1,BlockingQueue
生产者-消费者模型即有界缓存模型,生产者线程在仓库装满之后被阻塞,消费者线程则在仓库清空后阻塞。
它包括三个基本部分:
1) 产品仓库,用于存放产品。
2) 生产者,生产出来的产品存入仓库。
3) 消费者,消费仓库里的产品。
java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue,是一个阻塞队列接口,当BlockingQueue操作无法立即响应时,有四种处理方式:
1) 抛出异常
2) 返回特定的值,根据操作不同,可能是null或者false中的一个。
3) 无限期的阻塞当前线程,直到操作可以成功为止。
4) 根据阻塞超时设置来进行阻塞。
BlockingQueue的核心方法和未响应处理的对应形式如下:
|
|
抛出异常 |
返回特定值 |
无限阻塞 |
超时 |
|
插入 |
add(e) |
offer(e) |
put(e) |
offer(e,time,unit) |
|
移除 |
remove() |
poll() |
take() |
poll(time,unit) |
|
查询 |
element() |
peek() |
|
|
其中add、remove、elemnt三个方法具体实现都是调用offer、poll、peek三个方法,在BlockingQueue的各个实现类中,通过重写这几个方法类达到多线程安全的目的。
BlockingQueue有很多实现类:
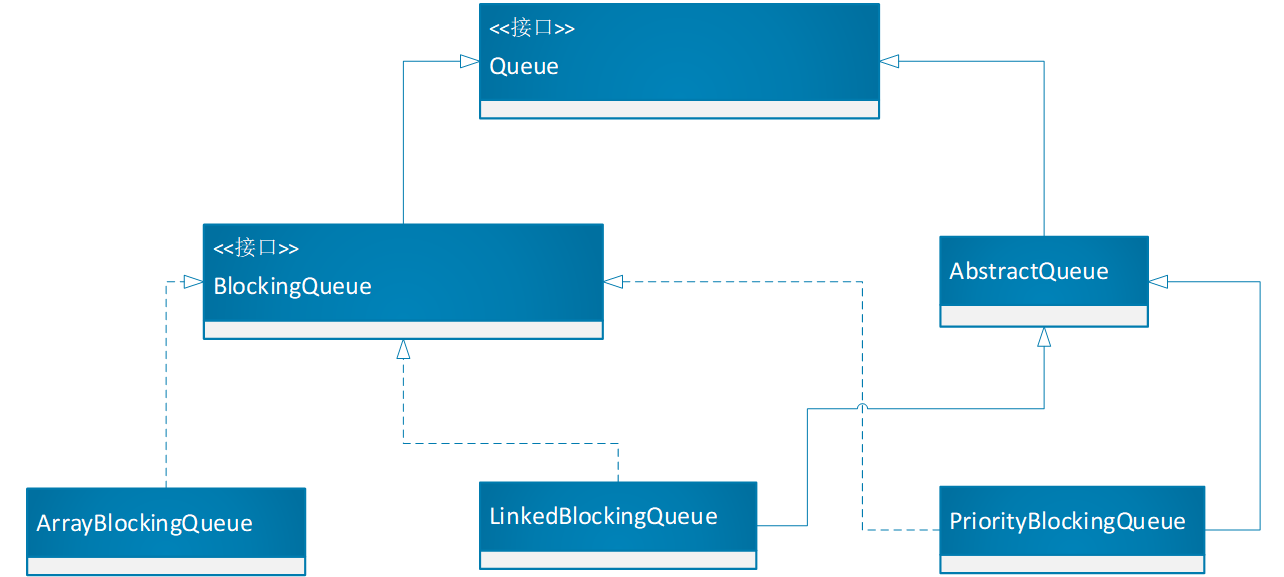
2,ArrayBlockingQueue
ArrayBlockingQueue是基于数组实现的有界BlockingQueue,该队列满足先入先出的特性,它是一个典型的有界缓存,有一个固定大小的数组保存元素,一旦创建好了以后,容量就不能改变了。
1 //队列元素存储数组
2 final Object[] items;
3 //队头下标,下一次take/pool/peek/remove方法执行位置下标
4 int takeIndex;
5 //队尾下标,下一次put/offer/add方法执行下标
6 int putIndex;
7 //队列元素数量
8 int count;
9 //访问锁
10 final ReentrantLock lock;
11 //阻塞取值类型方法 take/poll/peek/remove的控制条件
12 private final Condition notEmpty;
13 //阻塞存值类型方法put/offer/add的控制条件
14 private final Condition notFul;
ArrayBlockingQueue提供add/offer/put三种方法都用于插入数据。
add(E)的实现体现在AbstractQueue中,通过调用offer(E)作为实现,如果offer(E)返回false,则抛出异常。
offer(E)方法用于入队,入队失败则返回false,反之返回true,
1 public boolean offer(E e) {
2 checkNotNull(e);
3 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
4 lock.lock();
5 try {
6 //该队列用于判断队列是否已满,满队时返回false
7 if(count == items.length) {
8 return false;
9 } else {
10 enqueue(e);
11 return true;
12 }
13 } finally {
14 lock.unlock();
15 }
16 }
offer(E,long,TimeUnit)方法会通过反复入队来保证offer成功,除非线程中断。
1 public boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUint unit) throws InterruptedException {
2 checkNotNull(e);
3 long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
4 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
5 lock.lockInterruptibly();
6 try {
7 //尝试入队,如果入队失败那么阻塞当前线程指定时长之后,再次尝试
8 while(count == items.length) {
9 if(nanos <= 0) {
10 return false;
11 }
12 nanos = notFull.awaitNanos(nanos);
13 }
14 enqueue(e);
15 return true;
16 }
17 finally {
18 lock.unlock();
19 }
20 }
put(E)方法用于入队,队满则等待notFull被唤醒,或者发起了中断
1 public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
2 checkNotNull(e);
3 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
4 //当前线程为终端的情况下获取锁
5 lock.lockInterruptibly();
6 try {
7 //队列已满时,阻塞当前线程,直到可以插入值
8 while(count == items.length) {
9 notFull.await();
10 }
11 enqueue(e);
12 } finally {
13 lock.unlock();
14 }
15 }
add/offer/put方法特点
1) 这三个方法使用了重入锁,都是线程安全的
2) offer方法只会尝试入队一次,入队失败则返回false
3) add方法入队失败则抛出异常
4) put方法在未中断的情况下,会一直尝试入队,如果被中断则抛出中断异常,那么需要有使用者自行处理,notFull对象监视器会在出队时唤醒。
enqueue(E x)方法
该方法执行了真正的入队,源码实现很简单,主要思路是把x添加到队尾,然后唤醒notEmpty对象监视器。
1 private void enqueue(E x) {
2 final Object[] items = this.items;
3 items[putIndex] = x;
4 //putIndex达到数组上限的时候,归零,这说明这是个循环队列
5 if(++putIndex == item.length) {
6 putIndex = 0
7 }
8 count++;
9 notEmpty.signal();
10 }
add/offer/put方法都会调用enqueue方法,而唤醒notEmpty对象监视器的作用在于,通知可以被notEmpty阻塞的方法poll/take,以中断阻塞。
remove(Object o)方法用于移除指定元素,而poll、take则从队列取元素。
1 public boolean remove(Object o) {
2 if(o == null) return false;
3 final Object[] items = this.items;
4 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
5 lock.lock();
6 try {
7 if(count > 0) {
8 final int putIndex = this.putIndex;
9 int i = takeIndex;
10 do {
11 //循环比较对象是否一致,取得对应下标
12 if(o.equals(item[i])) {
13 //移除指定下标位置的对象
14 removeAt(i);
15 return true;
16 }
17 if(++i == items.length) {
18 i = 0;
19 }
20 } while (i != putIndex);
21 }
22 return false;
23 }
24 finally {
25 lock.unlock();
26 }
27 }
removeAt(int)方法的逻辑并不复杂,实现思路如下:
1) 如果需要被移除的index处于队尾,那么直接移除队尾元素,不移动其他元素
2) 反之,则移除指定index后,把所有元素前移一位。
3) 唤醒notFull对象监视器
take方法用于去除队头元素,如果队列为空,那么它会等待notEmpty被唤醒,或者发起中断。
1 public E take() throws InterruptedException {
2 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
3 lock.lockInterruptibly();
4 try {
5 //容器没有数据时,使用notmpty对象监视器阻塞当前线程
6 while(count == 0) {
7 notEmpty.await();
8 }
9 return dequeue();
10 } finally {
11 lock.unlock();
12 }
13 }
poll方法用于去除队头元素,如果队列为空,那么返回null。
1 public E poll() {
2 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
3 lock.lock();
4 try {
5 //容器没有数据时,返回null
6 return (count == 0) ? null : dequeue();
7 } finally {
8 lock.unlock();
9 }
10 }
remove、poll、take特点:
这三个方法都是现成安全的。
1) remove方法可以移除任意对象,需要遍历比对对象来确定下标位置,并且可能需要移动大量数据位置,效率较低。
2) removeAt方法可以移除指定下标的元素,比之remove少了比对过程,但它也需要移动大量数据位置,效率稍微好一点。
3) poll和take只能移除队头元素,效率极高。
dequeue方法,它的逻辑很简单
1) 移除容器里的指定对象
2) 迭代器执行elementDequed来保证一致性
3) 唤醒notFull对象监视器
1 private E dequeue() {
2 final Object[] items = this.itmes;
3 @SuppresswArnings("unchecked")
4 E x = (E)item.[takeIndex];
5 items[takeIndex] = null;
6 if(++takeIndex == items.length) {
7 takeIndex = 0;
8 }
9 count--;
10 it(itrs != null) {
11 itrs.elementDequeued();
12 }
13 notFull.signal();
14 return x;
15 }
peek()方法用于查看队头元素,代码略。
总结,ArrayBlockingQueue特点:
1) 使用数组进行存储
2) enqueue()和dequeue()方法是入队和出队的核心方法,他们分别通知”队列非空”和”队列非满”,从而使阻塞中的入队和出队方法能够继续执行,以实现生产者消费者模式。
3) 插入只能从队尾开始,移除可以是任意位置,但是移除队头以外的元素效率很低。
4) ArrayBlockingQueue是个循环队列