PyTorch 中对 tensor 的很多操作如 sum、softmax 等都可以设置 dim 参数用来指定操作在哪一维进行。PyTorch 中的 dim 类似于 numpy 中的 axis,这篇文章来总结一下 PyTorch 中的 dim 操作。
dim 与方括号的关系
创建一个矩阵
a = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
print(a)
输出
tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])
因为a是一个矩阵,所以a的左边有 2 个括号
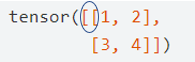
括号之间是嵌套关系,代表了不同的维度。从左往右数,两个括号代表的维度分别是 0 和 1 ,在第 0 维遍历得到向量,在第 1 维遍历得到标量

同样地,对于 3 维 tensor
b = torch.tensor([[[3, 2], [1, 4]], [[5, 6], [7, 8]]])
print(b)
输出
tensor([[[3, 2],
[1, 4]],
[[5, 6],
[7, 8]]])
则 3 个括号代表的维度从左往右分别为 0, 1, 2,在第 0 维遍历得到矩阵,在第 1 维遍历得到向量,在第 2 维遍历得到标量
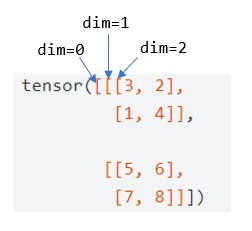
更详细一点
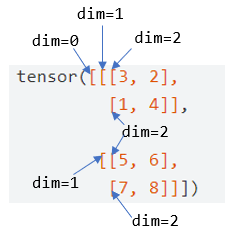
在指定的维度上进行操作
在某一维度求和(或者进行其他操作)就是对该维度中的元素进行求和。
对于矩阵 a
a = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
print(a)
输出
tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])
求 a 在第 0 维的和,因为第 0 维代表最外边的括号,括号中的元素为向量[1, 2],[3, 4],第 0 维的和就是第 0 维中的元素相加,也就是两个向量[1, 2],[3, 4]相加,所以结果为
s = torch.sum(a, dim=0)
print(s)
输出
tensor([4, 6])
可以看到,a 是 2 维矩阵,而相加的结果为 1 维向量,可以使用参数keepdim=True来保证维度数目不变。
s = torch.sum(a, dim=0, keepdim=True)
print(s)
输出
tensor([[4, 6]])
在 a 的第 0 维求和,就是对第 0 维中的元素(向量)进行相加。同样的,对 a 第 1 维求和,就是对 a 第 1 维中的元素(标量)进行相加,a 的第 1 维元素为标量 1,2 和 3,4,则结果为
s = torch.sum(a, dim=1)
print(s)
输出
tensor([3, 7])
保持维度不变
s = torch.sum(a, dim=1, keepdim=True)
print(s)
输出
tensor([[3],
[7]])
对 3 维 tensor 的操作也是这样
b = torch.tensor([[[3, 2], [1, 4]], [[5, 6], [7, 8]]])
print(b)
输出
tensor([[[3, 2],
[1, 4]],
[[5, 6],
[7, 8]]])
将 b 在第 0 维相加,第 0 维为最外层括号,最外层括号中的元素为矩阵[[3, 2], [1, 4]]和[[5, 6], [7, 8]]。在第 0 维求和,就是将第 0 维中的元素(矩阵)相加
s = torch.sum(b, dim=0)
print(s)
输出
tensor([[ 8, 8],
[ 8, 12]])
求 b 在第 1 维的和,就是将 b 第 1 维中的元素[3, 2]和[1, 4], [5, 6]和 [7, 8]相加,所以
s = torch.sum(b, dim=1)
print(s)
输出
tensor([[ 4, 6],
[12, 14]])
则在 b 的第 2 维求和,就是对标量 3 和 2, 1 和 4, 5 和 6 , 7 和 8 求和
s = torch.sum(b, dim=2)
print(s)
结果为
tensor([[ 5, 5],
[11, 15]])
除了求和,其他操作也是类似的,如求 b 在指定维度上的最大值
m = torch.max(b, dim=0)
print(m)
b 在第 0 维的最大值是第 0 维中的元素(两个矩阵[[3, 2], [1, 4]]和[[5, 6], [7, 8]])的最大值,取矩阵对应位置最大值即可
结果为
torch.return_types.max(
values=tensor([[5, 6],
[7, 8]]),
indices=tensor([[1, 1],
[1, 1]]))
b 在第 1 维的最大值就是第 1 维元素(4 个(2对)向量)的最大值
m = torch.max(b, dim=1)
print(m)
输出为
torch.return_types.max(
values=tensor([[3, 4],
[7, 8]]),
indices=tensor([[0, 1],
[1, 1]]))
b 在第 0 维的最大值就是第 0 为元素(8 个(4 对)标量)的最大值
m = torch.max(b, dim=2)
print(m)
输出
torch.return_types.max(
values=tensor([[3, 4],
[6, 8]]),
indices=tensor([[0, 1],
[1, 1]]))
总结
在 tensor 的指定维度操作就是对指定维度包含的元素进行操作,如果想要保持结果的维度不变,设置参数keepdim=True即可。