


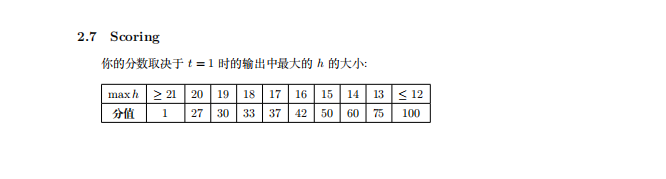


T1
就是左端点排序后,然后如果可以到达下面一个点,那么对于

看这个,f[i]表示到了i这个点的方案数,当前边覆盖到了a[i].r
a[i].l-1 ------ a[i].r-1都可以转移过来,
然后对于其后面的来说,当前的边选不选无所谓,a[i].r---m都乘2
1 #include<cstring> 2 #include<algorithm> 3 #include<cmath> 4 #include<iostream> 5 #include<cstdio> 6 7 #define ls p<<1 8 #define rs p<<1|1 9 #define mod 1000000009 10 #define ll long long 11 #define N 500007 12 using namespace std; 13 inline int read() 14 { 15 int x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar(); 16 while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if (ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();} 17 while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+ch-'0';ch=getchar();} 18 return x*f; 19 } 20 21 int n,m; 22 int b[N]; 23 struct Node 24 { 25 int l,r; 26 }a[N]; 27 struct Date 28 { 29 ll add,cf,sum; 30 }tr[N*4]; 31 32 bool operator<(Node x,Node y){return x.l<y.l;} 33 void build(int p,int l,int r) 34 { 35 tr[p].cf=1; 36 if (l==r)return; 37 int mid=(l+r)>>1; 38 build(p<<1,l,mid),build(p<<1|1,mid+1,r); 39 } 40 void downdate(int p) 41 { 42 ll cf=tr[p].cf,add=tr[p].add;tr[p].cf=1,tr[p].add=0; 43 (tr[ls].cf*=cf)%=mod,(tr[ls].add*=cf)%=mod,(tr[ls].add+=add)%=mod; 44 (tr[rs].cf*=cf)%=mod,(tr[rs].add*=cf)%=mod,(tr[rs].add+=add)%=mod; 45 (tr[ls].sum*=cf)%=mod,(tr[ls].sum+=add)%=mod; 46 (tr[rs].sum*=cf)%=mod,(tr[rs].sum+=add)%=mod; 47 } 48 void update(int p) 49 { 50 tr[p].sum=tr[ls].sum+tr[rs].sum; 51 } 52 void modify(int p,int l,int r,int x,int y,ll jia,ll cf) 53 { 54 if (l==x&&y==r) 55 { 56 if (jia){(tr[p].add+=jia)%=mod;(tr[p].sum+=(r-l+1)*jia)%=mod;} 57 else 58 { 59 (tr[p].sum*=cf)%=mod; 60 (tr[p].add*=cf)%=mod; 61 (tr[p].cf*=cf)%=mod; 62 } 63 return; 64 } 65 downdate(p); 66 int mid=(l+r)>>1; 67 if (y<=mid) modify(p<<1,l,mid,x,y,jia,cf); 68 else if(x>mid) modify(p<<1|1,mid+1,r,x,y,jia,cf); 69 else modify(p<<1,l,mid,x,mid,jia,cf),modify(p<<1|1,mid+1,r,mid+1,y,jia,cf); 70 update(p); 71 } 72 int query(int p,int l,int r,int x,int y) 73 { 74 if (l==x&&y==r) return tr[p].sum; 75 downdate(p); 76 int mid=(l+r)>>1; 77 if (y<=mid) return query(p<<1,l,mid,x,y); 78 else if (x>mid) return query(p<<1|1,mid+1,r,x,y); 79 else return (query(p<<1,l,mid,x,mid)+query(p<<1|1,mid+1,r,mid+1,y))%mod; 80 update(p); 81 } 82 int main() 83 { 84 n=read(),m=read(); 85 for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)a[i].l=read(),a[i].r=read(); 86 sort(a+1,a+n+1); 87 for (int i=1;i<=m;i++)b[i]=read(); 88 sort(b+1,b+m+1); 89 for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) 90 { 91 (a[i].l=lower_bound(b+1,b+m+1,a[i].l)-b); 92 (a[i].r=upper_bound(b+1,b+m+1,a[i].r)-b)--; 93 // cout<<"i="<<i<<" "<<a[i].l<<" "<<a[i].r<<endl; 94 } 95 build(1,0,m); 96 modify(1,0,m,0,0,1,1); 97 int num=0; 98 for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) 99 { 100 if (a[i].l>a[i].r) 101 { 102 num++; 103 continue; 104 } 105 ll x=query(1,0,m,a[i].l-1,a[i].r-1); 106 modify(1,0,m,a[i].r,m,0,2); 107 modify(1,0,m,a[i].r,a[i].r,x,1); 108 } 109 ll ans=query(1,0,m,m,m); 110 for (int i=1;i<=num;i++)(ans*=(ll)2)%=mod; 111 printf("%lld ",ans); 112 }
T2
因为x,y不同,所以一定有一位二进制不同,
但是无法区分谁大谁小
所以我们把其映射到12位上去,6个0,6个1,这样有924>920种
然后因为不同,所以找出哪一位,就是x为1,y为0的那一位,一定存在
然后就可以k=12来判断了。
代码很好实现

1 // Copyright (C) 2017 __debug. 2 3 // This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or 4 // modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as 5 // published by the Free Software Foundation; version 3 6 7 // This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, 8 // but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of 9 // MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the 10 // GNU General Public License for more details. 11 12 // You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License 13 // along with this program; If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. 14 15 16 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 17 #include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp> 18 #include <ext/pb_ds/priority_queue.hpp> 19 20 #define x first 21 #define y second 22 #define MP std::make_pair 23 #define SZ(x) ((int)(x).size()) 24 #define ALL(x) (x).begin(), (x).end() 25 #define DEBUG(...) fprintf(stderr, __VA_ARGS__) 26 #ifdef __linux__ 27 #define getchar getchar_unlocked 28 #define putchar putchar_unlocked 29 #endif 30 31 using std::pair; 32 using std::vector; 33 using std::string; 34 35 typedef long long LL; 36 typedef pair<int, int> Pii; 37 38 const int oo = 0x3f3f3f3f; 39 40 template<typename T> inline bool chkmax(T &a, T b) { return a < b ? a = b, true : false; } 41 template<typename T> inline bool chkmin(T &a, T b) { return b < a ? a = b, true : false; } 42 string procStatus() 43 { 44 std::ifstream t("/proc/self/status"); 45 return string(std::istreambuf_iterator<char>(t), std::istreambuf_iterator<char>()); 46 } 47 template<typename T> T read(T &x) 48 { 49 int f = 1; 50 char ch = getchar(); 51 for (; !isdigit(ch); ch = getchar()) 52 f = (ch == '-' ? -1 : 1); 53 for (x = 0; isdigit(ch); ch = getchar()) 54 x = 10 * x + ch - '0'; 55 return x *= f; 56 } 57 template<typename T> void write(T x) 58 { 59 if (x == 0) { 60 putchar('0'); 61 return; 62 } 63 if (x < 0) { 64 putchar('-'); 65 x = -x; 66 } 67 static char s[20]; 68 int top = 0; 69 for (; x; x /= 10) 70 s[++top] = x % 10 + '0'; 71 while (top) 72 putchar(s[top--]); 73 } 74 // EOT 75 76 const int LIM = 12; 77 78 int type, N; 79 vector<int> code; 80 81 void init() 82 { 83 for (int s = 0; s < (1 << LIM) && SZ(code) < N; ++s) { 84 if (__builtin_popcount(s) == LIM / 2) 85 code.push_back(s); 86 } 87 assert(SZ(code) == N); 88 } 89 90 int encode(int x, int y) 91 { 92 return 32 - __builtin_clz((code[x - 1] ^ code[y - 1]) & code[x - 1]); 93 } 94 95 bool decode(int q, int h) 96 { 97 return code[q - 1] >> (h - 1) & 1; 98 } 99 100 int main() 101 { 102 int T; 103 read(type); read(N); read(T); 104 init(); 105 while (T--) { 106 int x, y; 107 read(x); read(y); 108 if (type == 1) 109 printf("%d ", encode(x, y)); 110 else 111 puts(decode(x, y) ? "yes" : "no"); 112 } 113 } 114 115 // 鍜�畾闈掑北涓嶆斁鏉撅紝绔嬫牴鍘熷湪鐮村博涓�€? 116 // -- 閮戠嚠銆婄�鐭炽€?
T3
因为要最大化,编号不断增大,所以选了其父亲后一定会选最小的点,
但是不能直接贪心,要对于全局所有的点贪心,转化很巧妙。
代码附上,慢慢理解,
两个判断意思是,以前的原来点是没用的,并且不能是根,没有父亲。
1 #include<cstring> 2 #include<cmath> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 #include<cmath> 5 #include<cstdio> 6 #include<queue> 7 8 #define ll long long 9 #define N 100007 10 using namespace std; 11 inline int read() 12 { 13 int x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar(); 14 while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if (ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();} 15 while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+ch-'0';ch=getchar();} 16 return x*f; 17 } 18 19 struct Node 20 { 21 int u,s,t;//u鍝�釜鐐癸紝s鏄�潈鍊煎拰锛宼鏄痵iz銆? 22 }; 23 bool operator >(Node x,Node y) 24 { 25 return (ll)x.s*y.t>(ll)y.s*x.t; 26 } 27 priority_queue<Node,vector<Node>,greater<Node> >q; 28 int n; 29 int par[N],fa[N],siz[N],sum[N],val[N*2],w[N],r[N]; 30 int cnt,hed[N],nxt[N*2],rea[N*2]; 31 ll res,ans[N]; 32 33 void add(int u,int v) 34 { 35 nxt[++cnt]=hed[u]; 36 hed[u]=cnt; 37 rea[cnt]=v; 38 } 39 void dfs(int u,int f) 40 { 41 for (int i=hed[u];i!=-1;i=nxt[i]) 42 { 43 int v=rea[i]; 44 if (v==f)continue; 45 par[v]=u,dfs(v,u); 46 } 47 } 48 int find(int num) 49 { 50 if (fa[num]!=num)fa[num]=find(fa[num]); 51 return fa[num]; 52 } 53 void solve(int rt) 54 { 55 for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) 56 { 57 fa[i]=i,siz[i]=1; 58 sum[i]=ans[i]=w[i]; 59 q.push((Node){i,w[i],1}); 60 } 61 dfs(rt,0); 62 for (int i=1;i<n;) 63 { 64 Node now=q.top();q.pop(); 65 if (now.t!=siz[now.u]||now.u==rt)continue; 66 i++; 67 int u=find(par[now.u]),v=now.u; 68 ans[u]+=ans[v]+(ll)sum[v]*siz[u]; 69 res=max(res,ans[u]); 70 fa[v]=u,siz[u]+=siz[v],sum[u]+=sum[v]; 71 q.push((Node){u,sum[u],siz[u]}); 72 } 73 while(!q.empty())q.pop(); 74 } 75 int main() 76 { 77 memset(hed,-1,sizeof(hed)); 78 n=read(); 79 for (int i=1;i<n;i++) 80 { 81 int x=read(),y=read(); 82 add(x,y),add(y,x); 83 } 84 for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) 85 w[i]=read(),r[i]=read(); 86 for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) 87 if (r[i])solve(i); 88 printf("%lld ",res); 89 }
