1.何为前缀树?TrieTree
在计算机科学中,trie,又称前缀树或字典树,是一种有序树,用于保存关联数组,其中的键通常是字符串。与二叉查找树不同,键不是直接保存在节点中,而是由节点在树中的位置决定。一个节点的所有子孙都有相同的前缀,也就是这个节点对应的字符串,而根节点对应空字符串。一般情况下,不是所有的节点都有对应的值,只有叶子节点和部分内部节点所对应的键才有相关的值。
trie中的键通常是字符串,但也可以是其它的结构。
举例:
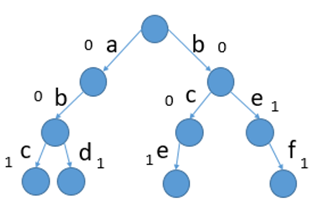
当有四个字符串时:“abc”,”bce”,”abd”,”bef”.下图中:边上的是字符,树内的数字是以当前字符结尾的字符串有多少个。比如,加入”bef”后,f后面的数字就由0-->1,再加入”be”后,‘e’处的数值就由0变成了1;求:有多少个字符串以“be”做为前缀?直接找到“be”处的'e'的数字即可。
1 /* 2 * 前缀树,查看两个字符串数组内元素; 3 */ 4 public class Code_01_TrieTree { 5 6 public static class TrieNode { 7 public int path;//经过该节点的次数 8 public int end;//以该节点为结尾的字符串的个数; 9 public TrieNode[] nexts; 10 public TrieNode() { 11 path = 0; 12 end = 0; 13 nexts = new TrieNode[26];//26个字母对应0--25下标 14 } 15 } 16 17 public static class Trie { 18 private TrieNode root;//根节点 19 public Trie() { 20 root = new TrieNode(); 21 } 22 23 public void insert(String word) { 24 if (word == null) { 25 return; 26 } 27 char[] chs = word.toCharArray(); 28 TrieNode node = root; 29 int index = 0; 30 for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) { 31 index = chs[i]-'a';//将字母对应成下标 32 if (node.nexts[index] == null) { 33 node.nexts[index] = new TrieNode(); 34 } 35 node = node.nexts[index]; 36 node.path++; 37 } 38 node.end++; 39 } 40 41 public void delete(String word) { 42 if (search(word) != 0) { 43 char[] chs = word.toCharArray(); 44 int index = 0; 45 TrieNode node = root; 46 for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) { 47 index = chs[i] - 'a'; 48 if (--node.nexts[index].path == 0) { 49 node.nexts[index] = null; 50 return; 51 } 52 node = node.nexts[index]; 53 } 54 node.end--; 55 } 56 } 57 58 public int search(String word) { 59 if (word == null) { 60 return 0; 61 } 62 char[] chs = word.toCharArray(); 63 int index = 0; 64 TrieNode node = root; 65 for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) { 66 index = chs[i] - 'a'; 67 if (node.nexts[index] == null) { 68 return 0; 69 } 70 node = node.nexts[index]; 71 } 72 return node.end; 73 } 74 } 75 76 77 78 public static void main(String[] args) { 79 test(); 80 81 } 82 83 84 85 private static void test() { 86 Trie trie = new Trie(); 87 System.out.println(trie.search("zuo")); 88 trie.insert("zuo"); 89 System.out.println(trie.search("zuo")); 90 trie.delete("zuo"); 91 System.out.println(trie.search("zuo")); 92 trie.insert("zuo"); 93 trie.insert("zuo"); 94 trie.delete("zuo"); 95 System.out.println(trie.search("zuo")); 96 trie.delete("zuo"); 97 System.out.println(trie.search("zuo")); 98 trie.insert("zuoa"); 99 trie.insert("zuoac"); 100 trie.insert("zuoab"); 101 trie.insert("zuoad"); 102 trie.delete("zuoa"); 103 System.out.println(trie.search("zuoa")); 104 System.out.println(trie.search("zuoac")); 105 System.out.println(trie.search("zuoab")); 106 System.out.println(trie.search("zuoad")); 107 } 108 109 }
2.字符串数组拼接—贪心策略
(对数器小样本测,不纠结证明过程)
字符串数组,将各字符串拼接,使得最低词典顺序。如:“ab”,“cd”,“ef”,拼接成“abcdef”最小,其他方式都比它大。到这里可能想到排序,再拼接,有一种情况是,“b”和“ba”拼接,排序后是“b”,“ba”,拼接后是“b ba”,但是按照“b ab”拼接的话,更小,故刚才对字符串按照字典的排序进行拼接是不对的。所以排序策略需要改变一下。
对str1,str2排序:
原先的拼接策略是:str1<=str2,str1放前,否则str2放前;
改进后拼接策略是:str1+str2<=str2+str1,str1放前,否则str2放前;
证明过程:
证明排序的传递性:a.b表示a后拼接b,拼接后可以看成a在高位,b在低位,a.b表示a是向左移动了b的长度个位数再加上b。a.b可以看成是k进制的拼接,即a*Kb长度+b,令
Kb长度=m(b),故a.b=a*m(b)+b;





/* * 给定一个字符串类型的数组strs,找到一种拼接方式,使得把所 * 有字 符串拼起来之后形成的字符串具有最低的字典序。 */ public class Code_05_LowestLexicography { public static class MyComparator implements Comparator<String>{ @Override public int compare(String o1, String o2) { return (o1+o2).compareTo(o2+o1); } } public static String lowestString(String[] strs) { if (strs == null || strs.length < 1) { return null; } Arrays.sort(strs, new MyComparator()); String res = ""; for (int i = 0; i < strs.length; i++) { res = res + strs[i] + "-"; } return res; } private static void test() { String[] strs1 = { "jibw", "ji", "jp", "bw", "jibw" }; System.out.println(lowestString(strs1)); String[] strs2 = { "ba", "b" }; System.out.println(lowestString(strs2)); } public static void main(String[] args) { test(); } }
在这里:

3. 切割金条问题—贪心策略
一块金条切成两半,是需要花费和长度数值一样的铜板的。比如长度为20的 金条,不管切成长度多大的两半,都要花费20个铜板。一群人想整分整块金 条,怎么分最省铜板?例如,给定数组{10,20,30},代表一共三个人,整块金条长度为10+20+30=60. 金条要分成10,20,30三个部分。 如果先把长度60的金条分成10和50,花费60 再把长度50的金条分成20和30,花费50 一共花费110铜板。但是如果, 先把长度60的金条分成30和30,花费60 再把长度30金条分成10和20,花费30 一共花费90铜板。输入一个数组,返回分割的最小代价。
思路:通过定义不同的比较器,来实现不同的堆。该题利用最小堆,每次从堆里找出最小的两个数,合并之后再插入堆中,依次循环,直至堆中只剩下一个数停止。其实本质是哈夫曼问题。

1 public static class MinHeapComparator implements Comparator<Integer>{ 2 @Override 3 public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) { 4 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 5 return o1.compareTo(o2);//负数第一个前 6 } 7 } 8 9 public static int lessMoney(int[] arr) { 10 int sum = 0; 11 if (arr == null || arr .length <1) { 12 return 0; 13 } 14 PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(new MinHeapComparator()); 15 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { 16 pq.add(arr[i]); 17 } 18 int temp = 0; 19 while (pq.size() > 1) { 20 temp = pq.poll() + pq.poll(); 21 sum += temp; 22 pq.add(temp); 23 } 24 25 return sum; 26 }
4. 代价利润问题—贪心策略
给定两个数组,Costs[…….]和Profits[…....],数组大小相等,一次只能做一个项目,一共最多做k个项目,初始资金W,求最大收益(钱剩下多少)。
输入:参数1,正数数组costs;参数2,正数数组profits;参数3,正数k;参数4,正数m。costs[i]表示第i个项目的花费,profits[i]表示第i个项目在扣除花费之后还能挣到的钱(利润),k表示你不能并行、只能串行的最多做k个项目,m表示你初始的资金。说明:你每做完一个项目,马上获得的收益,可以支持你去做下一个项目。
输出:你最后获得的最大钱数。
思路:运用小根堆+大根堆,把所有项目按照cost放入小根堆中,然后从小根堆中取出所有比此时的总钱小的项目放入按照profit排序的大根堆,意思是利用现在的钱将能做的项目都放入大根堆,然后从大根堆中每次取出一个栈顶项目(利润最大项目),然后再将总钱数增加,再去小根堆里找出所有比当前总钱数要少的项目,依次循环,直至大根堆里没有项目。


1 /* 2 给定两个数组,Costs[…….]和Profits[…....],数组大小相等,一次只能做一个项目, 3 一共最多做k个项目,初始资金W,求最大收益(钱剩下多少)。 4 输入:参数1,正数数组costs 参数2,正数数组profits 参数3,正数k 参数4,正数m。 5 costs[i]表示第i个项目的花费,profits[i]表示第i个项目在扣除花费之后还能挣到的钱(利润), 6 k表示你不能并行、只能串行的最多做k个项目,m表示你初始的资金。 7 说明:你每做完一个项目,马上获得的收益,可以支持你去做下一个项目。 8 输出: 你最后获得的最大钱数。 9 10 */ 11 public class Code_03_IPO { 12 13 public static class Node{ 14 public int cost; 15 public int profit; 16 public Node(int c, int p){ 17 cost = c; 18 profit = p; 19 } 20 } 21 22 public static class MinHeapComparator implements Comparator<Node>{ 23 @Override 24 public int compare(Node o1, Node o2) { 25 return o1.cost-o2.cost;//负数第一个前 26 } 27 } 28 public static class MaxHeapComparator implements Comparator<Node>{ 29 @Override 30 public int compare(Node o1, Node o2) { 31 return o2.profit-o1.profit;//负数第一个前 32 } 33 } 34 public static int findMaximizedCapital(int k, int W, int[] Profits, int[] Capital) { 35 if (Profits == null || Capital == null || Profits.length < 1 || Capital.length < 1) { 36 return W ; 37 } 38 Node[] nodes = new Node[Profits.length]; 39 for (int i = 0; i < Profits.length; i++) { 40 nodes[i] = new Node(Profits[i], Capital[i]); 41 } 42 PriorityQueue<Node> minPQ = new PriorityQueue<>(new MinHeapComparator()); 43 PriorityQueue<Node> maxPQ = new PriorityQueue<>(new MaxHeapComparator()); 44 for (int i = 0; i < nodes.length; i++) { 45 minPQ.add(nodes[i]); 46 } 47 int time = 0; 48 while (time < k) { 49 while(!minPQ.isEmpty() && minPQ.peek().cost < W) { 50 maxPQ.add(minPQ.poll()); 51 } 52 if (maxPQ.isEmpty()) { 53 return W; 54 } 55 W+=maxPQ.poll().profit; 56 time++; 57 } 58 return W; 59 } 60 public static void main(String[] args) { 61 } 62 }
自己做:带输入输出
1 public class Code_03_IPO1 { 2 3 public static class MyMinComparator implements Comparator<projest>{ 4 5 @Override 6 public int compare(projest o1, projest o2) { 7 return o1.cost-o2.cost; 8 } 9 10 } 11 public static class MyMaxComparator implements Comparator<projest>{ 12 13 @Override 14 public int compare(projest o1, projest o2) { 15 return o2.profit-o1.profit; 16 } 17 18 } 19 20 public static class projest { 21 int cost; 22 int profit; 23 public projest(int c,int p) { 24 this.cost = c; 25 this.profit = p; 26 } 27 } 28 29 public static void main(String[] args) { 30 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 31 String costStr = sc.nextLine(); 32 // System.out.println("999"); 33 String profitStr = sc.nextLine(); 34 // System.out.println("888"); 35 int k = sc.nextInt(); 36 int m = sc.nextInt(); 37 String[] costs = costStr.split(" "); 38 String[] profits = profitStr.split(" "); 39 int[] cost = new int[costs.length]; 40 int[] profit = new int[profits.length]; 41 projest[] ps = new projest[cost.length]; 42 for (int i = 0; i < profit.length; i++) { 43 cost[i] = Integer.valueOf(costs[i]); 44 profit[i] = Integer.valueOf(profits[i]); 45 ps[i] = new projest(cost[i], profit[i]); 46 } 47 48 Queue<projest> minQueue = new PriorityQueue<projest>(new MyMinComparator()); 49 Queue<projest> maxQueue = new PriorityQueue<projest>(new MyMaxComparator()); 50 for (int i = 0; i < ps.length; i++) { 51 minQueue.add(ps[i]); 52 } 53 int k1 = 0; 54 while (!minQueue.isEmpty() || !maxQueue.isEmpty()) { 55 while (!minQueue.isEmpty() && minQueue.peek().cost<=m) { 56 maxQueue.add(minQueue.poll()); 57 } 58 if (k1<k) { 59 m += maxQueue.poll().profit; 60 k1++; 61 }else { 62 break; 63 } 64 } 65 System.out.println(m); 66 67 } 68 69 }
5. 求数据流中的中位数
如何得到一个数据流中的中位数?如果从数据流中读出奇数个数值,那么中位数就是所有数值排序之后位于中间的数值。如果从数据流中读出偶数个数值,那么中位数就是所有数值排序之后中间两个数的平均值。我们使用Insert()方法读取数据流,使用GetMedian()方法获取当前读取数据的中位数。
思路:一个大根堆,一个小根堆。小根堆里放的是较大的数,大根堆里放的是较小的数,然后每次进来的数与小根堆的堆顶相比较,再记一个变量记录当前进来的数是第几个,如果是序号是奇数。
1 public class Code_04_MadianQuick { 2 3 public static class MyMinComparator implements Comparator<Integer> { 4 @Override 5 public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) { 6 return o1.compareTo(o2); 7 } 8 } 9 public static class MyMaxComparator implements Comparator<Integer> { 10 @Override 11 public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) { 12 return o2.compareTo(o1); 13 } 14 } 15 16 public static void main(String[] args) { 17 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 18 String[] dataStr = sc.nextLine().split(" "); 19 int[] datas = new int[dataStr.length]; 20 for (int i = 0; i < datas.length; i++) { 21 datas[i] = Integer.valueOf(dataStr[i]); 22 } 23 24 Queue<Integer> minQueue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(new MyMinComparator()); 25 Queue<Integer> maxQueue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(new MyMaxComparator()); 26 27 for (int i = 0; i < datas.length; i++) { 28 if (maxQueue.isEmpty()) { 29 maxQueue.add(datas[i]); 30 continue; 31 } 32 if (maxQueue.peek()>=datas[i]) { 33 maxQueue.add(datas[i]); 34 }else { 35 if (minQueue.isEmpty()) { 36 minQueue.add(datas[i]); 37 continue; 38 } 39 if (minQueue.peek()<datas[i]) { 40 minQueue.add(datas[i]); 41 }else { 42 maxQueue.add(datas[i]); 43 } 44 } 45 //调整堆的大小 46 if (maxQueue.size() == minQueue.size()+2) { 47 minQueue.add(maxQueue.poll()); 48 } 49 if (maxQueue.size() == minQueue.size()-2) { 50 maxQueue.add(minQueue.poll()); 51 } 52 }//endfor 53 //取中位数 54 if ((datas.length&1)==0) {//偶数 55 System.out.printf("%.6f",(maxQueue.peek()+minQueue.peek())/2.0); 56 }else { 57 System.out.println(maxQueue.size()>minQueue.size()?maxQueue.peek():minQueue.peek()); 58 } 59 } 60 }
另:保留小数点后几位的三种写法:

6. 求举办宣讲会场最多—贪心策略
一些项目要占用一个会议室宣讲,会议室不能同时容纳两个项目的宣讲。 给你每一个项目开始的时间和结束的时间(给你一个数组,里面 是一个个具体的项目),你来安排宣讲的日程,要求会议室进行 的宣讲的场次最多。返回这个最多的宣讲场次。
其中一种: 按照开始时间最早,错!按照每个持续的时间长短,也不行。
正确思路:按照结束时间的早晚。找出最早结束的项目,然后过滤掉因该项目而不能举办的项目,依次循环。
1 public class Code_06_BestArrange1 { 2 3 public static class Program { 4 int start; 5 int end; 6 public Program(int start, int end) { 7 this.start = start; 8 this.end = end; 9 } 10 } 11 12 public static class MyComparator implements Comparator<Program> { 13 @Override 14 public int compare(Program o1, Program o2) { 15 return o1.end-o2.end;//小根堆 16 } 17 } 18 //左神写 19 public static int bestArrange(Program[] programs,int cur) { 20 Arrays.sort(programs, new MyComparator()); 21 int count = 0; 22 for (int i = 0; i < programs.length; i++) { 23 if (cur <= programs[i].start) { 24 cur = programs[i].end; 25 System.out.println(programs[i].start+"---"+programs[i].end); 26 } 27 } 28 return 0; 29 } 30 31 public static void main(String[] args) { 32 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 33 String[] startStr = sc.nextLine().split(" "); 34 String[] endStr = sc.nextLine().split(" "); 35 int[] start = new int[startStr.length]; 36 int[] end = new int[endStr.length]; 37 Program[] programs = new Program[end.length]; 38 for (int i = 0; i < end.length; i++) { 39 start[i] = Integer.valueOf(startStr[i]); 40 end[i] = Integer.valueOf(endStr[i]); 41 programs[i] = new Program(start[i], end[i]); 42 } 43 Queue<Program> queue = new PriorityQueue<Program>(new MyComparator()); 44 for (int i = 0; i < programs.length; i++) { 45 queue.add(programs[i]); 46 } 47 while (!queue.isEmpty()) { 48 Program pTemp = queue.poll(); 49 // System.out.println(pTemp.start+"--"+pTemp.end); 50 while (!queue.isEmpty() && queue.peek().start<pTemp.end) { 51 queue.poll(); 52 } 53 } 54 //法2 55 bestArrange(programs,0); 56 } 57 }
结果:
