1. 问题:给定集合S,是否能找到subset使其加和为1000
方法一:用n bits表示集合中的所有元素,每一个bit代表集合中的一个元素,如果bit取值为1则A[i]属于subset,反之不属于
如:A[ ]={1,2,3,5}, 则1100表示subset={1,2}
共有2n种情况,故而时间复杂度为O(2n)
方法二:递归
subset(A,n,k)
若第n个value (A[n-1]) 是solution的一部分,则前n-1个value总和为k – A[n-1]
若不是则总和仍为k
base case: k=0 (return True); n=0(unsolvable if k>0, return False,此时没有可选element)
最坏的情况下依然要遍历所有,故而时间复杂度依然为O(2n) (C1 = 2, Cn = 2 + 2·Cn-1)
2. 0b1101, 0b means which is based on 2 (binary system)
0x3AF1, 0x measn which is based on 16 (hexadecimal system) 0~9, A~F
decimal system is based on 10
3. 74=64+8+2=0b1001010
0x2D=2*16+13=45
0b1011 1110 0010 1001=0xBE29
0x12D=0b100101101
4. memory的存储总是将更高的memory放在上面,一个变量被声明后,操作系统会在memory中存储相应的字节数量
其中character为1 byte,int和float为4 bytes,double为8 bytes
如果我们声明了一个变量k, 则存储k的地方为&k
5. %p为地址的占位符,存放pointer value
6. scanf中一定要明确可以input的变量类型,且需要变量地址,如:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 … 3 int answer; 4 printf("Enter your answer: "); 5 scanf("%d", &answer);
7. pointer是一种特殊形式的变量,用于存储另一个变量的地址。pointer所需要占用的内存又电脑本身的功能结构决定
如64位电脑需要8memory cells,理论上可存储264 bytes,但实际内存由CPU限制
8. *被用来进入pointer所指向的目标,pointer将被限制只能指向一种类型的变量
1 int *p; int *q; // this is how pointers are declared 2 int a[5]; 3 int x = 10, y; 4 5 p = &x; // p now points to x 6 *p = 20; // whatever p points to is now equal to 20 7 y = *p; // y is now equal to whatever p points to 8 p = &a[2]; // p points to an element of array a[] 9 q = p; // q and p now point to the same thing
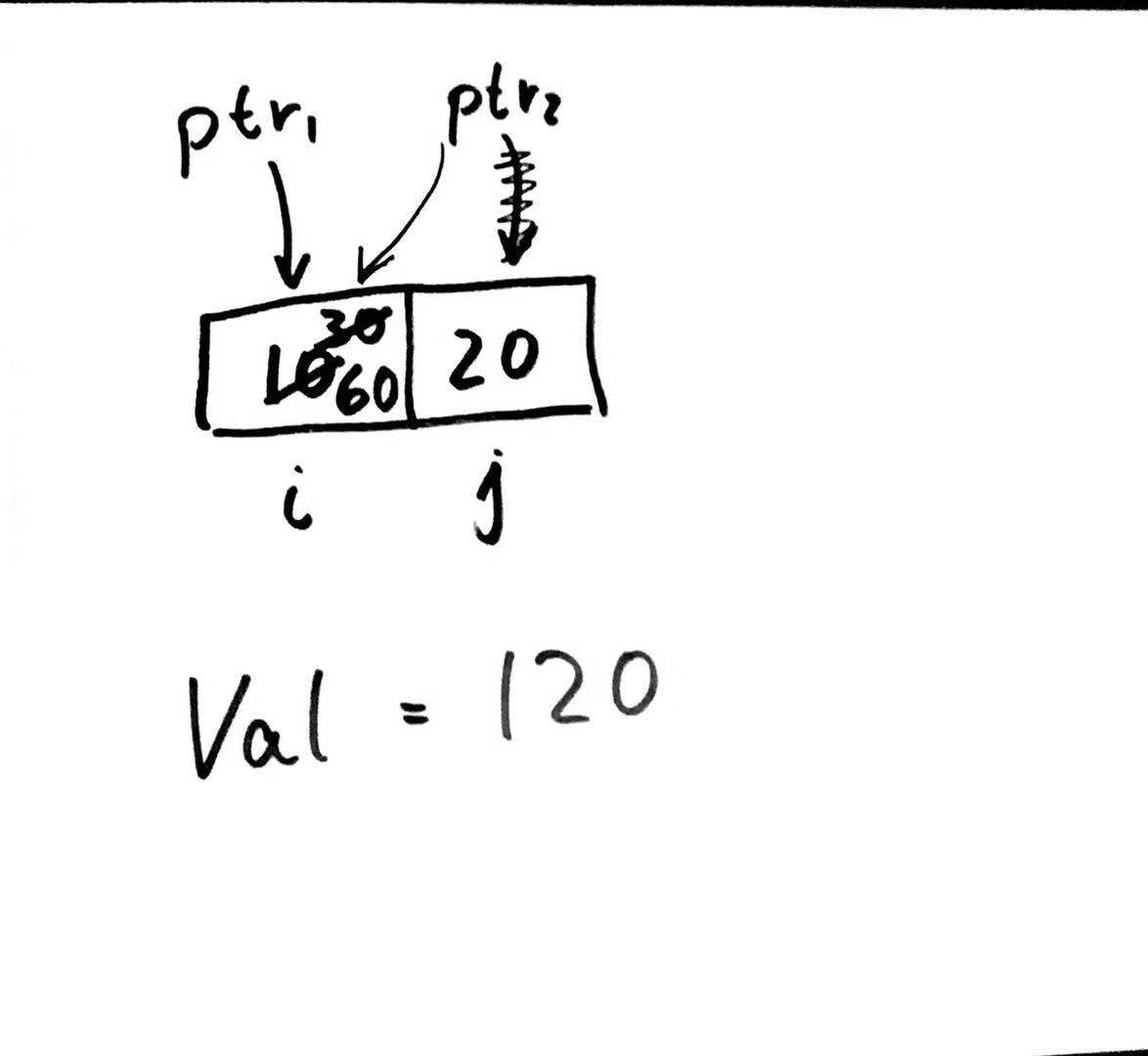
9. exercise: What is the output of the following program?
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 int main(void) { 4 int *ptr1, *ptr2; 5 int i = 10, j = 20; 6 7 ptr1 = &i; 8 ptr2 = &j; 9 10 *ptr1 = *ptr1 + *ptr2; 11 ptr2 = ptr1; 12 *ptr2 = 2 * (*ptr2); 13 printf("Val = %d ", *ptr1 + *ptr2); 14 return 0; 15 }
10. pointer作用:如想对两个数利用一个临时辅助变量进行数值交换,由于这种操作只能在function内有效(local),pointer可以帮忙改变变量实际的数值
11. 由于C语言知道pointer所指向的变量,故而它可以计算出下一个目标的位置。如若一个pointer被声明为T *p (T为变量类型),若pointer现在指向的地址为A,执行p=p+k,p的值将被修改为A+k*sizeof(T)
12. array中的pointer
决定array中的第一个元素以及最后一个元素,设定一个动态pointer指向array中的第一个元素,利用循环使pointer逐一向后遍历,即
1 int *p; 2 int a[6]; 3 for {p = &a[0];p < &a[6];p++} 4 printf("%2d",*p)
a[i]=*(a+1), *a指向array[0]
13. 利用命令行指令时,一开始输入的总是string格式,但是可以convert成别的形式(atoi(char *s) converts string to int)
argc存储command-line arguments的数量+1(因为包含文件名)
argv存储内容
14. double pointer: 指向pointer的pointer