简言
机器学习的项目,不可避免的需要补充一些优化算法,对于优化算法,爬山算法还是比较重要的.鉴于此,花了些时间仔细阅读了些爬山算法的paper.基于这些,做一些总结.
目录
1. 爬山算法简单描述
2. 爬山算法的主要算法
2.1 首选爬山算法
2.2 最陡爬山算法
2.3 随机重新开始爬山算法
2.4 模拟退火算法(也是爬山算法)
3. 实例求解
正文
爬山算法,是一种局部贪心的最优算法. 该算法的主要思想是:每次拿相邻点与当前点进行比对,取两者中较优者,作为爬坡的下一步.
举一个例子,求解下面表达式
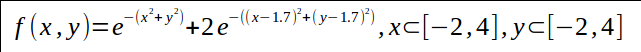 的最大值. 且假设 x,y均按为0.1间隔递增.
的最大值. 且假设 x,y均按为0.1间隔递增.
为了更好的描述,我们先使用pyhton画出该函数的图像:
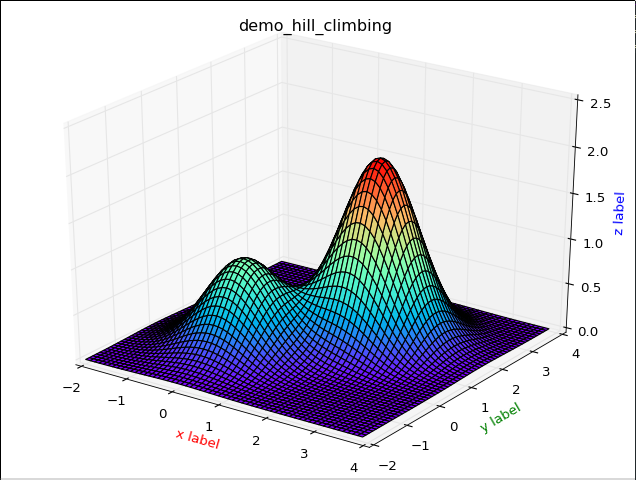
图像的python代码:

1 # encoding:utf8 2 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt 3 import numpy as np 4 from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D 5 6 7 def func(X, Y, x_move=0, y_move=0): 8 def mul(X, Y, alis=1): 9 return alis * np.exp(-(X * X + Y * Y)) 10 11 return mul(X, Y) + mul(X - x_move, Y - y_move, 2) 12 13 14 def show(X, Y): 15 fig = plt.figure() 16 ax = Axes3D(fig) 17 X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y) 18 Z = func(X, Y, 1.7, 1.7) 19 plt.title("demo_hill_climbing") 20 ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap='rainbow', ) 21 ax.set_xlabel('x label', color='r') 22 ax.set_ylabel('y label', color='g') 23 ax.set_zlabel('z label', color='b') 24 # 具体函数方法可用 help(function) 查看,如:help(ax.plot_surface) 25 # ax.scatter(X,Y,Z,c='r') #绘点 26 plt.show() 27 28 if __name__ == '__main__': 29 X = np.arange(-2, 4, 0.1) 30 Y = np.arange(-2, 4, 0.1) 31 32 show(X,Y)
对于上面这个问题,我们使用爬山算法该如何求解呢? 下面我们从爬山算法中的几种方式分别求解一下这个小题.
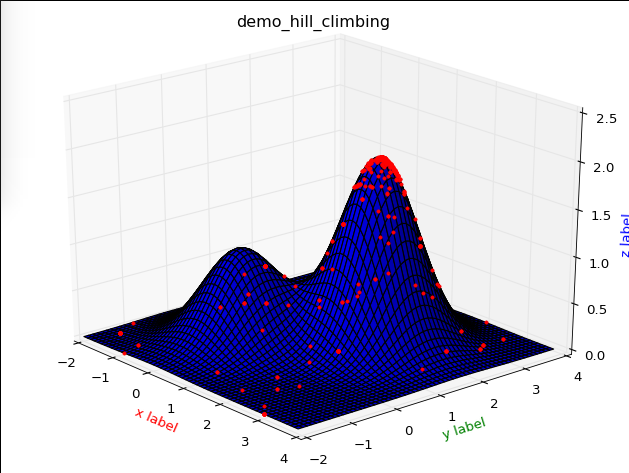
1. 首选爬山算法
依次寻找该点X的邻近点中首次出现的比点X价值高的点,并将该点作为爬山的点(此处说的价值高,在该题中是指Z或f(x,y)值较大). 依次循环,直至该点的邻近点中不再有比其大的点. 我们成为该点就是山的顶点,又称为最优点.
那么解题思路就有:
1. 随机选择一个登山的起点S(x0,y0,z0),并以此为起点开始登山.直至"登顶".
下面是我们实现的代码:

1 # encoding:utf8 2 from random import random, randint 3 4 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt 5 import numpy as np 6 from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D 7 8 9 def func(X, Y, x_move=1.7, y_move=1.7): 10 def mul(X, Y, alis=1): 11 return alis * np.exp(-(X * X + Y * Y)) 12 13 return mul(X, Y) + mul(X - x_move, Y - y_move, 2) 14 15 16 def show(X, Y, Z): 17 fig = plt.figure() 18 ax = Axes3D(fig) 19 plt.title("demo_hill_climbing") 20 ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap='rainbow', ) 21 ax.set_xlabel('x label', color='r') 22 ax.set_ylabel('y label', color='g') 23 ax.set_zlabel('z label', color='b') 24 # ax.scatter(X,Y,Z,c='r') #绘点 25 plt.show() 26 27 28 def drawPaht(X, Y, Z,px,py,pz): 29 fig = plt.figure() 30 ax = Axes3D(fig) 31 plt.title("demo_hill_climbing") 32 ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap='rainbow', ) 33 ax.set_xlabel('x label', color='r') 34 ax.set_ylabel('y label', color='g') 35 ax.set_zlabel('z label', color='b') 36 ax.plot(px,py,pz,'r.') #绘点 37 plt.show() 38 39 40 def hill_climb(X, Y): 41 global_X = [] 42 global_Y = [] 43 44 len_x = len(X) 45 len_y = len(Y) 46 # 随机登山点 47 st_x = randint(0, len_x-1) 48 st_y = randint(0, len_y-1) 49 50 def argmax(stx, sty, alisx=0, alisy=0): 51 cur = func(X[0][st_x], Y[st_y][0]) 52 next = func(X[0][st_x + alisx], Y[st_y + alisy][0]) 53 54 return cur < next and True or False 55 56 while (len_x > st_x >= 0) or (len_y > st_y >= 0): 57 if st_x + 1 < len_x and argmax(st_x, st_y, 1): 58 st_x += 1 59 elif st_y + 1 < len_x and argmax(st_x, st_y, 0, 1): 60 st_y += 1 61 elif st_x >= 1 and argmax(st_x, st_y, -1): 62 st_x -= 1 63 elif st_y >= 1 and argmax(st_x, st_y, 0, -1): 64 st_y -= 1 65 else: 66 break 67 global_X.append(X[0][st_x]) 68 global_Y.append(Y[st_y][0]) 69 return global_X, global_Y, func(X[0][st_x], Y[st_y][0]) 70 71 72 if __name__ == '__main__': 73 X = np.arange(-2, 4, 0.1) 74 Y = np.arange(-2, 4, 0.1) 75 X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y) 76 Z = func(X, Y, 1.7, 1.7) 77 px, py, maxhill = hill_climb(X, Y) 78 print px,py,maxhill 79 drawPaht(X, Y, Z,px,py,func(np.array(px), np.array(py), 1.7, 1.7))
对比几次运行的结果:


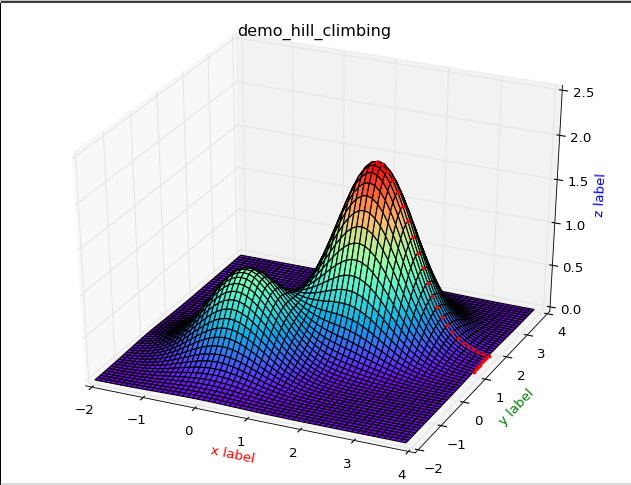

从上图中,我们可以比较清楚的观察到,首选爬山算法的缺陷.
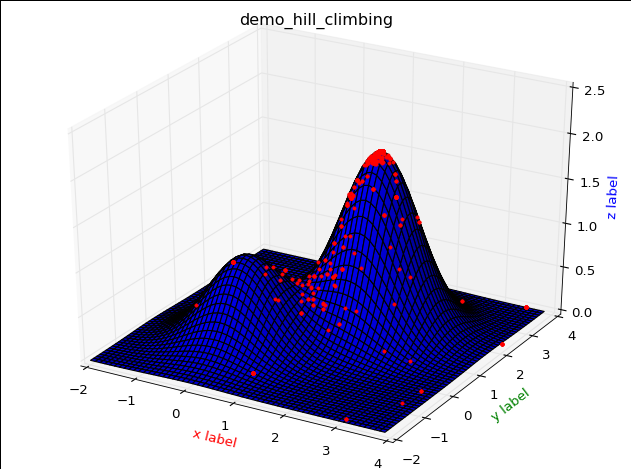
2.那么最陡爬山算法呢?
简单描述:
最陡爬山算法是在首选爬山算法上的一种改良,它规定每次选取邻近点价值最大的那个点作为爬上的点.
下面我们来实现一下它:

1 # encoding:utf8 2 from random import random, randint 3 4 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt 5 import numpy as np 6 from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D 7 8 9 def func(X, Y, x_move=1.7, y_move=1.7): 10 def mul(X, Y, alis=1): 11 return alis * np.exp(-(X * X + Y * Y)) 12 13 return mul(X, Y) + mul(X - x_move, Y - y_move, 2) 14 15 16 def show(X, Y, Z): 17 fig = plt.figure() 18 ax = Axes3D(fig) 19 plt.title("demo_hill_climbing") 20 ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap='rainbow', ) 21 ax.set_xlabel('x label', color='r') 22 ax.set_ylabel('y label', color='g') 23 ax.set_zlabel('z label', color='b') 24 # ax.scatter(X,Y,Z,c='r') #绘点 25 plt.show() 26 27 28 def drawPaht(X, Y, Z, px, py, pz): 29 fig = plt.figure() 30 ax = Axes3D(fig) 31 plt.title("demo_hill_climbing") 32 ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap='rainbow', ) 33 ax.set_xlabel('x label', color='r') 34 ax.set_ylabel('y label', color='g') 35 ax.set_zlabel('z label', color='b') 36 ax.plot(px, py, pz, 'r.') # 绘点 37 plt.show() 38 39 40 def hill_climb(X, Y): 41 global_X = [] 42 global_Y = [] 43 44 len_x = len(X) 45 len_y = len(Y) 46 # 随机登山点 47 st_x = randint(0, len_x - 1) 48 st_y = randint(0, len_y - 1) 49 50 def argmax(stx, sty, alisx, alisy): 51 cur = func(X[0][stx], Y[sty][0]) 52 next = func(X[0][alisx], Y[alisy][0]) 53 if cur < next: 54 return alisx, alisy 55 return stx, sty 56 #return cur < next and alisx, alisy or stx, sty 57 58 tmp_x = st_x 59 tmp_y = st_y 60 while (len_x > st_x >= 0) or (len_y > st_y >= 0): 61 if st_x + 1 < len_x: 62 tmp_x, tmp_y = argmax(tmp_x, tmp_y, (st_x + 1), st_y) 63 64 if st_x >= 1: 65 tmp_x, tmp_y = argmax(tmp_x, tmp_y, st_x - 1, st_y) 66 67 if st_y + 1 < len_x: 68 tmp_x, tmp_y = argmax(tmp_x, tmp_y, st_x, st_y + 1) 69 70 if st_y >= 1: 71 tmp_x, tmp_y = argmax(tmp_x, tmp_y, st_x, st_y - 1) 72 73 if tmp_x != st_x or tmp_y != st_y: 74 st_x = tmp_x 75 st_y = tmp_y 76 else: 77 break 78 global_X.append(X[0][st_x]) 79 global_Y.append(Y[st_y][0]) 80 return global_X, global_Y, func(X[0][st_x], Y[st_y][0]) 81 82 83 if __name__ == '__main__': 84 X = np.arange(-2, 4, 0.1) 85 Y = np.arange(-2, 4, 0.1) 86 X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y) 87 Z = func(X, Y, 1.7, 1.7) 88 px, py, maxhill = hill_climb(X, Y) 89 print px, py, maxhill 90 drawPaht(X, Y, Z, px, py, func(np.array(px), np.array(py), 1.7, 1.7))


从这个结果来看,因为范围扩大了一点,所以效果会好一点点,当依旧是一个局部最优算法.
3.随机重新开始爬山算法呢?
简单的描述:
随机重新开始爬山算法是基于最陡爬山算法,其实就是加一个达到全局最优解的条件,如果满足该条件,就结束运算,反之则无限次重复运算最陡爬山算法.
由于此题,并没有结束的特征条件,我们这里就不给予实现.
4.模拟退火算法
简单描述:
(1)随机挑选一个单元k,并给它一个随机的位移,求出系统因此而产生的能量变化ΔEk。
(2)若ΔEk⩽0,该位移可采纳,而变化后的系统状态可作为下次变化的起点;
若ΔEk>0,位移后的状态可采纳的概率为
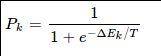
式中T为温度,然后从(0,1)区间均匀分布的随机数中挑选一个数R,若R<Pk,则将变化后的状态作为下次的起点;否则,将变化前的状态作为下次的起点。
(3)转第(1)步继续执行,知道达到平衡状态为止。
代码实现为:

1 # encoding:utf8 2 from random import random, randint 3 4 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt 5 import numpy as np 6 from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D 7 8 9 def func(X, Y, x_move=1.7, y_move=1.7): 10 def mul(X, Y, alis=1): 11 return alis * np.exp(-(X * X + Y * Y)) 12 13 return mul(X, Y) + mul(X - x_move, Y - y_move, 2) 14 15 16 def show(X, Y, Z): 17 fig = plt.figure() 18 ax = Axes3D(fig) 19 plt.title("demo_hill_climbing") 20 ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap='rainbow', ) 21 ax.set_xlabel('x label', color='r') 22 ax.set_ylabel('y label', color='g') 23 ax.set_zlabel('z label', color='b') 24 # ax.scatter(X,Y,Z,c='r') #绘点 25 plt.show() 26 27 28 def drawPaht(X, Y, Z, px, py, pz): 29 fig = plt.figure() 30 ax = Axes3D(fig) 31 plt.title("demo_hill_climbing") 32 ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, color='b' ) 33 ax.set_xlabel('x label', color='r') 34 ax.set_ylabel('y label', color='g') 35 ax.set_zlabel('z label', color='b') 36 ax.plot(px, py, pz, 'r.') # 绘点 37 plt.show() 38 39 40 def hill_climb(X, Y): 41 global_X = [] 42 global_Y = [] 43 # 初始温度 44 temperature = 105.5 45 # 温度下降的比率 46 delta = 0.98 47 # 温度精确度 48 tmin = 1e-10 49 50 len_x = len(X) 51 len_y = len(Y) 52 53 # 随机登山点 54 st_x = X[0][randint(0, len_x - 1)] 55 st_y = Y[randint(0, len_y - 1)][0] 56 st_z = func(st_x, st_y) 57 58 def argmax(stx, sty, alisx, alisy): 59 cur = func(st_x, st_y) 60 next = func(alisx, alisy) 61 62 return cur < next and True or False 63 64 while (temperature > tmin): 65 # 随机产生一个新的邻近点 66 # 说明: 温度越高幅度邻近点跳跃的幅度越大 67 tmp_x = st_x + (random() * 2 - 1) * temperature 68 tmp_y = st_y + + (random() * 2 - 1) * temperature 69 if 4 > tmp_x >= -2 and 4 > tmp_y >= -2: 70 if argmax(st_x, st_y, tmp_x, tmp_y): 71 st_x = tmp_x 72 st_y = tmp_y 73 else: # 有机会跳出局域最优解 74 pp = 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-(func(tmp_x, tmp_y) - func(st_x, st_y)) / temperature)) 75 if random() < pp: 76 st_x = tmp_x 77 st_y = tmp_y 78 temperature *= delta # 以一定的速率下降 79 global_X.append(st_x) 80 global_Y.append(st_y) 81 return global_X, global_Y, func(st_x, st_y) 82 83 84 if __name__ == '__main__': 85 X = np.arange(-2, 4, 0.1) 86 Y = np.arange(-2, 4, 0.1) 87 X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y) 88 Z = func(X, Y, 1.7, 1.7) 89 px, py, maxhill = hill_climb(X, Y) 90 print px, py, maxhill 91 drawPaht(X, Y, Z, px, py, func(np.array(px), np.array(py), 1.7, 1.7))
效果: