List容器类图
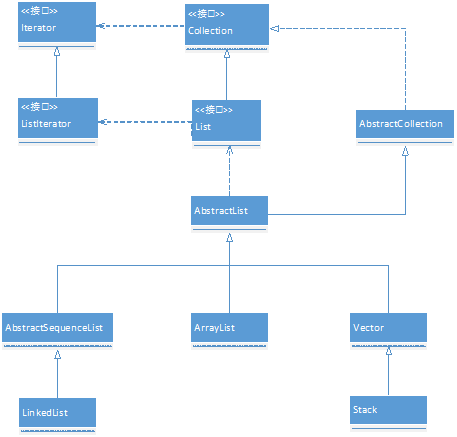
List是一个接口,它继承自Collection和Iterable,它的实现类有AbstractList,AbstrackSequenceList,ArrayList,LinkedList,Vector,Stack;
AbstractList是一个抽象类,它实现了最基本的List接口,它的子类包括AbstrackSequenceList,ArrayList和Vector;
AbstractSequenceList是一个抽象类,它实现了Iterable,Collection,List接口,它的子类包括LinkedList;
LinkedList是List接口的链表实现,此类还实现了Deque接口;
ArrayList是List接口的可变数组的实现;
Vector是实现可增长的对象数组,与数组一样,它包含可以使用整数索引进行访问的组件。但是,Vector 的大小可以根据需要增大或缩小,以适应创建 Vector 后进行添加或移除项的操作。
Stack是表示后进先出(LIFO)的对象堆栈。它通过五个操作对类 Vector 进行了扩展 ,允许将向量视为堆栈。
List
基本描述:有序的 collection(也称为序列)。此接口的用户可以对列表中每个元素的插入位置进行精确地控制。用户可以根据元素的整数索引(在列表中的位置)访问元素,并搜索列表中的元素。List接口的最常用的实现类包括ArrayList(可变数组的实现)和LinkedList(链表实现),在实际使用中,如果主要的操作是访问元素则使用ArrayList,如果主要的操作室插入删除元素则使用LinkedList效率高。
接口方法:
|
int size(); boolean isEmpty(); boolean contains(Object o); Iterator<E> iterator(); Object[] toArray(); <T> T[] toArray(T[] a); boolean add(E e); boolean remove(Object o); boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c); boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c); boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c); boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c); boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c); void clear(); boolean equals(Object o); int hashCode(); E get(int index); E set(int index, E element); void add(int index, E element); E remove(int index); int indexOf(Object o); int lastIndexOf(Object o); ListIterator<E> listIterator(); ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index); List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex); |
ArrayList实现及使用
基本描述:List 接口的大小可变数组的实现。实现了所有可选列表操作,并允许包括 null 在内的所有元素。除了实现 List 接口外,此类还提供一些方法来操作内部用来存储列表的数组的大小。(此类大致上等同于 Vector 类,除了此类是不同步的。)每个 ArrayList 实例都有一个容量。该容量是指用来存储列表元素的数组的大小。它总是至少等于列表的大小。随着向 ArrayList 中不断添加元素,其容量也自动增长。在添加大量元素前,应用程序可以使用 ensureCapacity 操作来增加 ArrayList 实例的容量。这可以减少递增式再分配的数量。
注意,此实现不是同步的。如果多个线程同时访问一个 ArrayList 实例,而其中至少一个线程从结构上修改了列表,那么它必须 保持外部同步。(结构上的修改是指任何添加或删除一个或多个元素的操作,或者显式调整底层数组的大小;仅仅设置元素的值不是结构上的修改。)这一般通过对自然封装该列表的对象进行同步操作来完成。
方法实现:
构造函数
|
//构造一个具有指定初始容量的空列表,它的super为类AbstractList public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { super(); if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; } //构造一个初始容量为10的空列表 public ArrayList() { super(); this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } //构造一个包含指定Collection的元素的列表 public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { elementData = c.toArray(); size = elementData.length; // c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652) if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); } |
添加元素add方法
|
//add方法添加元素之前会先确保size在数组范围内 public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! elementData[size++] = e; return true; } private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { if (elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); } private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { modCount++; // overflow-conscious code if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity); } private void grow(int minCapacity) { // overflow-conscious code int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } |
使用实例:
LinkedList实现及使用
基本描述:
方法实现:
使用实例:
Vector实现及使用
基本描述:
方法实现:
使用实例:
Stack实现及使用
基本描述:
方法实现:
使用实例: