Java数据结构之---Queue队列
队列(简称作队,Queue)也是一种特殊的线性表,队列的数据元素以及数据元素间的逻辑关系和线性表完全相同,其差别是线性表允许在任意位置插入和删除,而队列只允许在其一端进行插入操作在其另一端进行删除操作。
队列中允许进行插入操作的一端称为队尾,允许进行删除操作的一端称为队头。队列的插入操作通常称作入队列,队列的删除操作通常称作出队列。最简单的例子就是我们平时的排队,先进先出。
顺序队列的存储结构
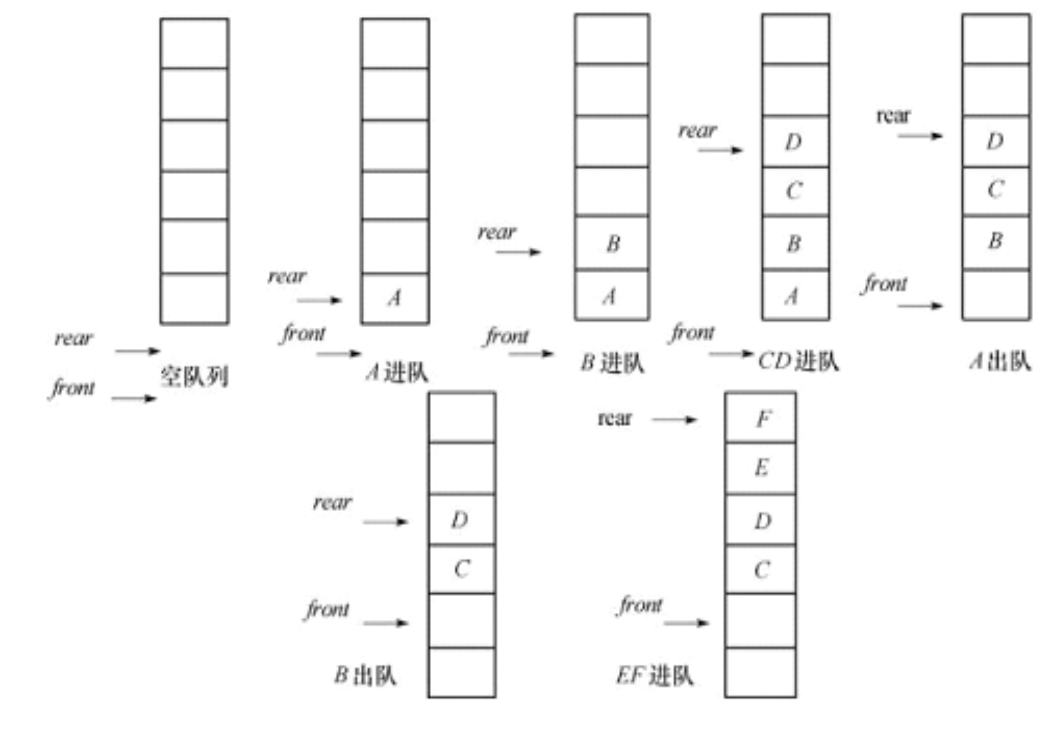
下图是一个有6个存储空间的顺序队列的动态示意图,图中front指示队头,rear指示队尾。
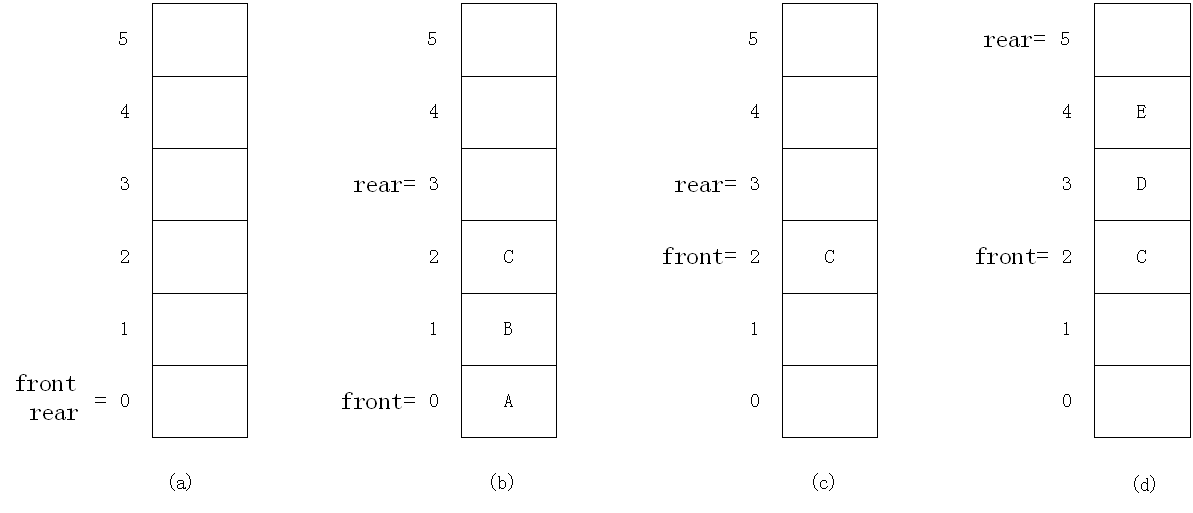
~顺序队列的假溢出现象
假溢出是由于队尾rear的值和队头front的值不能由所定义数组下界值自动转为数组上界值而产生的。因此,解决的方法是把顺序队列所使用的存储空间构造成一个逻辑上首尾相连的循环队列( Circular Queue)。
~解决方法
当rear和front达到maxSize-1后,再加1就自动到0。这样,就不会出现顺序队列数组的头部已空出许多存储空间,但队尾却因数组下标越界而引起溢出的假溢出问题。这里在代码里面会详细解释~
在操作完成后,该队列中会有两个空格没有数据元素保存,造成资源浪费,这就是假溢出现象。
//==========================
//使用自定义的queue接口

1 //队列接口 2 public interface Queue { 3 4 // 入队 5 public void append(Object obj) throws Exception; 6 7 // 出队 8 public Object delete() throws Exception; 9 10 // 获得对头元素 11 public Object getFront() throws Exception; 12 13 // 判断是否为空 14 public boolean isEmpty(); 15 16 }
//循环链表的具体实现
1 /* 2 * 循环顺序队列 3 */ 4 public class CircleSequenceQueue implements Queue { 5 6 static final int defaultsize = 10;// 默认队列的长度 7 int front; // 对头 8 int rear; // 队尾 9 int count;// 统计元素个数的计数器 10 int maxSize; // 队的最大长度 11 Object[] queue; // 队列,使用数组实现 12 13 // 默认构造 14 public CircleSequenceQueue() { 15 init(defaultsize); 16 } 17 18 public CircleSequenceQueue(int size) { 19 // 通过给定长度进行构造 20 init(size); 21 } 22 23 public void init(int size) { 24 maxSize = size; 25 front = rear = 0; 26 count = 0; 27 queue = new Object[size]; 28 } 29 30 @Override 31 public void append(Object obj) throws Exception { 32 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 33 if (count > 0 && front == rear) { 34 throw new Exception("队列已满"); 35 } 36 // 队尾插入数据 37 queue[rear] = obj; 38 // 通过这种方法让对标索引值不停的重复!!! 39 rear = (rear + 1) % maxSize; 40 count++; 41 } 42 43 @Override 44 public Object delete() throws Exception { 45 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 46 if (isEmpty()) { 47 throw new Exception("队列为空"); 48 } 49 // 去除对头的元素,同时修改对头的索引值 50 Object obj = queue[front]; 51 // 对头索引值,一样通过+1驱魔运算来实现循环索引效果 52 front = (front + 1) % maxSize; 53 count--; 54 return obj; 55 } 56 57 @Override 58 public Object getFront() throws Exception { 59 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 60 if (!isEmpty()) { 61 return queue[front]; 62 } else { 63 // 对为空返回null 64 return null; 65 } 66 } 67 68 @Override 69 public boolean isEmpty() { 70 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 71 return count == 0; 72 } 73 74 }
//得到循环链表后,对其进行应用,之类主要是模拟卖票窗口
· 实例:使用顺序循环队列和多线程实现一个排队买票的例子。
· 生产者(等候买票)
· 消费者 (买票离开)
//代码的分割线,使用生产者消费者模式进行设计,主要是使用同步机制
1 //卖票窗口 2 public class WindowQueue { 3 4 // 卖票的队列默认长度10 5 int maxSize = 10; 6 CircleSequenceQueue queue = new CircleSequenceQueue(maxSize); 7 // 用来统计卖票的数量,一天最多卖100张票? 8 int num = 0; 9 boolean isAlive = true; // 判断是否继续卖票 10 11 // 排队买票,使用同步机制 12 public synchronized void producer() throws Exception { 13 // count队列中的元素个数,如果该值小于maxSize则可以买票 14 if (queue.count < maxSize) { 15 queue.append(num++); // 等待买票的数量+1 16 System.out.println("第" + num + "个客户排队等待买票"); 17 this.notifyAll(); // 通知卖票线程可以卖票了 18 } 19 // 如果满了 20 else { 21 try { 22 23 System.out.println("队列已满...请等待"); 24 this.wait(); // 队列满时,排队买票线程等待,其实等待卖票队伍里面离开一个人后来唤醒自己 25 26 } catch (Exception e) { 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 32 // 排队卖票,使用同步机制 33 public synchronized void consumer() throws Exception { 34 // count队列中的元素个数,如果该值大于0,则说明有票可以继续卖票 35 if (queue.count > 0) { 36 37 Object obj = queue.delete(); 38 // 第几个人买到票了 39 int temp = Integer.parseInt(obj.toString()); 40 System.out.println("第" + (temp + 1) + "个客户排队买到票离开队列"); 41 // 如果当前队列为空,并且卖出票的数量的大于等于100说明卖票要结束 42 if (queue.isEmpty() && this.num >= 100) { 43 this.isAlive = false; 44 } 45 // 排队队伍离开一个人,可以进来一个人进行买票了。 46 this.notifyAll(); // 通知买票线程可以买了,唤醒买票线程 47 } 48 // 如果满了 49 else { 50 try { 51 52 System.out.println("队列已空...请进入队伍准备买票"); 53 this.wait();// 队列空时,排队卖票线程等待,其实等待买票队伍里面进来一个人后买票来唤醒自己 54 55 } catch (Exception e) { 56 e.printStackTrace(); 57 } 58 } 59 } 60 }
//下面的两个类是生产者与消费者的具体实现,实现runnable接口
1 //买票者 2 3 public class Producer implements Runnable { 4 // 买票窗口 5 WindowQueue queue; 6 7 // 保证和消费者使用同一个对象 8 public Producer(WindowQueue queue) { 9 this.queue = queue; 10 } 11 12 @Override 13 public void run() { 14 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 15 // 16 while (queue.num < 100) { 17 try { 18 //执行买票,消费者 19 queue.producer(); 20 } catch (Exception e) { 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 } 23 } 24 } 25 }
1 //卖票者 2 public class Consumer implements Runnable { 3 WindowQueue queue; 4 5 // 保证卖票与买票同步 6 public Consumer(WindowQueue queue) { 7 this.queue = queue; 8 } 9 10 @Override 11 public void run() { 12 // 判断是否可以继续卖票 13 while (queue.isAlive) { 14 try { 15 // 卖票 16 queue.consumer(); 17 18 } catch (Exception e) { 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 }
//测试。。。。。

1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 3 /* 4 * CircleSequenceQueue queue = new CircleSequenceQueue(); 5 * queue.append("a"); queue.append("b"); queue.append("c"); 6 * queue.append("d"); queue.append("e"); 7 * 8 * while (!queue.isEmpty()) { System.out.print(queue.delete() + " "); } 9 */ 10 11 // 卖票与买票模拟,使用同一个窗口对象 12 WindowQueue queue = new WindowQueue(); 13 // 生产者 14 Producer P = new Producer(queue); 15 // 消费者 16 Consumer c = new Consumer(queue); 17 18 // 排队买票线程 19 Thread pThread = new Thread(P); 20 // 买票线程 21 Thread cThread = new Thread(c); 22 23 pThread.start(); // 开始排队买票 24 cThread.start(); // 卖票 25 } 26 }
