1.什么是算法
算法是解决特定问题的一系列步骤
使用不同算法解决同意问题的效率可能相差很大
2.如何评价一个算法好坏
2.1事后统计法
2.2常用分析指标
正确性 可读性 健壮性
时间复杂度
空间复杂度
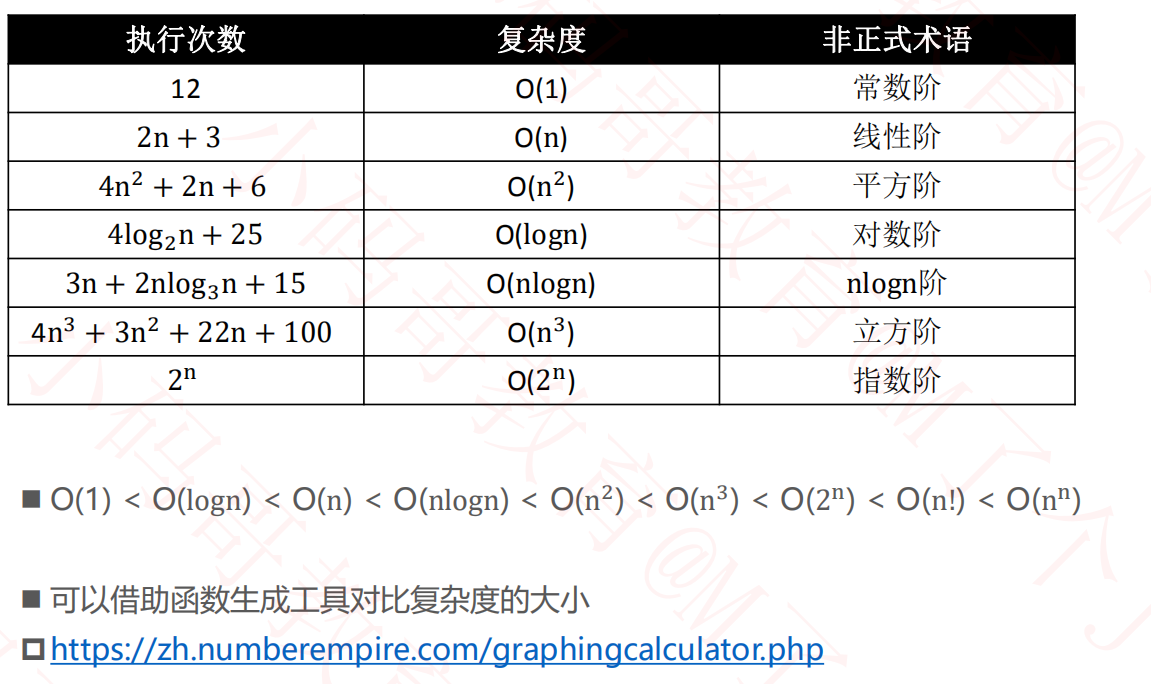
3.大O表示法

3.1对数阶的细节

3.2常见的复杂度
4.常见一些函数的复杂度表示
public static void test2(int n) { // O(n) // 1 + 3n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { System.out.println("test"); } } public static void test3(int n) { // 1 + 2n + n * (1 + 3n) // 1 + 2n + n + 3n^2 // 3n^2 + 3n + 1 // O(n^2) // O(n) for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { System.out.println("test"); } } } public static void test4(int n) { // 1 + 2n + n * (1 + 45) // 1 + 2n + 46n // 48n + 1 // O(n) for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 15; j++) { System.out.println("test"); } } } public static void test5(int n) { // 8 = 2^3 // 16 = 2^4 // 3 = log2(8) // 4 = log2(16) // 执行次数 = log2(n) // O(logn) while ((n = n / 2) > 0) { System.out.println("test"); } } public static void test6(int n) { // log5(n) // O(logn) while ((n = n / 5) > 0) { System.out.println("test"); } } public static void test7(int n) { // 1 + 2*log2(n) + log2(n) * (1 + 3n) // 1 + 3*log2(n) + 2 * nlog2(n) // O(nlogn) for (int i = 1; i < n; i = i * 2) { // 1 + 3n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { System.out.println("test"); } } } public static void test10(int n) { // O(n) int a = 10; int b = 20; int c = a + b; int[] array = new int[n]; for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { System.out.println(array[i] + c); } }
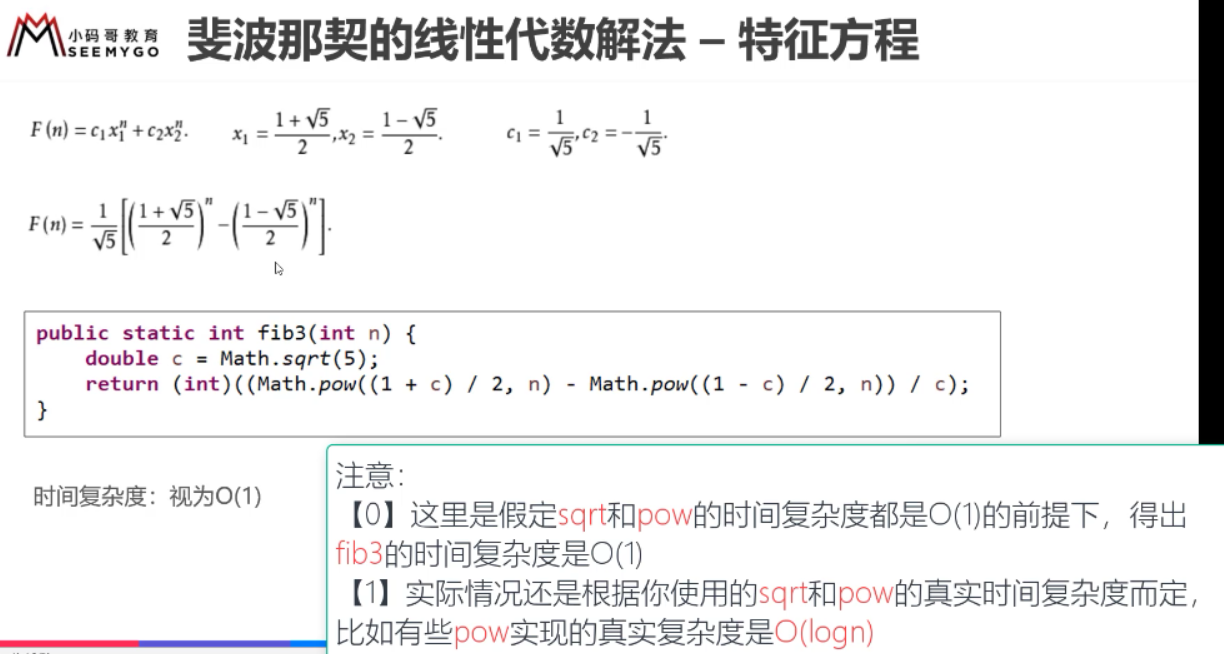
4.1斐波拉切数
/* 0 1 2 3 4 5 * 0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 .... */ // O(2^n) public static int fib1(int n) { if (n <= 1) return n; return fib1(n - 1) + fib1(n - 2); } // O(n) public static int fib2(int n) { if (n <= 1) return n; int first = 0; int second = 1; for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) { int sum = first + second; first = second; second = sum; } return second; } public static int fib3(int n) { if (n <= 1) return n; int first = 0; int second = 1; while (n-- > 1) { second += first; first = second - first; } return second; }
4.2斐波拉切函数的时间复杂度分析


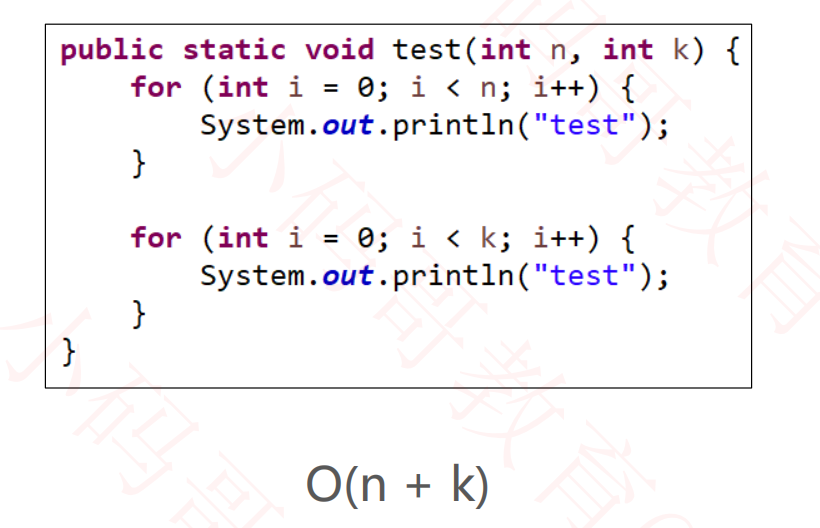
4.3多个数据规模的情况