一.一个牛逼闪闪的知识点Promise
npm install bluebird
二.Promise实例
ball.html
<!doctype> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Promise animation</title> <style> .ball { width: 40px; height: 40px; border-radius: 20px; } .ball1 { background: red; } .ball2 { background: yellow; } .ball3 { background: green; } </style> <script src="./node_modules/bluebird/js/browser/bluebird.js"></script> </head> <body> <div class="ball ball1" style="margin-left: 0;"></div> <div class="ball ball2" style="margin-left: 0;"></div> <div class="ball ball3" style="margin-left: 0;"></div> <script type="text/javascript"> var ball1 = document.querySelector('.ball1') var ball2 = document.querySelector('.ball2') var ball3 = document.querySelector('.ball3') function animate(ball, distance, cb) { setTimeout(function() { var marginLeft = parseInt(ball.style.marginLeft, 10) if(marginLeft === distance) { cb && cb() }else { if(marginLeft < distance) { marginLeft++ }else { marginLeft-- } ball.style.marginLeft = marginLeft animate(ball, distance, cb) } }, 13) } animate(ball1, 100, function() { animate(ball2, 200, function() { animate(ball3, 300, function(){ animate(ball3, 150, function(){ animate(ball2, 150, function(){ animate(ball1, 150, function(){ // }) }) }) }) }) }) </script> </body> </html>
使用Promise改造后,ball2.html如下:
<!doctype> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Promise animation</title> <style> .ball { width: 40px; height: 40px; border-radius: 20px; } .ball1 { background: red; } .ball2 { background: yellow; } .ball3 { background: green; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="ball ball1" style="margin-left: 0;"></div> <div class="ball ball2" style="margin-left: 0;"></div> <div class="ball ball3" style="margin-left: 0;"></div> <script type="text/javascript"> var ball1 = document.querySelector('.ball1') var ball2 = document.querySelector('.ball2') var ball3 = document.querySelector('.ball3') var Promise = window.Promise function promiseAnimate(ball, distance) { return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) { function _animate() { setTimeout(function() { var marginLeft = parseInt(ball.style.marginLeft, 10) if(marginLeft === distance) { resolve }else { if(marginLeft < distance) { marginLeft++ }else { marginLeft-- } ball.style.marginLeft = marginLeft + 'px' _animate() } }, 13) } _animate() }) } promiseAnimate(ball1, 100) .then(function() { return promiseAnimate(ball2, 200) }) .then(function() { return promiseAnimate(ball3, 300) }) .then(function() { return promiseAnimate(ball3, 150) }) .then(function() { return promiseAnimate(ball2, 150) }) .then(function() { return promiseAnimate(ball1, 150) }) </script> </body> </html>
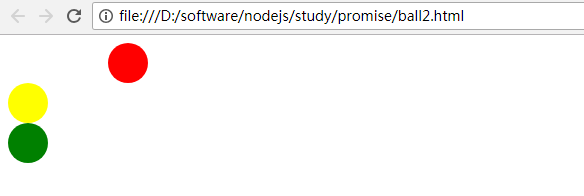
运行效果:
三.牛逼闪闪的Promise只需三点
1.Promise是JS针对异步操作场景的解决方案
针对异步的场景,业界有很多解决方案,如回调、事件机制
Promise是一个对象,同时它也一种规范,针对异步操作约定了统一的接口,表示一个异步操作的最终结果以同步的方式来写代码,执行的操作是异步的,但是又保证程序的执行顺序是同步的。
原本是社区的一个规范的构想,被加入到ES6的语言标准里面,比如Chrom,Firefox浏览器已对它进行了实现。
2.Promise对象三种状态
未完成(pending)
已完成(fulfilled)
失败(rejected)
只能从未完成到已完成,或者从未完成到失败,不可逆的。
3.ES6的Promise语言标准、Promise/A+规范
Promise/A+规范算是之前的Promise/A规范的升级版,规定了行为标准,扩展了原来的规范,并且覆盖了一些约定俗成的行为,总之,它就是一个更为标准的Promise能力和使用的规范。
Promise/A与A+不同点
a.A+规范通过术语thenable来区分promise对象
b.A+定义onFulfilled/onRejected必须是作为函数来调用,而且调用过程必须是异步的
c.A+严格定义了then方式链式调用时onFulfilled/onRejected的调用顺序
4.如何使用Promise then方法
promiseObj.then(onFulfilled, onRejected) onFulfilled = function(value) { return promiseObj2 } onRejected = function(err) {}
Promise会保证then方法回调的顺序,依次调用,会等前面的promise方法执行完成后才会执行后面then中的方法。
Promise最大的特点是:回调函数可以写成规范的链式的写法,程序流程可以很清楚。它的一整套接口可以实现很强大的功能,比如为多个异步操作部署一个回调函数,为多个回调函数中抛出的错误统一指定处理的方法等等。
5.在什么场景下使用
只要是异步编程的地方,都可以使用Promise,但不能Promise而Promise,如业务场景是很简单的异步操作,维护很容易了,没必要引入一个Promise库来重构。
6.Promise库
Promise库市面上有不少,如下所示:
bluebird
Q
then.js
es6-promise
ypromise
async
nativeo-promise-only
四.重写爬虫,更优雅的异步编程
https协议是基于ssl/tls的http协议,所有数据都是在ssl/tls协议的封装之上传输的。

也就是说,https协议是在http协议的基础之上添加了ssl/tls握手及数据加密传输,因此,ssl/tls协议就是http和https最大区别。
在搭建https服务器的时候,需要有一个ssl证书。
https.js
var https = require('https') var fs = require('fs') var options = { key: fs.readFileSync('ssh_key.pem'), cert: fs.readFileSync('ssh_cert.pem') } https.createServer(options, function(req, res) { res.writeHead(200) res.end('Hello Imooc') }).listen(8090)
重写爬虫,更优雅的异步编程,promise_crawler.js
var http = require('http') var Promise = require('bluebird') var cheerio = require('cheerio') var baseUrl = 'http://www.imooc.com/learn/' var url = 'http://www.imooc.com/learn/348' var videoIds = [348, 259, 197, 134, 75] function filterChapters(html) { var $ = cheerio.load(html) var chapters = $('.learnchapter') var title = $('#page_header .path span').text() var number = parseInt($($('.info_num i')[0]).text().trim(), 10) // var courseData = { // title: title, // number: number, // videos: [{ // chapterTitle: '', // videos: [ // title: '', // id: '' // ] // }] // } var courseData = { title: title, number: number, videos: [] } chapters.each(function(item) { var chapter = $(this) var charterTitle = chapter.find('strong').text() var videos = chapter.find('.video').children('li') var chapterData = { chapterTitle: chapterTitle, videos : [] } videos.each(function(item) { var video = $(this).find('.studyvideo') var videoTitle = video.text() var id = video.attr('href').split('video/')[1] chapterData.videos.push({ title: videoTitle, id: id }) }) courseData.videos.push(chapterData) }) return courseData; } function printCourseInfo(coursesData) { coursesData.forEach(function(courseData) { console.log(courseData.number + ' 人学过 ' + courseData.title + ' ') }) coursesData.forEach(function(courseData) { console.log('###' + courseData.title + ' ') courseData.videos.forEach(function(item) { var chapterTitle = item.chapterTitle console.log(charterTitle + ' ') item.videos.forEach(function(video) { console.log(' [' + video.id + ']' + video.title + ' ') }) }) }) } function getPageAsync(url) { return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) { console.log('正在爬取' + url) http.get(url, function(res) { var html = '' res.on('data', function(data) { html += data }) res.on('end', function() { resolve(html) }) }).on('error', function(e) { reject(e) console.log('获取课程数据出错!') }) }) } var fetchCourseArray = [] videoIds.forEach(function(id) { fetchCourseArray.push(getPageAsync(baseUrl + id)) }) Promise .all(fetchCourseArray) .then(function(pages) { var coursesData = [] pages.forEach(function(html) { var courses = filterChapters(html) coursesData.push(courses) }) coursesData.sort(function(a, b) { return a.number < b.number }) printCourseInfo(coursesData) })
运行结果:

五.Nodejs API
1.横扫Nodejs API-Buffer的实例
Buffer:用来处理二进制的数据。因为JS字符串是UTF-8的编码存储的,处理二进制的能力是很弱的,而网络层对于不同资源的请求、响应,甚至是文件都是二进制的方式来交互的,所以Node.js有这么一个接口,专门用于存放二进制数据的缓存区,并提供了一些方法来对缓存区数据进行进一步的处理。Buffer在Node.js中是要以全局访问的,不需要用require来加载。
> Buffer { [Function: Buffer] poolSize: 8192, from: [Function: from], of: [Function: of], alloc: [Function: alloc], allocUnsafe: [Function: allocUnsafe], allocUnsafeSlow: [Function: allocUnsafeSlow], isBuffer: [Function: isBuffer], compare: [Function: compare], isEncoding: [Function: isEncoding], concat: [Function: concat], byteLength: [Function: byteLength], [Symbol(kIsEncodingSymbol)]: [Function: isEncoding] } > new Buffer('Hello Node.js') <Buffer 48 65 6c 6c 6f 20 4e 6f 64 65 2e 6a 73> > new Buffer('Hello Node.js', 'base64'); <Buffer 1d e9 65 a0 da 1d 7a 3b> > var buf = new Buffer(8); undefined > buf.length 8 > var buf = new Buffer('12345678');console.log(buf); <Buffer 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38> undefined > var buf = new Buffer(7);buf.write('12345678');console.log(buf); <Buffer 31 32 33 34 35 36 37> undefined > var buf = new Buffer([1,2,3,4]);console.log(buf); <Buffer 01 02 03 04> undefined > console.log(buf[1]) 2 undefined > var buf = new Buffer([1,2.33,3.11,4]);console.log(buf); <Buffer 01 02 03 04> undefined > console.log(buf[1]) 2 undefined

a.buffer.write(string, offset=0, length, encoding='utf8')方法
> var buf = new Buffer('Hello 慕课网') undefined > buf.length 15 > buf.write('Hi 慕课网') 12 > buf.toString() 'Hi 慕课网网' > buf.length 15 > buf.write(' ImoocImoocImooc', 2, 16) 13 > buf.toString() 'Hi ImoocImoocIm'
b.buffer.copy(target, tStart, sStart, sEnd=buffer.length)
> var buf = new Buffer('Hello Imooc') undefined > buf.length 11 > var buf2 = new Buffer(5) undefined > buf.copy(buf2) 5 > buf2.toString() 'Hello' > buf.copy(buf2, 0, 6, 11) 5 > buf2.toString() 'Imooc'
c.buffer.js源码
var buffer = process.binding('buffer'); process.binding它是一个桥梁,javaScript代码就可以和C++代码进行交互,这条语句获取到C++里面实现的buffer模块 > var buf = new Buffer('imooc'); undefined > var str = buf.toString('base64'); undefined > str 'aW1vb2M=' > var buf = new Buffer('aW1vb2M=', 'base64') undefined > var str = buf.toString() undefined > str 'imooc' > var buf = new Buffer('aW1vb2M=', 'base64') undefined > var str = buf.toString('hex') undefined > str '696d6f6f63' > var buf = new Buffer('696d6f6f63', 'hex') undefined > var str = buf.toString('utf8') undefined > str 'imooc' >
2.buffer实例buffer_image.js
var fs = require('fs') fs.readFile('logo.png', function(err, origin_buffer) { console.log(Buffer.isBuffer(origin_buffer)) fs.writeFile('logo_buffer.png', origin_buffer, function(err) { if(err) { console.log(err) } }) //var base64Image = new Buffer(origin_buffer).toString('base64') var base64Image = origin_buffer.toString('base64') console.log(base64Image) var decodedImage = new Buffer(base64Image, 'base64') console.log(Buffer.compare(origin_buffer, decodedImage)) fs.writeFile('logo_decoded.png', decodedImage, function(err) { if(err) { console.log(err) } }) }) //把打印出来的base64Image,然后 data:image/png;base64,base64Image串,把data:image/png;base64,base64Image串拷贝到网页图片的url()的这个括号中,就可以查看到这张图片。
运行结果:
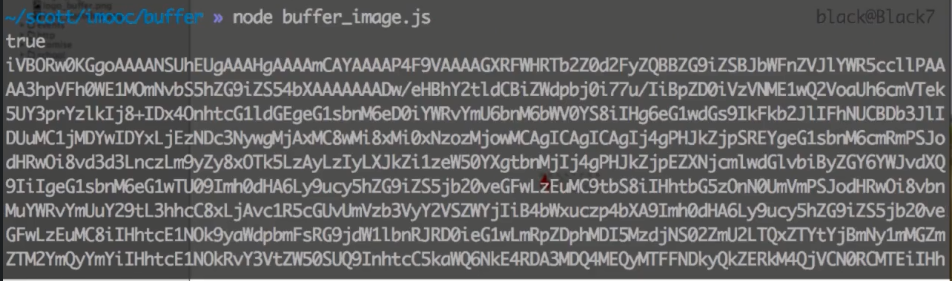
在当前目录下将会看到logo_buffer.png和logo_decoded.png两个文件。
当然,可以把输入的base64的串拷贝出来,然后在编辑器中编写如下所示:data:image/png;base64,输出的base64的串,可以把这整个串拷贝,如放到慕课网的背景url中,也能达到和慕课网本身图片一样的效果。
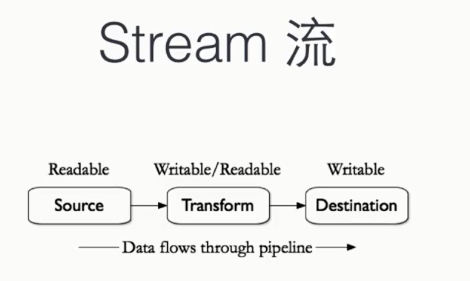
3.Stream流
stream_copy_logo.js
var fs = require('fs') var source = fs.readFileSync('logo.png') fs.writeFileSync('stream_copy_logo.png', source)
运行后,在当前目录下产生stream_copy_logo.png文件,且和logo.png一样。
stream_event.js
var fs = require('fs') var readStream = fs.createReadStream('stream_copy_logo.js') readStream.on('data', function(chunk) { console.log('data emits') console.log(Buffer.isBuffer(chunk)) console.log(chunk.toString('utf8')) }).on('readable', function() { console.log('data readable') }).on('end', function() { console.log('data ends') }).on('close', function() { console.log('data close') }).on('error', function(e) { console.log('data read error' + e) })
运行结果:

stream_event02.js,流的暂停和重启
var fs = require('fs') var readStream = fs.createReadStream('stream_copy_logo.js') var n = 0 readStream.on('data', function(chunk) { n++ console.log('data emits') console.log(Buffer.isBuffer(chunk)) //console.log(chunk.toString('utf8')) readStream.pause() console.log('data pause') setTimeout(function() { console.log('data pause end') readStream.resume() }, 3000) }).on('readable', function() { console.log('data readable') }).on('end', function() { console.log(n) console.log('data ends') }).on('close', function() { console.log('data close') }).on('error', function(e) { console.log('data read error' + e) })
运行结果:

stream_copy_logo2.js,重构复制文件的代码
var fs = require('fs') var readStream = fs.createReadStream('1.mp4') var writeStream = fs.createWriteStream('1-stream.mp4') readStream.on('data', function(chunk) { //数组还在缓存区 if(writeStream.write(chunk) === false) { console.log('still cached') readStream.pause() } }) readStream.on('end', function() { writeStream.end() }) //对于writeStream来说,有一个drain事件,表明数据已经消费完了(写到目标了) writeStream.on('drain', function() { console.log('data drains') //告诉readStream可以来读了 readStream.resume() })
运行结果:


Readable:可读流,负责读取外部的数据,并把数据缓存到内部的Buffer数组
Writable:可写流,负责消费数据,从可读流里获取到数据,然后对得到的数据块进行处理
Duplex:双工流,实现了Readable、Writable两个接口,如TcpSocket
Transform:转换流,也是双工的,可读可写,实现了Readable、Writable两个接口,但不保留数据
request_logo.js
var http = require('http') var fs = require('fs') var request = require('request') http.createServer(function(req, res){ // fs.readFile('logo.png', function(err, data) { // if(err) { // res.end('file not exist!') // }else { // res.writeHeader(200, {'Context-Type': 'text/html'}) // res.end(data) // } // }) //pipe方法会自动帮我们监听data和end事件,图片文件中每一小段数据都会源源不断地发送给客户端,除此以外它还可以自动控制后端压力,这样在客户端连接缓慢时,node可以将尽可能少的缓存放到内存里面,通过对内存空间的调度就能自动控制流量,从而避免目标被快速读取的流而淹没 //并且数据在pipe时,只有pipe链末端的目标流真正需要数据时,数据才会从源头被取出来。所以是被动消费。 //fs.createReadStream('logo.png').pipe(res) request('https://www.imooc.com/static/img/index/logo.png').pipe(res) }).listen(8090)
运行node request_logo.js后,在浏览器中输入http://localhost:8090,就能展示logo图片。
pipe_video.js
var fs = require('fs') fs.createReadStream('1.mp4').pipe(fs.createWriteStream('1-pipe.mp4'))
运行后就会在当前目录下新产生1-pipe.mp4,和1.mp4一模一样。
stream_read_write.js
var Readable = require('stream').Readable var Writable = require('stream').Writable var readStream = new Readable() var writStream = new Writable() readStream.push('I ') readStream.push('Love ') readStream.push('Imooc ') readStream.push(null) writStream._write = function(chunk, encode, cb) { console.log(chunk.toString()) cb() } readStream.pipe(writStream)
运行结果:

custom_stream.js
var stream = require('stream') var util = require('util') function ReadStream() { stream.Readable.call(this) } util.inherits(ReadStream, stream.Readable) ReadStream.prototype._read = function() { this.push('I ') this.push('Love ') this.push('Imooc ') this.push(null) } function WritStream() { stream.Writable.call(this) this._cached = new Buffer('') } util.inherits(WritStream, stream.Writable) WritStream.prototype._write = function(chunk, encode, cb) { console.log(chunk.toString()) cb() } function TransformStream() { stream.Transform.call(this) } util.inherits(TransformStream, stream.Transform) TransformStream.prototype._transform = function(chunk, encode, cb) { this.push(chunk) cb() } TransformStream.prototype._flush = function(cb) { this.push('Oh Yeah!') cb() } var rs = new ReadStream() var ws = new WritStream() var ts = new TransformStream() rs.pipe(ts).pipe(ws)
运行结果:

学习视频《进击Node.js基础(二)》。