源代码实现 - octrees(1)- insert objects
基于 RTCD-7.3.a Octrees进行源代码实现。
insert spheres
#include <iostream>
struct Point {
float x{0.0f};
float y{0.0f};
float z{0.0f};
float operator[](int i) {
float b[3] = {x,y,z};
return b[i];
}
};
Point operator+(const Point& a, const Point& b) {
return Point{a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y, a.z + b.z};
}
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const Point& pt) {
os << "{" << pt.x << ", " << pt.y << ", " << pt.z << "}";
return os;
}
struct Object {
Point center{0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f};
float radius{0.0f};
Object *pNextObject{nullptr};
};
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const Object& obj) {
os << "Obj Center: " << obj.center << " radius: " << obj.radius;
return os;
}
struct Node {
Point center{0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f}; //< The center of the node
float halfWidth{0.0f}; //< The half width of the node
Node *pChild[8]{nullptr}; //< The child of the node
Object *pObjList{nullptr}; //< The objects in the node
};
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const Node& node) {
os << "Node Center: " << node.center << " halfWidth: " << node.halfWidth;
return os;
}
// Preallocates an octree down to a specific depth
Node *BuildOctree(Point center, float halfWidth, int stopDepth)
{
if (stopDepth < 0) return NULL;
else {
// Construct and fill in 'root' of this subtree
Node *pNode = new Node;
pNode->center = center;
pNode->halfWidth = halfWidth;
pNode->pObjList = NULL;
// Recursively construct the eight children of the subtree
Point offset;
float step = halfWidth * 0.5f;
for (int i=0; i<8; ++i) {
// 赞
offset.x = ((i & 1) ? step : -step);
offset.y = ((i & 2) ? step : -step);
offset.z = ((i & 4) ? step : -step);
pNode->pChild[i] = BuildOctree(center + offset, step, stopDepth-1);
}
return pNode;
}
}
// Insert object
void InsertObject(Node *pTree, Object *pObject)
{
int index = 0, straddle = 0;
// Compute the octant number [0..7] the object sphere center is in
// If straddling any of the dividing x, y, or z planes, exit directly
for (int i=0; i<3; ++i)
{
float delta = pObject->center[i] - pTree->center[i];
if (std::abs(delta) < pTree->halfWidth + pObject->radius) // TODO CHECK
{
straddle = 1;
break;
}
if (delta > 0.0f) index |= (1 << i);
}
if (!straddle && pTree->pChild[index]) {
InsertObject(pTree->pChild[index], pObject);
} else {
pObject->pNextObject = pTree->pObjList;
pTree->pObjList = pObject;
}
}
void PrintNodeInfo(Node *pNode, int depth)
{
if (pNode)
{
int nextDepth = depth + 1;
while (depth) {
std::cout << " ";
depth--;
}
std::cout << *pNode << " | ";
if (pNode->pObjList != nullptr)
{
Object* pObjCur = pNode->pObjList;
while (pObjCur) {
std::cout << *pObjCur << " | ";
pObjCur = pObjCur->pNextObject;
}
}
std::cout << std::endl;
for (int i=0; i<8; ++i)
{
PrintNodeInfo(pNode->pChild[i], nextDepth);
}
}
}
int main()
{
// Assuming the depth of octree is 1
// The root center is (0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
// The root width is 2.0
Node* pRoot = BuildOctree(Point{0.0, 0.0, 0.0}, 1.0, 1);
Object objs[2];
objs[0].radius = 0.5;
objs[0].center = Point{0.0, 0.0, 0.0};
objs[1].radius = 0.1;
objs[1].center = Point{-0.5, -0.5, -0.5};
InsertObject(pRoot, &objs[0]);
InsertObject(pRoot, &objs[1]);
std::cout << "=================================" << std::endl;
PrintNodeInfo(pRoot, 0);
return 0;
}
基于上面的实现,发现得到的结果如下:
Node Center: {0, 0, 0} halfWidth: 1 | Obj Center: {-0.5, -0.5, -0.5} radius: 0.1 | Obj Center: {0, 0, 0} radius: 0.5 |
Node Center: {-0.5, -0.5, -0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |
Node Center: {0.5, -0.5, -0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |
Node Center: {-0.5, 0.5, -0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |
Node Center: {0.5, 0.5, -0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |
Node Center: {-0.5, -0.5, 0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |
Node Center: {0.5, -0.5, 0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |
Node Center: {-0.5, 0.5, 0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |
Node Center: {0.5, 0.5, 0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |
很显然这个答案是有问题的。两个sphere竟然都挂载到了第一个node节点上。其实从理论出发,节点:Obj Center: {-0.5, -0.5, -0.5} radius: 0.1 应该挂载在node,Node Center: {-0.5, -0.5, -0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |上。
按照之前文章中InsertObject实现给出的注释,对该实现进行修正如下:
void InsertObject(Node *pTree, Object *pObject)
{
int index = 0, straddle = 0;
// Compute the octant number [0..7] the object sphere center is in
// If straddling any of the dividing x, y, or z planes, exit directly
for (int i=0; i<3; i++)
{
float delta = pObject->center[i] - pTree->center[i];
if (Abs(delta) < pObject->radius)
{
straddle = 1;
break;
}
if (delta > 0.0f) index |= (1 << i);
}
if (!straddle && pTree->pChild[index]) {
// Fully contained in existing child node; insert in that subtree
InsertObject(pTree->pChild[index], pObject);
} else {
// Straddling, or no child node to descend into, so
// link object into linked list at this node
pObject->pNextObject = pTree->pObjList;
pTree->pObjList = pObject;
}
}
此时得到的结果为:
Node Center: {0, 0, 0} halfWidth: 1 | Obj Center: {0, 0, 0} radius: 0.5 |
Node Center: {-0.5, -0.5, -0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 | Obj Center: {-0.5, -0.5, -0.5} radius: 0.1 |
Node Center: {0.5, -0.5, -0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |
Node Center: {-0.5, 0.5, -0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |
Node Center: {0.5, 0.5, -0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |
Node Center: {-0.5, -0.5, 0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |
Node Center: {0.5, -0.5, 0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |
Node Center: {-0.5, 0.5, 0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |
Node Center: {0.5, 0.5, 0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |
这个结果就是正确的了。
insert triangles
上面一节中给出了如何向八叉树中insert球。但是,更加common的场景是,用八叉树对三角网格进行划分。此时被处理的对象就是三角形,那么怎么将三角形insert到八叉树合适的节点中么?
要实现这个功能,最关键的是,需要知道如何判断一个三角形位于哪个节点?基本原理如下:
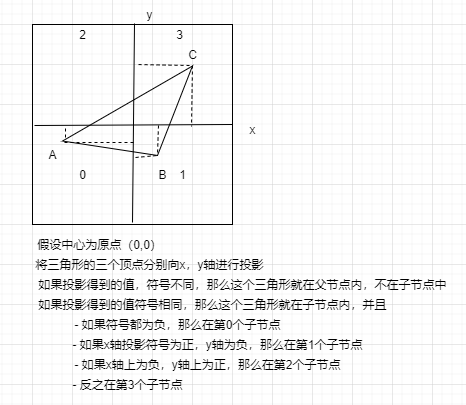
相对于上面的示例,需要修改的代码如下:
struct Object {
Point vertexs[3];
Object *pNextObject{nullptr};
};
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const Object& obj) {
os << "Tri vertexs : " << obj.vertexs[0] << ", " << obj.vertexs[1] << ", " << obj.vertexs[2];
return os;
}
// ....
// Insert object
void InsertObject(Node *pTree, Object *pObject)
{
int index = 0, straddle = 0;
// Compute the octant number [0..7] the object sphere center is in
for (int i=0; i<3; ++i)
{
// Check if the projection of tree points on every axis (xyz) are equal or not
int delta0 = pObject->vertexs[0][i] - pTree->center[i] > 0 ? 1 : -1;
int delta1 = pObject->vertexs[1][i] - pTree->center[i] > 0 ? 1 : -1;
int delta2 = pObject->vertexs[2][i] - pTree->center[i] > 0 ? 1 : -1;
int checkSign = delta0 + delta1 + delta2;
// Not equal
if (std::abs(checkSign) != 3)
{
straddle = 1;
break;
}
if (checkSign > 0) index |= (1 << i);
}
if (!straddle && pTree->pChild[index]) {
InsertObject(pTree->pChild[index], pObject);
} else {
pObject->pNextObject = pTree->pObjList;
pTree->pObjList = pObject;
}
}
// ...
int main()
{
// Assuming the depth of octree is 1
// The root center is (0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
// The root width is 2.0
Node* pRoot = BuildOctree(Point{0.0, 0.0, 0.0}, 1.0, 1);
Object triangles[2];
triangles[0].vertexs[0] = Point{ 0.5, 0.5, 0.5 };
triangles[0].vertexs[1] = Point{ -0.5, -0.5, -0.2 };
triangles[0].vertexs[2] = Point{ 0.6, 0. - 0.5, -0.3 };
triangles[1].vertexs[0] = Point{ 0.1, 0.1, 0.1 };
triangles[1].vertexs[1] = Point{ 0.6, 0.1, 0.1 };
triangles[1].vertexs[2] = Point{ 0.6, 0.6, 0.1 };
InsertObject(pRoot, &triangles[0]);
InsertObject(pRoot, &triangles[1]);
std::cout << "=================================" << std::endl;
PrintNodeInfo(pRoot, 0);
return 0;
}
得到结果如下:
Node Center: {0, 0, 0} halfWidth: 1 | Tri vertexs : {0.5, 0.5, 0.5}, {-0.5, -0.5, -0.2}, {0.6, -0.5, -0.3} |
Node Center: {-0.5, -0.5, -0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |
Node Center: {0.5, -0.5, -0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |
Node Center: {-0.5, 0.5, -0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |
Node Center: {0.5, 0.5, -0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |
Node Center: {-0.5, -0.5, 0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |
Node Center: {0.5, -0.5, 0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |
Node Center: {-0.5, 0.5, 0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 |
Node Center: {0.5, 0.5, 0.5} halfWidth: 0.5 | Tri vertexs : {0.1, 0.1, 0.1}, {0.6, 0.1, 0.1}, {0.6, 0.6, 0.1} |