一,工具简介
1.1 ansible简介
批量管理服务器工具
无需部署agent,通过ssh进行管理
中小型公司常用的自动化运维工具
1.2 jenkins简介
可视化运维(主要用在可视化部署)
持续构建,可以和git,snv结合
可结合ssh实现可视化运维
可结合ansible实现可视化运维
1.3 环境说明
Centos7.5 (yum -y install net-tools vim)
关闭防火墙(systemctl stop firewalld关闭防火墙,systemctl disable firewalld关闭防火墙开机启动)
二,Ansible服务的部署和安装
2.1 ansible安装 ——————通过yum源的方式安装ansible
yum -y install epel-release
yum -y install ansible
2.2 生产环境ansible管理服务器ssh登录安全策略
2.2.1 生产环境ssh登录策略
运维修改时提前备份是好习惯 cp /etc/ssh/shhd_config{,.bak}
[root@gaowei ~]# cat -n /etc/ssh/sshd_config.bak | sed -n '17p;38p;43p;47p;65p;79p;115p' 17 #Port 22 #修改ssh连接端口 38 #PermitRootLogin yes #是否允许root账号远程登陆 43 #PubkeyAuthentication yes #是否开启公钥连接认证 47 AuthorizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys #公钥文件的放置位置 65 PasswordAuthentication yes #是否开启密码验证登陆 79 GSSAPIAuthentication yes #是否关闭GSSAPI认证 115 #UseDNS yes #是否关闭DNS反向解析 [root@gaowei ~]# cat -n /etc/ssh/sshd_config | sed -n '17p;38p;43p;47p;65p;79p;115p' 17 Port 22221 #工作中需要设定到1万以上的端口,避免被扫描出来。 38 PermitRootLogin yes #如果不是超大规模的服务器,为了方便我们可以暂时开启root远程登录 43 PubkeyAuthentication yes #开启公钥认证模式 47 AuthorizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys #公钥放置位置 65 PasswordAuthentication no #为了安全我们关闭服务器的密码认证方式 79 GSSAPIAuthentication no #关闭GSSAPI认证,极大提高ssh连接速度 115 UseDNS no #关闭DNS反向解析,极大提高ssh连接速度
2.2.2 设置xshell私钥登录linux
#查看服务器端IP [root@ansible .ssh]# hostname -I 192.168.200.134 #在Linux服务器端生成rsa密钥对 [root@ansible ~]# ssh-keygen #一直回车 Generating public/private rsa key pair. Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa): Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): Enter same passphrase again: Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa. Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub. The key fingerprint is: SHA256:royhAEKx9bhe4jLZ3SzfZ/yvhkzPgToDIx+1gSxoOLM root@www The keys randomart image is: +---[RSA 2048]----+ | . . | | + o | | o..... . | |.+ o.. o o | |o =o .. S o . | |oE= +.o= . o . | |.+ +.ooo= = + . | | .o. +oo.+ * + | | . . o. .= ooo. | +----[SHA256]-----+ #将生成的公钥导入到服务器端的~/.ssh/authorized_keys文件里 [root@ansible ~]# cd .ssh/ [root@ansible .ssh]# ls id_rsa id_rsa.pub [root@ansible .ssh]# cat id_rsa.pub > authorized_keys [root@ansible .ssh]# chmod 600 authorized_keys #权限必须600否则不生效 [root@ansible .ssh]# cat authorized_keys ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQDS7U4vgjCpWrMFwnWjUlrebldvPw5NNQpnyGT/1cTsyI6ryPm19J+IQ2wNn67BpYz0NKyLjq/hYlSxlQmD7xHwNM5KQirUYPgwPhhDqGuNE+UrBZ2lUkknt358YWGpEC+TUPy/MLNbnIepPpZr0y0qyXmtp7KpeXJwLeKLzZLpHnzA8Vr3A7w/jNaDnQJmKYvDvD0Q6O54CVkkSdxaYPAT1hVfX1pKz0dSNQbJpl5ZJXigQo26M+7qYXeUBxI5Guaapl6uT5sySzTBwwd9Yt49NKE/kIivClegVfHPGF4iSqfCiCd2BTJGTuCVBS2j4lhrjTLyWRO8po7BM4yImRGf root@www #将私钥文件id_rsa复制一份改名为rd_rsa_root并导出到宿主机桌面上 [root@ansible .ssh]# ls authorized_keys id_rsa id_rsa.pub [root@ansible .ssh]# cp id_rsa id_rsa_root [root@ansible .ssh]# ls authorized_keys id_rsa.pub id_rsa id_rsa_root
查看导入到桌面上的私钥文件
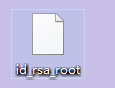
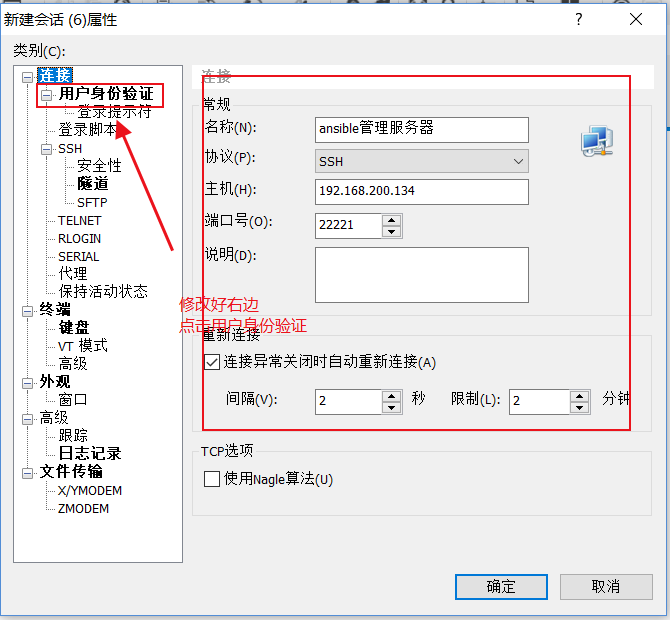
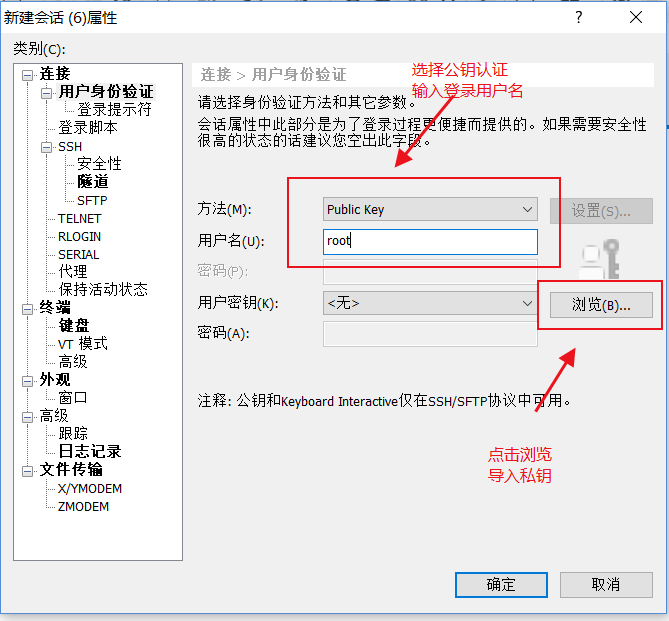

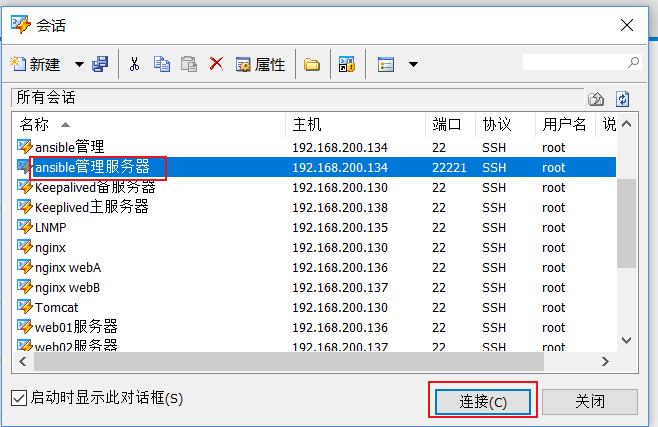
最后 xshell显示登陆成功!
2.2.3 用户权限策略
在生产环境中,如果遇到禁止root用户远程登录系统,授权仅普通用户登陆系统,那么需要管理员权限执行sudo提权即可,避免root用户之间登陆。
1 #创建一个普通用户yunjisuan 2 [root@ansible ~]# useradd yunjisuan 3 [root@ansible ~]# echo "123123" | passwd --stdin yunjisuan 4 更改用户 yunjisuan 的密码 。 5 passwd:所有的身份验证令牌已经成功更新。 6 #以root账号授权普通用户yunjisuan所有权限并免输入密码 7 [root@ansible ~]# sed -n '93p' /etc/sudoers 8 yunjisuan ALL=(ALL) ALL 9 #切换到yunjisuan用户测试提权 10 [root@ansible ~]# su - yunjisuan 11 [yunjisuan@ansible ~]$ sudo -l 12 我们信任您已经从系统管理员那里了解了日常注意事项。 13 总结起来无外乎这三点: 14 #1) 尊重别人的隐私。 15 #2) 输入前要先考虑(后果和风险)。 16 #3) 权力越大,责任越大。 17 [sudo] yunjisuan 的密码: 18 匹配 %2$s 上 %1$s 的默认条目: 19 !visiblepw, always_set_home, match_group_by_gid, env_reset, env_keep="COLORS DISPLAY HOSTNAME HISTSIZE KDEDIR LS_COLORS", 20 env_keep+="MAIL PS1 PS2 QTDIR USERNAME LANG LC_ADDRESS LC_CTYPE", env_keep+="LC_COLLATE LC_IDENTIFICATION LC_MEASUREMENT LC_MESSAGES", 21 env_keep+="LC_MONETARY LC_NAME LC_NUMERIC LC_PAPER LC_TELEPHONE", env_keep+="LC_TIME LC_ALL LANGUAGE LINGUAS _XKB_CHARSET XAUTHORITY", 22 secure_path=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin 23 用户 yunjisuan 可以在 ansible 上运行以下命令: 24 (ALL) ALL 25 #测试提权 26 [yunjisuan@ansible ~]$ ls /root 27 ls: 无法打开目录/root: 权限不够 28 [yunjisuan@ansible ~]$ sudo ls /root 29 anaconda-ks.cfg
2.2.4 配置xshell远程密钥登录服务器端普通用户
1 #给yunjisuan普通用户创建公钥认证。注意权限。权限过大,公钥验证会失败 2 [root@ansible ~]# mkdir -p /home/yunjisuan/.ssh 3 [root@ansible ~]# chmod 700 /home/yunjisuan/.ssh 4 [root@ansible ~]# chown yunjisuan.yunjisuan /home/yunjisuan/.ssh 5 [root@ansible ~]# cp ~/.ssh/authorized_keys /home/yunjisuan/.ssh/ 6 [root@ansible ~]# chmod 600 /home/yunjisuan/.ssh/authorized_keys 7 [root@ansible ~]# chown yunjisuan.yunjisuan /home/yunjisuan/.ssh/authorized_keys
然后我们xshell远程登录普通用户到ansible服务器端,xshell还是用刚才导入的哪个私钥文件即可,方法
和上面相同,只是用户名是yunjisuan,登录成功后,我们关闭ansible管理服务器端的root账号ssh远程登 录即可。
1 #在生产环境我们一般是要禁止服务器root账号远程登录功能的(一旦关闭,密钥和密码登陆方式都不能再登陆) 2 #如果我们想用root账号进行操作,那么远程密钥连接普通用户在切换成root账号即可 3 yunjisuan@ansible ~]$ sudo su - 4 [sudo] yunjisuan 的密码: 5 上一次登录:日 9月 9 21:01:31 CST 2018从 192.168.200.1pts/1 上 6 [root@ansible ~]# 7 #关闭Ansible管理服务器的root账号SSH远程登录功能 8 [root@ansible ~]# sed -n '38p' /etc/ssh/sshd_config 9 PermitRootLogin no 10 #重启动sshd服务 11 [root@ansible ~]# systemctl restart sshd
2.2.5 配置Ansible管理服务器sudo审计日志
1 #开启sudo日志 2 [root@ansible ~]# echo "local2.debug /var/log/sudo.log" >> /etc/rsyslog.conf 3 [root@ansible ~]# echo "Defaults logfile=/var/log/sudo.log" >> /etc/sudoers 4 [root@ansible ~]# systemctl restart rsyslog 5 #测试sudo日志记录 6 [root@ansible ~]# exit 7 登出 8 [yunjisuan@ansible ~]$ sudo su - 9 [sudo] yunjisuan 的密码: 10 上一次登录:日 9月 9 21:40:11 CST 2018pts/0 上 11 #查看/var/log/sudo.log日志 12 [root@ansible ~]# cat /var/log/sudo.log 13 Sep 9 21:49:12 : yunjisuan : TTY=pts/0 ; PWD=/home/yunjisuan ; USER=root ; 14 COMMAND=/bin/su -
2.2.6 配置主机清单
/etc/ansible/hosts文件中可以定义被管理主机,Ansible通过读取/etc/ansible/hosts文件内定义的主机清单批量做一些操作。
1 [root@ansible ~]# cat /etc/ansible/hosts 2 [nginx] 3 Web01 ansible_ssh_host=192.168.200.140 4 Web02 ansible_ssh_host=192.168.200.141 5 说明: 6 ansible_ssh_host:被管理主机IP 7 ansible_ssh_user:被管理主机用户名 8 ansible_ssh_pass:被管理主机用户的登陆密码 9 ansible_sudo_pass:被管理主机用户sudo时的密码
2.2.7 设置ssh免密码登录
为了避免Ansible下发指令时需要输入被管理主机的密码,可以通过证书签名达到SSH无密码登陆。使用ssh-keygen产生一对密钥,并通过ssh-copy-id命令来发送生成的公钥。
1 [root@ansible ~]# ls ~/.ssh/ 2 authorized_keys id_rsa id_rsa.pub 3 [root@ansible ~]# ssh-copy-id 192.168.200.184 4 [root@ansible ~]# ssh-copy-id 192.168.200.185
当然,我们也可以在控制端主机的hosts文件里直接写入连接方式,用户,密码也能下发指令。但是生产环境不建议这么做。因为这样明文密码容易泄露,另外如果被控制主机修改了密码,这里也需要一起更改,不便于管理。
2.2.8 Ansible服务器简单的综合安全管理策略
1 #禁止非root用户查看Ansible管理服务器端/etc/hosts文件 2 [root@ansible ~]# ll /etc/hosts 3 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 180 9月 9 00:38 /etc/hosts 4 [root@ansible ~]# chmod 600 /etc/hosts 5 #禁止非root用户查看Ansible的主机清单配置文件 6 [root@ansible ~]# ll /etc/ansible/hosts 7 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 87 9月 9 21:59 /etc/ansible/hosts 8 [root@ansible ~]# chmod 600 /etc/ansible/hosts
到此,我们Ansible服务器简单安全策略就算完成!
三,Ansible的基础应用
Ansible可以使用命令行的方式进行自动化管理。命令的基本语法如下所示:
1 ansible <被操控的主机或主机组或all> [-m 模块名] [-a 具体命令] 2 说明: 3 主机组名====> /etc/ansible/hosts里设定的nginx,apache,web 4 主机名====> Web01,Web02 5 all ====>/etc/ansible/hosts里设定的所有主机 6 模块名====> command,cron,shell,file等
3.1 ping模块
Ansible中使用ping模块来检测指定主机的连通性
1 #测试单主机 2 [root@ansible ~]# ansible Web01 -m ping 3 Web01 | SUCCESS => { 4 "changed": false, 5 "ping": "pong" 6 } 7 #测试单主机 8 [root@ansible ~]# ansible Web02 -m ping 9 Web02 | SUCCESS => { 10 "changed": false, 11 "ping": "pong" 12 } 13 #测试主机组 14 [root@ansible ~]# ansible nginx -m ping 15 Web02 | SUCCESS => { 16 "changed": false, 17 "ping": "pong" 18 } 19 Web01 | SUCCESS => { 20 "changed": false, 21 "ping": "pong" 22 } 23 #测试所有的被管理主机 24 [root@ansible ~]# ansible all -m ping 25 Web02 | SUCCESS => { 26 "changed": false, 27 "ping": "pong" 28 } 29 Web01 | SUCCESS => { 30 "changed": false, 31 "ping": "pong" 32 }
3.2 shell模块(command模块)
由于此模块在远程主机执行命令,不支持管道符和重定向等复杂命令,可完全呗shell模块代替,所以我们只讲shell模块。
1 #在Web01上创建用户yunjisuan,并非交互方式设定密码 2 [root@ansible ~]# ansible Web01 -m shell -a 'useradd yunjisuan' 3 Web01 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 4 [root@ansible ~]# ansible Web01 -m shell -a 'echo 123123 | passwd --stdin yunjisuan' 5 Web01 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 6 更改用户 yunjisuan 的密码 。 7 passwd:所有的身份验证令牌已经成功更新。 8 [root@ansible ~]# ansible Web01 -m shell -a 'id yunjisuan' 9 Web01 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 10 uid=1000(yunjisuan) gid=1000(yunjisuan) 组=1000(yunjisuan) 11 [root@ansible ~]# ansible Web01 -m shell -a 'tail -1 /etc/shadow' 12 Web01 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 13 yunjisuan:$6$4y7c1tkV$oPZW0psDdAzJp5RomBrOpSlTuvsdQ/5JaBYHU.LOPsYQ0o7EpPFRMuh/X9ruwcmBcZbN.l/glBTfDKm//jJP60:17782:0:99999:7::: 14 #在所有被管理的主机的/etc/hosts文件里添加Ansible管理服务器的IP地址映射 15 [root@ansible ~]# ansible all -m shell -a 'echo "ansible 192.168.200.134" >> /etc/hosts' 16 Web02 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 17 Web01 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 18 [root@ansible ~]# ansible all -m shell -a 'tail -1 /etc/hosts' 19 Web01 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 20 ansible 192.168.200.143 21 Web02 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 22 ansible 192.168.200.143
3.3 cron模块
Ansible中的cron模块用于定义任务计划。
crontab时间周期:分钟,小时,日期,月份,周
crontab任务:job 指明运行的命令是什么
crontab任务描述:name 定时任务描述(定时任务清楚的依据)
crontab任务的用户身份:user 指定定时任务以哪个用户身份执行
state状态:present 表示添加 (省略状态时默认使用);adsent 表示移除
1 #添加定时任务计划,在所有被管理的主机里每十分钟输出hello字符串,定时任务描述为test cron job 2 [root@ansible ~]# ansible all -m cron -a 'minute="*/10" job="/bin/echo hello" name="test cron job"' 3 Web02 | SUCCESS => { 4 "changed": true, 5 "envs": [], 6 "jobs": [ 7 "test cron job" 8 ] 9 } 10 Web01 | SUCCESS => { 11 "changed": true, 12 "envs": [], 13 "jobs": [ 14 "test cron job" 15 ] 16 } 17 [root@ansible ~]# ansible all -m shell -a 'crontab -l' 18 Web01 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 19 #Ansible: test cron job 20 */10 * * * * /bin/echo hello 21 Web02 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 22 #Ansible: test cron job 23 */10 * * * * /bin/echo hello 24 #删除描述为test cron job的定时任务 25 [root@ansible ~]# ansible all -m cron -a 'minute="*/10" job="/bin/echo hello" name="test cron job" state=absent' 26 Web02 | SUCCESS => { 27 "changed": true, 28 "envs": [], 29 "jobs": [] 30 } 31 Web01 | SUCCESS => { 32 "changed": true, 33 "envs": [], 34 "jobs": [] 35 } 36 [root@ansible ~]# ansible all -m shell -a 'crontab -l' 37 Web02 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 38 Web01 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 39 #给Web01服务器上的普通用户yunjisuan添加一个定时任务 40 [root@ansible ~]# ansible Web01 -m shell -a 'id yunjisuan' 41 Web01 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 42 uid=1000(yunjisuan) gid=1000(yunjisuan) 组=1000(yunjisuan) 43 [root@ansible ~]# ansible Web01 -m cron -a 'minute="*/10" job="/bin/echo hello" name="yunjisuan cron job" user="yunjisuan"' 44 Web01 | SUCCESS => { 45 "changed": true, 46 "envs": [], 47 "jobs": [ 48 "yunjisuan cron job" 49 ] 50 } 51 [root@ansible ~]# ansible Web01 -m shell -a 'crontab -u yunjisuan -l' 52 Web01 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 53 #Ansible: yunjisuan cron job 54 */10 * * * * /bin/echo hello 55 [root@ansible ~]# ansible Web01 -m cron -a 'minute="*/10" job="/bin/echo hello" name="yunjisuan cron job" user="yunjisuan" state="absent"' 56 Web01 | SUCCESS => { 57 "changed": true, 58 "envs": [], 59 "jobs": [] 60 } 61 [root@ansible ~]# ansible Web01 -m shell -a 'crontab -u yunjisuan -l' 62 Web01 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
3.4 copy模块
Ansible中的copy模块用于实现文件复制和批量下发文件。其中使用src来定义本地源文件路径;使用dest定义被管理主机文件路径;使用content则是使用指定信息内容来生成目标文件。
1 #将本地的/etc/hosts文件拷贝到所有被管理的主机的/etc/hosts路径下覆盖同名文件,并指定属主和权限,若拷贝的文件与目标文件内容不同,则备份目标文件再覆盖。 2 [root@ansible ~]# ansible all -m shell -a 'tail -1 /etc/hosts' 3 Web01 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 4 ansible 192.168.200.134 5 Web02 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 6 ansible 192.168.200.134 7 [root@ansible ~]# echo "web01 192.168.200.140" >> /etc/hosts 8 [root@ansible ~]# tail -1 /etc/hosts 9 web01 192.168.200.140 10 [root@ansible ~]# ansible all -m copy -a 'src=/etc/hosts dest=/etc/hosts owner=root mode=640 backup=yes' 11 Web01 | SUCCESS => { 12 "backup_file": "/etc/hosts.13083.2018-09-09@00:38:35~", 13 "changed": true, 14 "checksum": "80244bc6f9638a3505aae1a2bcf2228e69a00420", 15 "dest": "/etc/hosts", 16 "gid": 0, 17 "group": "root", 18 "md5sum": "de48f3cf45d11215fa7cfd0d558be954", 19 "mode": "0640", 20 "owner": "root", 21 "size": 180, 22 "src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1536424715.44-39054260112988/source", 23 "state": "file", 24 "uid": 0 25 } 26 Web02 | SUCCESS => { 27 "backup_file": "/etc/hosts.12643.2018-09-09@00:38:36~", 28 "changed": true, 29 "checksum": "80244bc6f9638a3505aae1a2bcf2228e69a00420", 30 "dest": "/etc/hosts", 31 "gid": 0, 32 "group": "root", 33 "md5sum": "de48f3cf45d11215fa7cfd0d558be954", 34 "mode": "0640", 35 "owner": "root", 36 "size": 180, 37 "src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1536424715.45-15307684711466/source", 38 "state": "file", 39 "uid": 0 40 } 41 [root@ansible ~]# ansible all -m shell -a 'tail -1 /etc/hosts' 42 Web02 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 43 web01 192.168.200.140 44 Web01 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 45 web01 192.168.200.140 46 [root@ansible ~]# ansible all -m shell -a 'ls /etc/hosts*' 47 Web01 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 48 /etc/hosts 49 /etc/hosts.13083.2018-09-09@00:38:35~ #这就是备份的文件 50 /etc/hosts.allow 51 /etc/hosts.deny 52 Web02 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 53 /etc/hosts 54 /etc/hosts.12643.2018-09-09@00:38:36~ #这就是备份的文件 55 /etc/hosts.allow 56 /etc/hosts.deny 57 #将本地/tmp/test.sh的脚本复制到远程主机上并远程激活 58 [root@ansible ~]# cat /tmp/test.sh 59 #!/bin/bash 60 echo "welcome to yunjisuan" 61 [root@ansible ~]# ansible all -m copy -a 'src=/tmp/test.sh dest=/tmp owner=root mode=500' 62 Web01 | SUCCESS => { 63 "changed": true, 64 "checksum": "70ae837e7367f5d4de9a3197709639ae14743000", 65 "dest": "/tmp/test.sh", 66 "gid": 0, 67 "group": "root", 68 "md5sum": "5ff4338de7d9ff0ded9fa3e0ecd15bab", 69 "mode": "0500", 70 "owner": "root", 71 "size": 41, 72 "src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1536425049.22-149074464676784/source", 73 "state": "file", 74 "uid": 0 75 } 76 Web02 | SUCCESS => { 77 "changed": true, 78 "checksum": "70ae837e7367f5d4de9a3197709639ae14743000", 79 "dest": "/tmp/test.sh", 80 "gid": 0, 81 "group": "root", 82 "md5sum": "5ff4338de7d9ff0ded9fa3e0ecd15bab", 83 "mode": "0500", 84 "owner": "root", 85 "size": 41, 86 "src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1536425049.23-32532320097185/source", 87 "state": "file", 88 "uid": 0 89 } 90 [root@ansible ~]# ansible all -m shell -a '/tmp/test.sh' 91 Web01 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 92 welcome to yunjisuan 93 Web02 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 94 welcome to yunjisuan
3.5 script模块
Ansible中的script模块可以将本地脚本复制到被管理主机的内存中并运行,不会在被管理主机中留下脚本文件。
1 #编写一个脚本,然后通过ansible的script模块远程向被管理主机执行此脚本 2 [root@ansible ~]# echo 'echo "1111" >> /tmp/test' >> /tmp/test.sh 3 [root@ansible ~]# cat /tmp/test.sh 4 echo "1111" >> /tmp/test 5 [root@ansible ~]# ansible all -m script -a '/tmp/test.sh' 6 Web01 | SUCCESS => { 7 "changed": true, 8 "rc": 0, 9 "stderr": "Shared connection to 192.168.200.184 closed. ", 10 "stderr_lines": [ 11 "Shared connection to 192.168.200.184 closed." 12 ], 13 "stdout": "", 14 "stdout_lines": [] 15 } 16 Web02 | SUCCESS => { 17 "changed": true, 18 "rc": 0, 19 "stderr": "Shared connection to 192.168.200.185 closed. ", 20 "stderr_lines": [ 21 "Shared connection to 192.168.200.185 closed." 22 ], 23 "stdout": "", 24 "stdout_lines": [] 25 } 26 [root@ansible ~]# ansible all -m shell -a 'cat /tmp/test' 27 Web02 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 28 1111 29 Web01 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 30 1111
3.6 yum模块
利用yum模块安装软件包,虽然能被shell模块替代
但是用yum模块更显专业一些
软件包名:name:指定软件包的名字
state状态:present:安装软件包(默认)
absent:卸载软件包
1 #安装nmap软件包 2 [root@ansible ~]# ansible all -m yum -a 'name=nmap' 3 #卸载nmap软件包 4 [root@ansible ~]# ansible all -m yum -a 'name=nmap state=absent'
3.7 service模块
服务名称:name:指定服务名字
state状态:started:启动服务
stopped:停止服务
restarted:重启服务
reloaded:平滑重启
ensbled开机自启动:true:设置开机自启动
false:设置开机不启动
1 #启动firewalld并设置开机自启动 2 [root@ansible ~]# ansible Web01 -m service -a 'name=firewalld state=started enabled=true' 3 #关闭firewalld并设置开机不启动 4 [root@ansible ~]# ansible Web01 -m service -a 'name=firewalld state=stopped enabled=false'
3.8 user模块
用户管理模块,管理用户账号
指定用户名:name:指定操作的用户的名字
用户描述:comment:指定用户的描述信息
createhome:是否创建家目录
uid:指定用户的uid号
groups:指定用户组
password:指定用户密码
update_password:更新用户密码
shell指定用户的登陆方式
/bin/bash :能登陆系统
/sbin/nologin:不能登陆系统
home:指定用户的家目录路径
stste状态:
present:创建用户
absent:删除用户
remove:当指定stat=absent时,确认是否删除用户家目录
true
false
利用ansible的user模块状态用户时要注意在password参数的后边添加密文,否则不能登陆用户
通过Python的pip程序安装passlib即可为密码加密
1 #安装Python2的pip工具,并通过pip工具安装Python的加密模块来给密码加密 2 [root@ansible ~]# yum -y install epel-release 3 [root@ansible ~]# yum -y install python2-pip 4 [root@ansible ~]# pip install passlib 5 #生成密文密码 6 [root@ansible ~]# python -c "from passlib.hash import sha512_crypt;import getpass;print sha512_crypt.encrypt(getpass.getpass())" 7 Password: #输入你想要加密的密码 8 $6$rounds=656000$Tw15COd8DLh/VS94$Mcmz/8CcjBKiEl0mYHcOQQCxEA5mz66EcGH2qXVk6o.Sm7FsRS.DsDVy6ET8iI6jDa045I94slZqWFwyYnRSW1 #加密后的密码 9 #在Web02上创建yunjisuan用户 10 [root@ansible ~]# ansible Web02 -m user -a 'name=yunjisuan comment="welcom to yunjisuan" uid=1066 groups=wheel password=$6$rounds=656000$Tw15COd8DLh/VS94$Mcmz/8CcjBKiEl0mYHcOQQCxEA5mz66EcGH2qXVk6o.Sm7FsRS.DsDVy6ET8iI6jDa045I94slZqWFwyYnRSW1 shell=/bin/bash' home=/home/yunjisuan' 11 [root@ansible ~]# ansible Web02 -m shell -a 'tail -1 /etc/shadow' 12 Web02 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 13 yunjisuan:$6$rounds=656000$Tw15COd8DLh/VS94$Mcmz/8CcjBKiEl0mYHcOQQCxEA5mz66EcGH2qXVk6o.Sm7FsRS.DsDVy6ET8iI6jDa045I94slZqWFwyYnRSW1:17783:0:99999:7::: #终于密文了
3.9 setup模块
Ansible中使用setup模块收集,查看被管理主机的facts(facts是Ansible采集被管理主机设备信息的一个功能)。每个被管理主机在接收并运行管理命令之前,都会将自己的相关信息(操作系统版本,IP地址等)发送给控制主机
1 #查看远程主机的facts信息 2 [root@ansible ~]# ansible Web01 -m setup | head 3 Web01 | SUCCESS => { 4 "ansible_facts": { 5 "ansible_all_ipv4_addresses": [ 6 "192.168.200.184" 7 ], 8 "ansible_all_ipv6_addresses": [ 9 "fe80::20c:29ff:fe77:16ad" 10 ], 11 "ansible_apparmor": { 12 "status": "disabled"