tomcat启动的时候, 起了异步起了两个类: Poller 和 Acceptor.
默认情况下, 是由 NioEndpoint 的 Acceptor 来监听接收请求的.
Acceptor.run()
代码片段:
//org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.Acceptor#run public void run() { int errorDelay = 0; // Loop until we receive a shutdown command while (running) { // Loop if endpoint is paused while (paused && running) { state = AcceptorState.PAUSED; try { Thread.sleep(50); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // Ignore } } if (!running) { break; } state = AcceptorState.RUNNING; try { //if we have reached max connections, wait //最大连接数量的限制 countUpOrAwaitConnection(); SocketChannel socket = null; try { // Accept the next incoming connection from the server // socket 监听阻塞 socket = serverSock.accept(); //调试添加 监听到之后, 继续往下执行 System.out.println("调试添加 : " + socket); } catch (IOException ioe) { // We didn't get a socket countDownConnection(); if (running) { // Introduce delay if necessary errorDelay = handleExceptionWithDelay(errorDelay); // re-throw throw ioe; } else { break; } } // Successful accept, reset the error delay errorDelay = 0; // Configure the socket if (running && !paused) { // setSocketOptions() will hand the socket off to // an appropriate processor if successful // 调用 NioEndpoint#setSocketOptions() 方法, 对socket进行处理 if (!setSocketOptions(socket)) { closeSocket(socket); } } else { closeSocket(socket); } } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail"), t); } } state = AcceptorState.ENDED; }
监听到请求后, 交给 setSocketOptions
protected boolean setSocketOptions(SocketChannel socket) { // Process the connection try { //disable blocking, APR style, we are gonna be polling it socket.configureBlocking(false); Socket sock = socket.socket(); socketProperties.setProperties(sock); //SocketChannel 转换成 NioChannel NioChannel channel = nioChannels.pop(); if (channel == null) { SocketBufferHandler bufhandler = new SocketBufferHandler( socketProperties.getAppReadBufSize(), socketProperties.getAppWriteBufSize(), socketProperties.getDirectBuffer()); if (isSSLEnabled()) { // HTTPS channel = new SecureNioChannel(socket, bufhandler, selectorPool, this); } else { //HTTP1.1 channel = new NioChannel(socket, bufhandler); } } else { channel.setIOChannel(socket); channel.reset(); } //注册到 Poller 中 getPoller0().register(channel); } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); try { log.error("",t); } catch (Throwable tt) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(tt); } // Tell to close the socket return false; } return true; }
getPoller0() 获取到的是 Poller 对象.
//org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.Poller#register public void register(final NioChannel socket) { socket.setPoller(this); NioSocketWrapper ka = new NioSocketWrapper(socket, NioEndpoint.this); socket.setSocketWrapper(ka); ka.setPoller(this); ka.setReadTimeout(getSocketProperties().getSoTimeout()); ka.setWriteTimeout(getSocketProperties().getSoTimeout()); ka.setKeepAliveLeft(NioEndpoint.this.getMaxKeepAliveRequests()); ka.setReadTimeout(getConnectionTimeout()); ka.setWriteTimeout(getConnectionTimeout()); PollerEvent r = eventCache.pop(); //生成 PollerEvent, 相当于将 Socket 加入到 EventQueue 中 ka.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);//this is what OP_REGISTER turns into. if ( r==null) r = new PollerEvent(socket,ka,OP_REGISTER); else r.reset(socket,ka,OP_REGISTER); addEvent(r); }
这里会创建一个 PollerEvent 来封装 socket 和 socket事件.
到这里, Acceptor 就结束了, 后续的处理工作, 其实是交给了 Poller 处理了.
Poller.run()
public void run() { // Loop until destroy() is called while (true) { boolean hasEvents = false; ......//either we timed out or we woke up, process events first if ( keyCount == 0 ) //获取了 EventQueue 中所有的 PollerEvent, 然后依次调用 PollerEvent#run() 方法. //将 socket 注册到 selector 中. hasEvents = (hasEvents | events()); Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = keyCount > 0 ? selector.selectedKeys().iterator() : null; // Walk through the collection of ready keys and dispatch // any active event. while (iterator != null && iterator.hasNext()) { SelectionKey sk = iterator.next(); NioSocketWrapper attachment = (NioSocketWrapper)sk.attachment(); // Attachment may be null if another thread has called // cancelledKey() if (attachment == null) { iterator.remove(); } else { iterator.remove(); //处理 OPEN_READ 和 OPEN_WRITE 事件 processKey(sk, attachment); } }//while //process timeouts timeout(keyCount,hasEvents); }//while getStopLatch().countDown(); }
这个方法是 while(true) 的, 会一直检测容器中是否有 PollerEvent .
Acceptor 封装了一个 PollerEvent 之后, 放到容器中, 这边会检测到. 相当于一个生产消费模式.
//org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.Poller#events public boolean events() { boolean result = false; PollerEvent pe = null; for (int i = 0, size = events.size(); i < size && (pe = events.poll()) != null; i++ ) { result = true; try { pe.run(); pe.reset(); if (running && !paused) { eventCache.push(pe); } } catch ( Throwable x ) { log.error("",x); } } return result; }
这里调用了 PollerEvent.run() 方法.
//org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.PollerEvent#run public void run() { if (interestOps == OP_REGISTER) { try { socket.getIOChannel().register( socket.getPoller().getSelector(), SelectionKey.OP_READ, socketWrapper); } catch (Exception x) { log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.registerFail"), x); } } else { final SelectionKey key = socket.getIOChannel().keyFor(socket.getPoller().getSelector()); try { if (key == null) { // The key was cancelled (e.g. due to socket closure) // and removed from the selector while it was being // processed. Count down the connections at this point // since it won't have been counted down when the socket // closed. socket.socketWrapper.getEndpoint().countDownConnection(); ((NioSocketWrapper) socket.socketWrapper).closed = true; } else { final NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper = (NioSocketWrapper) key.attachment(); if (socketWrapper != null) { //we are registering the key to start with, reset the fairness counter. int ops = key.interestOps() | interestOps; socketWrapper.interestOps(ops); key.interestOps(ops); } else { socket.getPoller().cancelledKey(key); } } } catch (CancelledKeyException ckx) { try { socket.getPoller().cancelledKey(key); } catch (Exception ignore) {} } } }
第一次进来, 是连接注册的, 这里会对其重新封装, 然后注册到 通道中去. 此次 Poller.run() 处理就完结了.
等待 Poller.run() 下一次轮询时,
1. 还是会先进 PollerEvent.run() 方法, 此时会走 else
2. iterator.hasNext() = true. 会进循环处理方法. 此时才会调用 processKey() 方法
processKey
//org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.Poller#processKey //处理 OPEN_READ 和 OPEN_WRITE 事件 protected void processKey(SelectionKey sk, NioSocketWrapper attachment) { try { if ( close ) { cancelledKey(sk); } else if ( sk.isValid() && attachment != null ) { if (sk.isReadable() || sk.isWritable() ) { if ( attachment.getSendfileData() != null ) { processSendfile(sk,attachment, false); } else { unreg(sk, attachment, sk.readyOps()); boolean closeSocket = false; // Read goes before write if (sk.isReadable()) { if (!processSocket(attachment, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ, true)) { closeSocket = true; } } if (!closeSocket && sk.isWritable()) { if (!processSocket(attachment, SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE, true)) { closeSocket = true; } } if (closeSocket) { cancelledKey(sk); } } } } else { //invalid key cancelledKey(sk); } } catch ( CancelledKeyException ckx ) { cancelledKey(sk); } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); log.error("",t); } }
不管是读事件还是写事件, 这里都是调用的 processSocket() 方法
//org.apache.tomcat.util.net.AbstractEndpoint#processSocket public boolean processSocket(SocketWrapperBase<S> socketWrapper, SocketEvent event, boolean dispatch) { try { if (socketWrapper == null) { return false; } //获取/创建 SocketProcessor SocketProcessorBase<S> sc = processorCache.pop(); if (sc == null) { sc = createSocketProcessor(socketWrapper, event); } else { sc.reset(socketWrapper, event); } //交给线程池处理 Executor executor = getExecutor(); if (dispatch && executor != null) {
//sc交给线程池去启动, 任然是调用 sc.run(), 最终调用 SocketProcessor#doRun()方法 executor.execute(sc); } else { //最终调用 SocketProcessor#doRun()方法 sc.run(); } } catch {
...... } return true; }
这里创建了一个新的对象: SocketProcessor
SocketProcessor#doRun()
//org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.SocketProcessor#doRun protected void doRun() { NioChannel socket = socketWrapper.getSocket(); SelectionKey key = socket.getIOChannel().keyFor(socket.getPoller().getSelector()); try { int handshake = -1; try { if (key != null) { if (socket.isHandshakeComplete()) { // No TLS handshaking required. Let the handler // process this socket / event combination. handshake = 0; } else if (event == SocketEvent.STOP || event == SocketEvent.DISCONNECT || event == SocketEvent.ERROR) { // Unable to complete the TLS handshake. Treat it as // if the handshake failed. handshake = -1; } else { handshake = socket.handshake(key.isReadable(), key.isWritable()); event = SocketEvent.OPEN_READ; } } } catch (IOException x) { handshake = -1; if (log.isDebugEnabled()) log.debug("Error during SSL handshake",x); } catch (CancelledKeyException ckx) { handshake = -1; } if (handshake == 0) { SocketState state = SocketState.OPEN; // Process the request from this socket if (event == null) { state = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ); } else {
//getHandler() 获取的是 AbstractProtocol 的内部类 ConnectionHandler state = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, event); } if (state == SocketState.CLOSED) { close(socket, key); } } else if (handshake == -1 ) { getHandler().process(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.CONNECT_FAIL); close(socket, key); } else if (handshake == SelectionKey.OP_READ){ socketWrapper.registerReadInterest(); } else if (handshake == SelectionKey.OP_WRITE){ socketWrapper.registerWriteInterest(); } } catch ...... } finally { socketWrapper = null; event = null; //return to cache if (running && !paused) { processorCache.push(this); } } }
org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocol.ConnectionHandler#process 代码片段:
public SocketState process(SocketWrapperBase<S> wrapper, SocketEvent status) { ......
try { ......
if (processor == null) { //getProtocal() -> Http11NioProtocol //processor -> Http11Processor processor = getProtocol().createProcessor(); register(processor); if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) { getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.processorCreate", processor)); } } processor.setSslSupport(wrapper.getSslSupport(getProtocol().getClientCertProvider())); // Associate the processor with the connection connections.put(socket, processor); SocketState state = SocketState.CLOSED; do { //AbstractProcessorLight#process() state = processor.process(wrapper, status); ...... } while ( state == SocketState.UPGRADING); ......
// Make sure socket/processor is removed from the list of current // connections connections.remove(socket); release(processor); return SocketState.CLOSED; }
processor 是前面创建的 Http11Processor. 实际调用的是父类方法
org.apache.coyote.AbstractProcessorLight#process:
public SocketState process(SocketWrapperBase<?> socketWrapper, SocketEvent status) throws IOException { SocketState state = SocketState.CLOSED; Iterator<DispatchType> dispatches = null; do { if (dispatches != null) { DispatchType nextDispatch = dispatches.next(); if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) { getLog().debug("Processing dispatch type: [" + nextDispatch + "]"); } state = dispatch(nextDispatch.getSocketStatus()); if (!dispatches.hasNext()) { state = checkForPipelinedData(state, socketWrapper); } } else if (status == SocketEvent.DISCONNECT) { // Do nothing here, just wait for it to get recycled } else if (isAsync() || isUpgrade() || state == SocketState.ASYNC_END) { state = dispatch(status); state = checkForPipelinedData(state, socketWrapper); } else if (status == SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE) { // Extra write event likely after async, ignore state = SocketState.LONG; } else if (status == SocketEvent.OPEN_READ) { //抽象方法, 需要子类实现 //此处调用的是子类 Http11Processor#service() 方法 state = service(socketWrapper); } else if (status == SocketEvent.CONNECT_FAIL) { logAccess(socketWrapper); } else { // Default to closing the socket if the SocketEvent passed in // is not consistent with the current state of the Processor state = SocketState.CLOSED; } ......if (isAsync()) { state = asyncPostProcess(); if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) { getLog().debug("Socket: [" + socketWrapper + "], State after async post processing: [" + state + "]"); } } if (dispatches == null || !dispatches.hasNext()) { // Only returns non-null iterator if there are // dispatches to process. dispatches = getIteratorAndClearDispatches(); } } while (state == SocketState.ASYNC_END || dispatches != null && state != SocketState.CLOSED); return state; }
此方法中, 调用了抽象方法 service , 实际调用的是 Http11Processor#service()
public SocketState service(SocketWrapperBase<?> socketWrapper) throws IOException { RequestInfo rp = request.getRequestProcessor(); rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_PARSE); // Setting up the I/O setSocketWrapper(socketWrapper); // Flags keepAlive = true; openSocket = false; readComplete = true; boolean keptAlive = false; SendfileState sendfileState = SendfileState.DONE; while (!getErrorState().isError() && keepAlive && !isAsync() && upgradeToken == null && sendfileState == SendfileState.DONE && !endpoint.isPaused()) { // Parsing the request header try { if (!inputBuffer.parseRequestLine(keptAlive)) { if (inputBuffer.getParsingRequestLinePhase() == -1) { return SocketState.UPGRADING; } else if (handleIncompleteRequestLineRead()) { break; } } // Process the Protocol component of the request line // Need to know if this is an HTTP 0.9 request before trying to // parse headers. prepareRequestProtocol(); if (endpoint.isPaused()) { // 503 - Service unavailable response.setStatus(503); setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, null); } else { keptAlive = true; // Set this every time in case limit has been changed via JMX request.getMimeHeaders().setLimit(endpoint.getMaxHeaderCount()); // Don't parse headers for HTTP/0.9 if (!http09 && !inputBuffer.parseHeaders()) { // We've read part of the request, don't recycle it // instead associate it with the socket openSocket = true; readComplete = false; break; } if (!disableUploadTimeout) { socketWrapper.setReadTimeout(connectionUploadTimeout); } } } catch (IOException e) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug(sm.getString("http11processor.header.parse"), e); } setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CONNECTION_NOW, e); break; } catch (Throwable t) { ......// 400 - Bad Request response.setStatus(400); setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, t); } // Has an upgrade been requested? if (isConnectionToken(request.getMimeHeaders(), "upgrade")) { // Check the protocol String requestedProtocol = request.getHeader("Upgrade"); UpgradeProtocol upgradeProtocol = protocol.getUpgradeProtocol(requestedProtocol); if (upgradeProtocol != null) { if (upgradeProtocol.accept(request)) { // TODO Figure out how to handle request bodies at this // point. response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_SWITCHING_PROTOCOLS); response.setHeader("Connection", "Upgrade"); response.setHeader("Upgrade", requestedProtocol); action(ActionCode.CLOSE, null); getAdapter().log(request, response, 0); InternalHttpUpgradeHandler upgradeHandler = upgradeProtocol.getInternalUpgradeHandler( getAdapter(), cloneRequest(request)); UpgradeToken upgradeToken = new UpgradeToken(upgradeHandler, null, null); action(ActionCode.UPGRADE, upgradeToken); return SocketState.UPGRADING; } } } if (getErrorState().isIoAllowed()) { // Setting up filters, and parse some request headers rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_PREPARE); try { prepareRequest(); } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug(sm.getString("http11processor.request.prepare"), t); } // 500 - Internal Server Error response.setStatus(500); setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, t); } } if (maxKeepAliveRequests == 1) { keepAlive = false; } else if (maxKeepAliveRequests > 0 && socketWrapper.decrementKeepAlive() <= 0) { keepAlive = false; } // Process the request in the adapter if (getErrorState().isIoAllowed()) { try { rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_SERVICE); //调用 CoyoteAdaptor#service(req, resp) 方法, 进行适配 getAdapter().service(request, response); // Handle when the response was committed before a serious // error occurred. Throwing a ServletException should both // set the status to 500 and set the errorException. // If we fail here, then the response is likely already // committed, so we can't try and set headers. if(keepAlive && !getErrorState().isError() && !isAsync() && statusDropsConnection(response.getStatus())) { setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, null); } } catch (InterruptedIOException e) { setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CONNECTION_NOW, e); } catch (HeadersTooLargeException e) { log.error(sm.getString("http11processor.request.process"), e); // The response should not have been committed but check it // anyway to be safe if (response.isCommitted()) { setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_NOW, e); } else { response.reset(); response.setStatus(500); setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, e); response.setHeader("Connection", "close"); // TODO: Remove } } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); log.error(sm.getString("http11processor.request.process"), t); // 500 - Internal Server Error response.setStatus(500); setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, t); getAdapter().log(request, response, 0); } } // Finish the handling of the request rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDINPUT); if (!isAsync()) { // If this is an async request then the request ends when it has // been completed. The AsyncContext is responsible for calling // endRequest() in that case. endRequest(); } rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDOUTPUT); // If there was an error, make sure the request is counted as // and error, and update the statistics counter if (getErrorState().isError()) { response.setStatus(500); } if (!isAsync() || getErrorState().isError()) { request.updateCounters(); if (getErrorState().isIoAllowed()) { inputBuffer.nextRequest(); outputBuffer.nextRequest(); } } if (!disableUploadTimeout) { int soTimeout = endpoint.getConnectionTimeout(); if(soTimeout > 0) { socketWrapper.setReadTimeout(soTimeout); } else { socketWrapper.setReadTimeout(0); } } rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_KEEPALIVE); sendfileState = processSendfile(socketWrapper); } rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDED); if (getErrorState().isError() || (endpoint.isPaused() && !isAsync())) { return SocketState.CLOSED; } else if (isAsync()) { return SocketState.LONG; } else if (isUpgrade()) { return SocketState.UPGRADING; } else { if (sendfileState == SendfileState.PENDING) { return SocketState.SENDFILE; } else { if (openSocket) { if (readComplete) { return SocketState.OPEN; } else { return SocketState.LONG; } } else { return SocketState.CLOSED; } } } }
CoyoteAdapter.service() 方法中, 会启动 tomcat 的管道
public void service(org.apache.coyote.Request req, org.apache.coyote.Response res) throws Exception { //转换 request 和 response Request request = (Request) req.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES); Response response = (Response) res.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES); if (request == null) { // Create objects request = connector.createRequest(); request.setCoyoteRequest(req); response = connector.createResponse(); response.setCoyoteResponse(res); // Link objects //将 request 和 response 链接起来, 一对一 request.setResponse(response); response.setRequest(request); // Set as notes req.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, request); res.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, response); // Set query string encoding //获取 URI 的编码 : http://127.0.0.1:8080/webDemo req.getParameters().setQueryStringCharset(connector.getURICharset()); } if (connector.getXpoweredBy()) { response.addHeader("X-Powered-By", POWERED_BY); } boolean async = false; boolean postParseSuccess = false; req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(THREAD_NAME.get()); try { // Parse and set Catalina and configuration specific // request parameters 在 Map 中解析请求 postParseSuccess = postParseRequest(req, request, res, response); if (postParseSuccess) { //check valves if we support async //getContainer() -> StandardEngine request.setAsyncSupported( connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().isAsyncSupported()); // Calling the container // 调用 StandardEngineValve#invoke(), 开始执行管道方法. (责任链模式) // 如果有多个 valve , 这里 getFirst() 拿到的就是 first valve, // 然后在 first valve中, 需要调用 getNext().invoke(request, response) 来传递 connector.getService() .getContainer() .getPipeline() //-> StandardPipeLine .getFirst() //获取优先级: first > basic .invoke(request, response); } if (request.isAsync()) { async = true; ReadListener readListener = req.getReadListener(); if (readListener != null && request.isFinished()) { // Possible the all data may have been read during service() // method so this needs to be checked here ClassLoader oldCL = null; try { oldCL = request.getContext().bind(false, null); if (req.sendAllDataReadEvent()) { req.getReadListener().onAllDataRead(); } } finally { request.getContext().unbind(false, oldCL); } } Throwable throwable = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION); // If an async request was started, is not going to end once // this container thread finishes and an error occurred, trigger // the async error process if (!request.isAsyncCompleting() && throwable != null) { request.getAsyncContextInternal().setErrorState(throwable, true); } } else { request.finishRequest(); response.finishResponse(); } } catch (IOException e) { // Ignore } finally { AtomicBoolean error = new AtomicBoolean(false); res.action(ActionCode.IS_ERROR, error); if (request.isAsyncCompleting() && error.get()) { // Connection will be forcibly closed which will prevent // completion happening at the usual point. Need to trigger // call to onComplete() here. res.action(ActionCode.ASYNC_POST_PROCESS, null); async = false; } // Access log if (!async && postParseSuccess) { // Log only if processing was invoked. // If postParseRequest() failed, it has already logged it. Context context = request.getContext(); Host host = request.getHost(); // If the context is null, it is likely that the endpoint was // shutdown, this connection closed and the request recycled in // a different thread. That thread will have updated the access // log so it is OK not to update the access log here in that // case. // The other possibility is that an error occurred early in // processing and the request could not be mapped to a Context. // Log via the host or engine in that case. long time = System.currentTimeMillis() - req.getStartTime(); if (context != null) { context.logAccess(request, response, time, false); } else if (response.isError()) { if (host != null) { host.logAccess(request, response, time, false); } else { connector.getService().getContainer().logAccess( request, response, time, false); } } } req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(null); // Recycle the wrapper request and response if (!async) { updateWrapperErrorCount(request, response); request.recycle(); response.recycle(); } } }
前面看了那么多, 在多线程间跳来跳去, 终于找到管道方法了.
总结:
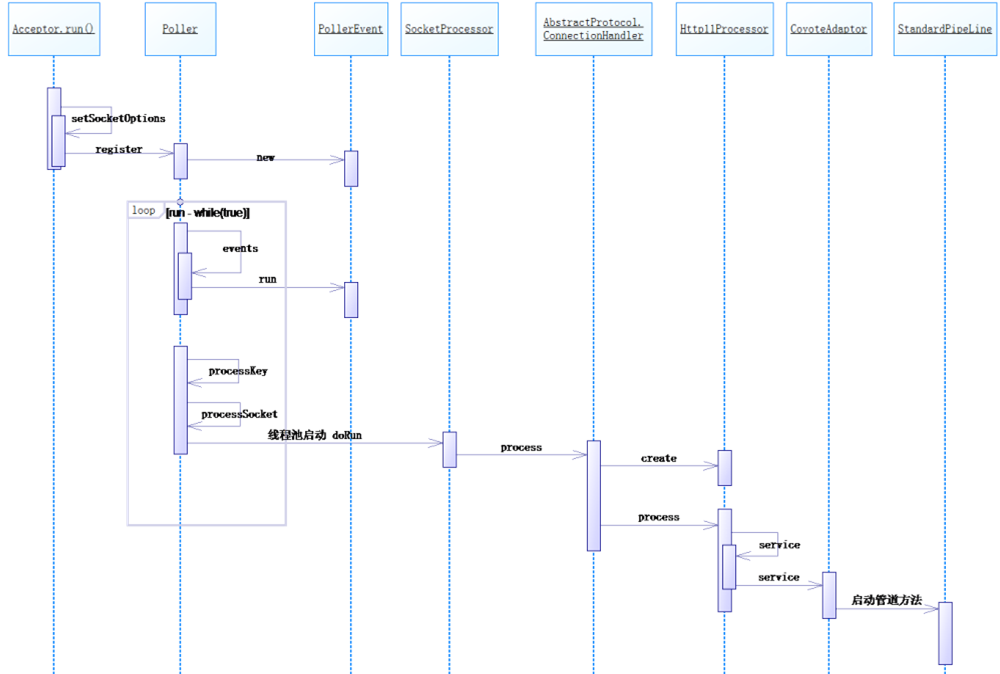
主要的调用流程时序图: