(4, "key");
- //重复key值
- map.put(3, "value");
- map.put(2, "value");
- System.out.println(map);
- }
- }
实则排序的类必须实现Comparable接口,即实现CompareTo()方法,所以在上例中Integer类一定实现了Comparable接口。
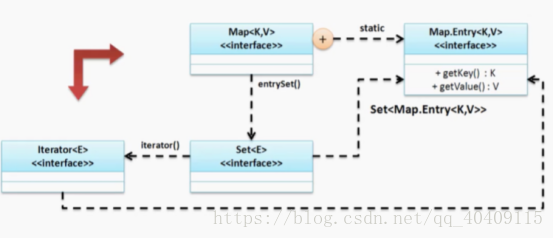
(5)Map使用Iterator进行集合输出
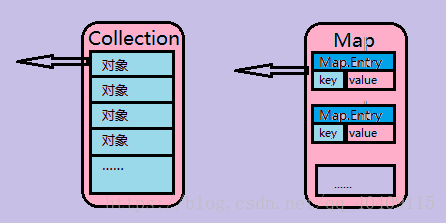
Map和Collection的接口不同,在Collection接口中提供有iterator()方法,使我们可以很方便的取到Iterator对象来进行输出,而在Map集合中并没有提供该方法,首先我们观察Collection和Map接口数据保存的区别:
在Map中提供有一个重要的方法将Map集合转换成Set集合:
Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet()
Map要想调用Iterator进行输出,走的是一个间接使用的模式。
- /*
- * Map的Iterator输出
- * */
- public class Test{
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
- map.put(4, "key");
- //重复key值
- map.put(3, "value");
- map.put(2, "value");
- //将Map集合转换成Set集合
- Set<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> set = map.entrySet();
- //取得Iterator对象
- Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer,String>> iterator = set.iterator();
- while(iterator.hasNext()) {
- //取得每一个Map.Entry的对象
- Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry =iterator.next();
- //取得key和value
- System.out.println("key = "+entry.getKey()+",value = "+entry.getValue());
- }
- }
- }
(6)关于Map中key的说明
在之前我们使用Map集合时都笼统的使用系统类作为key(Intreger、String),实则我们也可以使用自定义类来作为Map的key,此时一定要覆写Object类的hashCode()和equals()两个方法。
2、Properties属性文件操作
在Java中有一种属性文件(资源文件)的定义:.*properties文件,在这种文件中其内容的保存形式是“key = value”通过ResourceBundle类读取的时候只可以读取到内容,而若要对其内容进行编辑则需要Properties类来实现,这个类是专门做属性处理的。
Properties类定义:
public class Properties extends Hashtable<Object,Object>
常用方法:
设置属性:public synchronized Object setProperty(String key, String value) |
返回指定key对应的value值,若没有找到返回null: public String getProperty(String key) |
返回指定key对应的value值,若没有对应的value则给个默认值(指的是返回给当前的默认值,并不会写入文件中): public String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue) |
向对应输出流保存属性: public void store(OutputStream out, String comments) throws IOException |
将属性从文件中读出:public synchronized void load(InputStream inStream) throws IOException |
- /*
- * Properties属性文件操作
- * */
- public class Test{
- public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
- Properties properties = new Properties();
- //设置属性
- properties.setProperty("XN", "xi an");
- properties.setProperty("BJ", "bei jing");
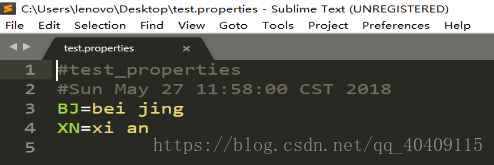
- File file = new File("C:\Users\lenovo\Desktop\test.properties");
- //向对应输出流中保存属性
- properties.store(new FileOutputStream(file), "test_properties");
- //在文件中读出属性
- properties.load(new FileInputStream(file));
- //返回key对应的value,不存在返回null
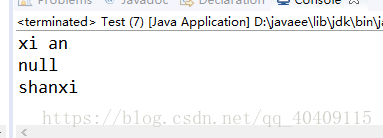
- System.out.println(properties.getProperty("XN"));
- System.out.println(properties.getProperty("SX"));
- //返回key对应的value,若没有找到对应的value则给出默认值,不会写入到资源文件中
- System.out.println(properties.getOrDefault("SX", "shanxi"));
- }
- }
Properties只能操作String,它可以进行远程属性内容的加载。