类的深入学习
a. Python中一切事物都是对象
b. class Foo:
pass
obj = Foo()
# obj是对象,Foo类
# Foo类也是一个对象,type的对象
c. 类都是type类的对象 type(..)
“对象”都是以类的对象 类()
d. 类实际上是type类型的对象,所有的类都是Object的子类
创建类的方法[2种]
# 第一种:类实际上是type类型的对象,所有的类都是Object的子类
Foo = type('Foo', (object,), {'func': 'function'})
# 第二种:
class Foo:
def func(self):
print(123)
f = Foo()
f.func()
利用metaclass创建类: 必须继承type类,同时init必须传递4个参数过去
必须继承type类 ---代码有误---
class MyType(type): # the metaclass of a derived class must be a (non-strict) subclass of the metaclasses of all its bases
# 必须给出4个参数
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): # __init__() takes 1 positional argument but 4 were given
print('Mytype创建类对象')
def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs):
print('Mytype的call方法')
def __new__(self, *args, **kwargs):
print('Mytype的new方法')
class Foo(object, metaclass=MyType):
def func(self):
print(123)
# 创建对象后执行init方法
def __new__(self, *args, **kwargs):
print('Foo的new方法')
return '返回Foo的对象'
f = Foo() # 调用MyType的__init__方法,Foo是MyType的对象,Foo()会调用MyType的__call__方法
f.func() # Mytype创建类对象,这里是有MyType的
# 123
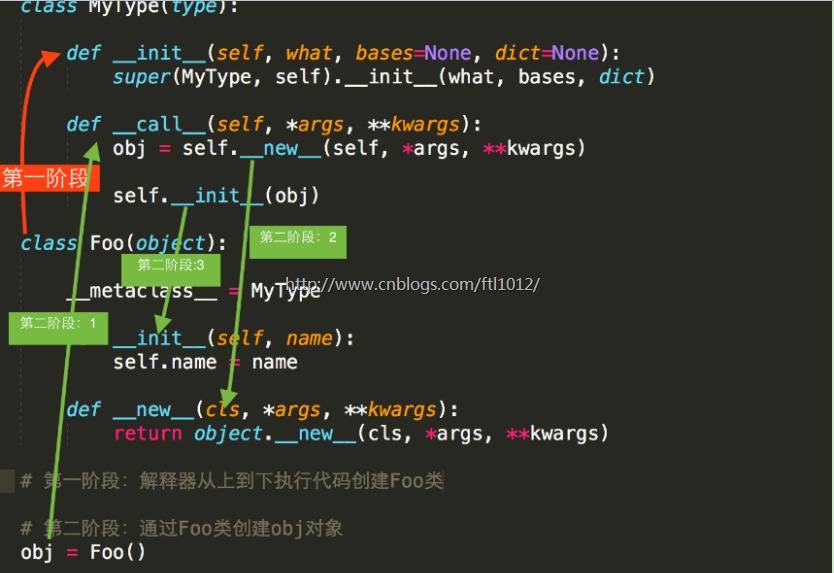
【转载】类的创建原理图:
异常处理
被动异常
try:
pass
except IndentationError as e:
pass
except ValueError as e: # 小的Exception放在Exception前面
pass
except Exception as e: # e是Exception的对象,封装了Exception信息
pass
else: # 正常代码正常,则执行else,否则执行else
pass
finally:
pass # 出错不出错,一定要执行的代码
主动触发异常: raise Exception("Sorry")
try:
raise Exception("Sorry")
except Exception as e:
print(e)
自定义异常:继承Exception类来实现
class HhH(Exception):
def __init__(self, msg):
self.message = msg
def __str__(self):
return self.message # 这里只需要返回就可以了,不能直接打印
try:
raise HhH('hhh, Wrong')
except HhH as e:
print(e)
断言assert
assert 比较的内容: 条件成立,则打印XXX,否则报错
一般用强制用户的服从,Java从1.2开始也添加了这个功能,但是一般实际中不用。Python源码中有用到
assert 1 < 5
print('hhh')
反射
1. 通过字符串操作对象的成员(方法,字段):
class Foo:
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def fun(self):
print('%s-%s' % (self.name, self.age))
obj = Foo('ftl', 23)
print(obj.name)
b = 'name'
print('obj.__dict__[b]:',obj.__dict__[b]) # 通过字典取值
print("getattr(obj, 'name'):",getattr(obj, 'name')) # 通过内置函数getattr取出值
fun = getattr(obj, 'fun')
fun()
setattr(obj, 'school', 'xupt')
print(hasattr(obj, 'school'))
print(delattr(obj, 'school'))
模块级别的反射:
class Foo():
NAME = 'ftl'
def hello(self):
print('hello')
print(getattr(Foo, 'NAME'))
hello = getattr(Foo(), 'hello') # 取到函数的内存地址
print(hello)
print(hello()) # 取到函数的对象
单例模式
class Foo:
__instance = None
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.age = age
self.name = name
@classmethod # 静态方法
def get_Instance(cls):
if cls.__instance:
return cls.__instance
else:
cls.__instance = Foo('hhh', 23)
return cls.__instance
def show(self):
print(self.age, self.name)
obj = Foo.get_Instance()
obj.show()
【更多学习】