问题描述:
(1)建堆:将数组A[1..n]变成一个最大堆。(课本6.3)
(2)堆排序:将一个堆中的元素按递减排序输出。
(3)用插入方法建堆:堆大小从1到n每次插入一个元素到堆中,直到n个元素入堆。(课本p83,6-1)
public class heap_Tools { //将一个元素插入堆中 public static void insert(List<Integer> heap,int value){ if(heap.size() == 0){ //0下标放置null heap.add(0, null); heap.add(1,value); }else { heap.add(value); heapUp(heap,heap.size()-1); } } //插入后向上调整位置,转变为大顶堆 public static void heapUp(List<Integer> heap,int index){ if(index >1){ int parent = index/2; if(heap.get(parent) < heap.get(index)){ swap(heap, parent, index); heapUp(heap, parent); } } } //对大顶堆排序 public static List<Integer> sort(List<Integer> heap){ for(int i = heap.size()-1;i>0;i--){ swap(heap, 1,i ); adjust(heap, 1, i-1);; } return heap; } //生成并输出一个大顶堆 public static List<Integer> adjust(List<Integer> heap){ for(int i =heap.size()/2;i>0;i--){ adjust(heap,i,heap.size()-1); } System.out.println("将数组转化为最大堆输出:"); print_heap(heap); return heap; } public static void adjust(List<Integer> heap,int index,int n){ int child = index*2; if((child+1)<=n&&heap.get(child)<heap.get(child+1)){ //判断如果左孩子<右孩子 child +=1; } if(child<n&&heap.get(index)<heap.get(child)){ swap(heap,index,child); } if(child<=n/2){ adjust(heap, child, n); //交换后,以child为根的子树不一定满足大顶堆定义,递推调整 } } //交换List中的两个值 public static void swap(List<Integer> heap,int a,int b) { int temp; temp = heap.get(a); heap.set(a, heap.get(b)); heap.set(b, temp); } public static void print_heap(List<Integer> heap){ int floors = 0; for(int i = 1;i<heap.size();i++){ System.out.print(heap.get(i)+" "); if(i == (2<<floors)-1){ floors++; System.out.print(" "); } } } }
二:下沉法获得最大堆
public class Max_heap { public static void main(String[] args){ //下沉法获得最大堆 int[] A = {1,2,5,10,3,7,11,15,17,20,10,9,5,8,6}; List<Integer> array = new ArrayList<Integer>(); array.add(0, null); for(int i = 0; i<A.length;i++){ array.add(A[i]); } heap_Tools.adjust(array); } }

三:将堆按照从大到小输出
public class heap_sort { public static void main(String[] args){ //下沉法获得最大堆 int[] A = {1,2,5,10,3,7,11,15,17,20,10,9,5,8,6}; List<Integer> array = new ArrayList<Integer>(); array.add(0, null); for(int i = 0; i<A.length;i++){ array.add(A[i]); } List<Integer> heap = heap_Tools.adjust(array); heap = heap_Tools.sort(heap); System.out.println("将堆中元素按递减顺序输出:"); for(int i = heap.size()-1;i>0;i--){ System.out.print(heap.get(i)+" "); } } }

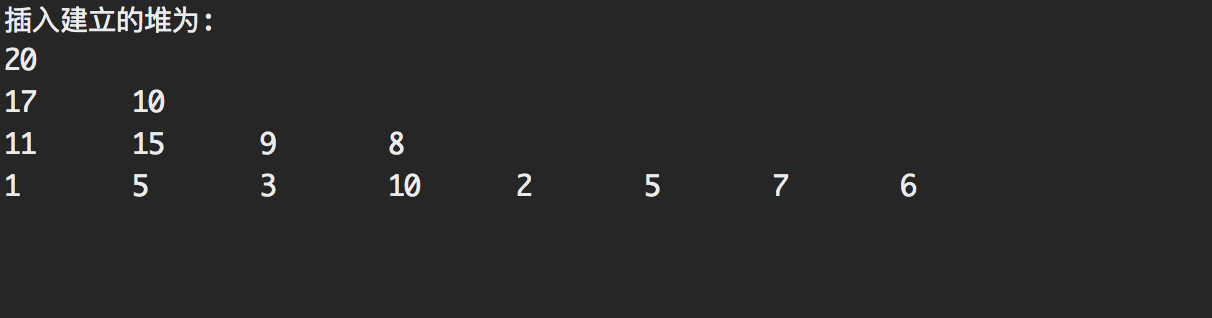
四:插入法建堆
public class insert_build_heap { public static void main(String[] args){ //下沉法获得最大堆 int[] A = {1,2,5,10,3,7,11,15,17,20,10,9,5,8,6}; List<Integer> array = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for(int i = 0; i<A.length;i++){ heap_Tools.insert(array,A[i]); } System.out.println("插入建立的堆为:"); heap_Tools.print_heap(array); } }