一. 安装OpenResty
创建OpenResty用户
# useradd -M www -s /usr/sbin/nologin
安装OpenResty
# apt-get install libpcre3-dev
libssl-dev perl make build-essential curl zlib1g-dev -y
# cd /usr/local/src/ && wget https://openresty.org/download/openresty-1.17.8.1rc1.tar.gz
# tar -xf openresty-1.17.8.1rc1.tar.gz
# cd openresty-1.17.8.1rc1
# ./configure --user=www -j2 #不指定--prefix, 默认安装位置在/usr/local/openresty
# make -j2
# make install
创建软连接
# ln -sv /usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/local/sbin/
启动openresty
# nginx
更多安装方式请阅读官网文档: http://openresty.org/en/installation.html
二. 第一个"hello world"
在OpenResty中写lua代码,主要包含这两步
- 修改nginx配置文件,将lua代码嵌入其中
- 重载OpenResty使之生效
下面写一个最简单的nginx.conf,在根目录新增content_by_lua_block;,利用ngx.say将“hello,world”打印出来。
user www;
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80;
location / {
content_by_lua_block {
ngx.say("hello world!")
}
}
}
}
检测并重载OpenResty
# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/openresty//nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/openresty//nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
# nginx -s reload
如果语法没有报错,并且重载成功,就可以在浏览器或者curl命令来查看返回结果了。
# curl -i 127.0.0.1
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: openresty/1.17.8.1rc1
Date: Fri, 22 May 2020 10:29:58 GMT
Content-Type: application/octet-stream
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Connection: keep-alive
hello world!
上面打印"hello world" 的方式是直接将lua代码嵌入到nginx配置文件中,我们也可以将lua代码抽离出来,保持代码的可读性和可维护性。
操作其实也很简单。
我们现在/usr/local/openresty/nginx/html目录下创建一个lua目录专门保存lua代码,将ngx.say 写到hello.lua文件中
# cd /usr/local/openresty/nginx/html
# mkdir lua
# cat lua/hello.lua
ngx.say("hello world!")
稍微修改一下上面nginx.conf配置文件,把content_by_lua_block 改成 content_by_lua_file。
user www;
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80;
location / {
default_type 'text/plain';
content_by_lua_file html/lua/hello.lua;
}
}
}
重载OpenResty
# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/openresty//nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/openresty//nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
nginx -s reload
使用curl命令来查看返回结果。
# curl -i 127.0.0.1
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: openresty/1.17.8.1rc1
Date: Fri, 22 May 2020 10:32:41 GMT
Content-Type: application/octet-stream
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Connection: keep-alive
hello world!
content_by_lua_block 语法
content_by_lua_file 语法
三. 收集日志
从这部分开始,我们将一直使用lua代码抽离的方式去完成。
在lua目录创建get_log.lua文件,先尝试获取一下client端的ip地址。
# cat /usr/local/openresty/nginx/html/lua/get_log.lua
local headers = ngx.req.get_headers()
local ip = headers["X-REAL-IP"] or headers["X_FORWARDED_FOR"] or ngx.var.remote_addr or "0.0.0.0"
ngx.say(ip)
在nginx虚拟主机新增一个/log的location,将get_log.lua代码放置在/log下。
location /log {
default_type 'text/plain';
content_by_lua_file html/lua/get_log.lua;
}
重载Openresty后用curl测试
# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/openresty//nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/openresty//nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
# nginx -s reload
# curl -i 127.0.0.1/log
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: openresty/1.17.8.1rc1
Date: Fri, 22 May 2020 10:38:42 GMT
Content-Type: application/octet-stream
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Connection: keep-alive
127.0.0.1
获取完client端ip后,我们再尝试获取更多的数据,举个栗子,获取url的请求参数和服务器时间。
继续编写get_log.lua代码文件
local dkjson = require "cjson"
local headers = ngx.req.get_headers()
local ip = headers["X-REAL-IP"] or headers["X_FORWARDED_FOR"] or ngx.var.remote_addr or "0.0.0.0"
local uri_args = ngx.req.get_uri_args()
local page_json = {}
if uri_args then
for key,val in pairs(uri_args) do
page_json[string.lower(key)] = val
end
end
page_json["client_ip"] = ip
page_json['server_time'] = ngx.now() * 1000
ngx.say(dkjson.encode(page_json))
检测重载
# curl -i '127.0.0.1/log?ak=abc&city=北京&name=guoew&age=18'
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: openresty/1.17.8.1rc1
Date: Fri, 22 May 2020 10:47:28 GMT
Content-Type: application/octet-stream
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Connection: keep-alive
{"client_ip":"127.0.0.1","city":"北京","ak":"abc","name":"guoew","age":"18","server_time":1590144448725}
我们也可以获取POST方式请求的data信息,利用
ngx.req.get_post_args方法,具体实现就不在这里写了。
当OpenResty接收到文件时,如果需要落地到本地磁盘,该怎么处理呢?
先在服务器创建/data/logs目录以存放日志文件。
# mkdir -p /data/logs/ && chown www.www -R /data/logs
继续修改get_log.lua代码文件,新增mylog函数,log文件命名为json_log.log。
local dkjson = require "cjson"
local headers = ngx.req.get_headers()
local log_file = 'json_log.log'
function mylog(msg,log_file)
local file, err = io.open("/data/logs/" .. log_file,"aw+")
if file == nil then
ngx.say(err)
else
file:write (msg..'
')
file:flush();
file:close();
end
end
local ip = headers["X-REAL-IP"] or headers["X_FORWARDED_FOR"] or ngx.var.remote_addr or "0.0.0.0"
local uri_args = ngx.req.get_uri_args()
local page_json = {}
if uri_args then
for key,val in pairs(uri_args) do
page_json[string.lower(key)] = val
end
end
page_json["client_ip"] = ip
page_json['server_time'] = ngx.now() * 1000
mylog(dkjson.encode(page_json),log_file)
ngx.say(dkjson.encode(page_json))
重载OpenResty,使用curl测试,会发现/data/logs/目录下生成json_log.log文件,内容如下
# cat /data/logs/json_log.log
{"client_ip":"127.0.0.1","city":"北京","ak":"abc","name":"guoew","age":"18","server_time":1590144899538}
ngx.req.get_headers用法
ngx.req.get_uri_args用法
ngx.req.get_post_args用法
四. 限流控制
限流控制会根据客户端ip与uri作为校验值进行判断,这部分将会使用到lua_share_dict。限流控制是参考赵班长的 使用Nginx+Lua实现的WAF改编而来。实现了 单个客户端ip访问某一个接口 30s内最多只能访问3次,否则返回403。
在/usr/local/openresty/nginx/html/lua/下创建 waf目录,作为限流相关代码的workspace。
# mkdir /usr/local/openresty/nginx/html/lua/waf
在nginx.conf的http context中申请名称为limit,大小为50m的共享内存。并添加waf目录到lua PATH路径中去。
lua_shared_dict limit 50m;
lua_package_path "/usr/local/openresty/nginx/html/lua/waf/?.lua;;";
方便日后进行横向扩展(IP黑白名单,URL黑白名单,SQL注入,User-Agent过滤,等等),将代码按功能拆分,编写对应代码,目录结构如下
waf/
├── access.lua #统一入口脚本
├── config.lua #配置开关
├── init.lua #初始化函数
└── lib.lua #依赖函数
对应代码如下
config.lua
--WAF config file,enable = "on",disable = "off"
-- Define waf switch
config_waf_enable = "on"
-- Define cc switch
config_cc_check = "on"
-- Define cc rate(CCcount/CCseconds)
config_cc_rate = "3/30"
lib.lua
--Get the client IP
function get_client_ip()
local headers = ngx.req.get_headers()
local CLIENT_IP = headers["X-REAL-IP"] or headers["X_FORWARDED_FOR"] or ngx.var.remote_addr
if CLIENT_IP == nil then
CLIENT_IP = "unknown"
end
return CLIENT_IP
end
--Get the client user agent
function get_user_agent()
local USER_AGENT = ngx.var.http_user_agent
if USER_AGENT == nil then
USER_AGENT = "unknown"
end
return USER_AGENT
end
--WAF log record for json,(use logstash codec => json)
function log_record(method,url,data,ruletag)
local cjson = require("cjson")
local io = require 'io'
local LOG_PATH = "/data/logs/"
local CLIENT_IP = get_client_ip()
local USER_AGENT = get_user_agent()
local SERVER_NAME = ngx.var.server_name
local LOCAL_TIME = ngx.localtime()
local log_json_obj = {
client_ip = CLIENT_IP,
local_time = LOCAL_TIME,
server_name = SERVER_NAME,
user_agent = USER_AGENT,
attack_method = method,
req_url = url,
req_data = data,
rule_tag = ruletag,
}
local LOG_LINE = cjson.encode(log_json_obj)
local LOG_NAME = LOG_PATH..'/'..ngx.today().."_waf.log"
local file, err = io.open(LOG_NAME,"aw+")
if file == nil then
return
else
file:write(LOG_LINE.."
")
file:flush()
file:close()
end
end
access.lua
require "init"
local function waf_main()
if cc_attack_check() then
else
return
end
end
-- main
waf_main()
init.lua
require 'lib'
require 'config'
--deny cc attack
function cc_attack_check()
if config_cc_check == "on" then
local ATTACK_URI = ngx.var.uri
local CC_TOKEN = get_client_ip() .. ATTACK_URI
local limit = ngx.shared.limit
local CCcount=tonumber(string.match(config_cc_rate,'(.*)/'))
local CCseconds=tonumber(string.match(config_cc_rate,'/(.*)'))
local req,_ = limit:get(CC_TOKEN)
if req then
if req >= CCcount then
log_record('CC_Acttack',ngx.var.request_uri,"-","-")
if config_waf_enable == "on" then
ngx.exit(403)
end
else
limit:incr(CC_TOKEN,1)
end
else
limit:set(CC_TOKEN,1,CCseconds)
end
end
return
end
在nginx.conf 中http context 添加初始化和入口脚本。截止当前,如下是nginx.conf所有的配置。
user www;
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
lua_shared_dict limit 50m;
lua_package_path "/usr/local/openresty/nginx/html/lua/waf/?.lua;;";
init_by_lua_file "/usr/local/openresty/nginx/html/lua/waf/init.lua";
access_by_lua_file "/usr/local/openresty/nginx/html/lua/waf/access.lua";
server {
listen 80;
location / {
default_type 'text/plain';
content_by_lua_file html/lua/hello.lua;
}
location /log {
default_type 'text/plain';
content_by_lua_file html/lua/get_log.lua;
}
}
}
重启nginx使之生效,然后使用curl进行10次测试,会发现同一个url地址在访问第四次时,直接返回403。
# for i in `seq 1 10` ; do curl -I 127.0.0.1/log 2>/dev/null | awk '/^HTTP/{print $2}' ; done
200
200
200
403
403
403
403
403
403
403
在这里再解释一下限流的功能,单个客户端ip访问某一个接口 30s内最多只能访问3次,否则返回403,也就是说该限流限制的是访问接口的频次,而非访问服务端域名的频次。
当客户端超过限制时,如果感觉返回403不太友好,也可以自定义内容,或者考虑重定向到其他页面。下面是重定向到 阿拉丁指数 首页的一段伪代码。
...
if config_waf_enable == "on" then
ngx.redirect('https://www.aldzs.com')
--ngx.exit(403)
end
...
lua_share_dict 用法
init_by_lua_file 用法
access_by_lua_file 用法
ngx.redirect 用法
五. 白名单
六. 灰度发布
灰度发布demo是基于客户端IP来实现的,是参考Openresty+Lua+Redis灰度发布 完成。流程图如下,在管理后台设置灰度IP名单,允许一部分用户(灰度IP名单)访问预发布环境,其他用户则访问原有生产环境。
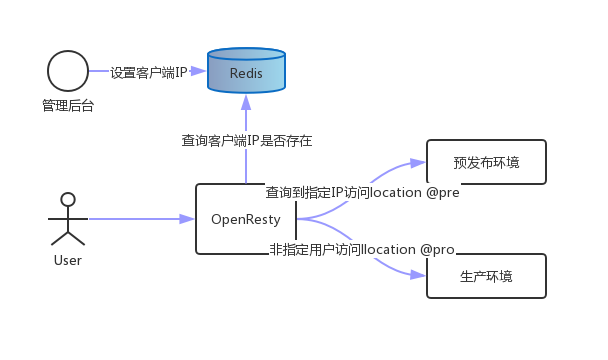
执行过程:
- 当用户请求到达前端web(代理)服务器Openresty,内嵌的lua模块解析Nginx配置文件中的lua脚本代码;
- Lua获取客户端IP地址,去查询Redis中是否有该键值,如果有返回值执行@pre,否则执行@pro。
- Location @pre把请求转发给预发布服务器,location @pro把请求转发给生产服务器,服务器返回结果,整个过程完成。
安装redis-server
# apt install redis-server -y
OpenResty部分配置如下
user www;
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
keepalive_timeout 65;
upstream pro {
server 127.0.0.1:81; #模拟生产环境
}
upstream pre {
server 127.0.0.1:82; #模拟预发布环境
}
lua_shared_dict limit 50m;
lua_package_path "/usr/local/openresty/nginx/html/lua/waf/?.lua;;";
init_by_lua_file "/usr/local/openresty/nginx/html/lua/waf/init.lua";
access_by_lua_file "/usr/local/openresty/nginx/html/lua/waf/access.lua";
server {
listen 80;
location /gray {
default_type 'text/plain';
content_by_lua_file html/lua/gray.lua ;
}
location @pro {
proxy_pass http://pro;
}
location @pre {
proxy_pass http://pre;
}
}
server {
listen 81;
default_type 'text/plain';
add_header Content-Type 'text/html; charset=htf-8';
return 200 "<h1>This is pro</h1>" ;
}
server {
listen 82;
default_type 'text/plain';
add_header Content-Type 'text/html; charset=htf-8';
return 200 "<h1>This is pre</h1>";
}
error_log /data/logs/error.log debug ;
}
在/usr/local/openresty/nginx/html/lua/下编写 gray.lua脚本,内容如下
require "lib"
local redis = require "resty.redis"
local red = redis:new()
red:set_timeouts(1000, 1000, 1000) -- 1 sec
local ok, err = red:connect("127.0.0.1", 6379)
if not ok then
ngx.say("failed to connect: ", err)
return
end
local local_ip = get_client_ip()
local intercept = red:get(local_ip)
if intercept == local_ip then
ngx.exec("@pre")
return
end
ngx.exec("@pro")
local ok, err = red:close()
if not ok then
ngx.say("failed to close:", err)
return
end
在redis里set本机回环ip的键值对,使用curl进行测试
# redis-cli
127.0.0.1:6379> set 127.0.0.1 127.0.0.1
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> exit
root@VM-0-2-ubuntu:/usr/local/openresty/nginx/html/lua# curl -i 127.0.0.1/gray
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: openresty/1.17.8.1rc1
Date: Wed, 27 May 2020 09:10:27 GMT
Content-Type: text/plain
Content-Length: 11
Connection: keep-alive
<h1>This is pre</h1>
通过其他服务器进行curl测试
# curl -i 118.24.64.250/gray
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: openresty/1.17.8.1rc1
Date: Wed, 27 May 2020 09:11:21 GMT
Content-Type: text/plain
Content-Length: 11
Connection: keep-alive
<h1>This is pro</h1>
为了方便进行测试验证,在118.24.64.250这个web服务,增加了一个/set接口,可以直接将客户端IP设置到redis中,过期时间15s。测试如下
# curl 118.24.64.250/set ; curl 118.24.64.250/gray ; sleep 16 ; curl 118.24.64.250/gray
{"code": 200,"message": "This key(182.254.208.xxx) is set successfully!"}
<h1>This is pre</h1>
<h1>This is pro</h1>
lua-resty-redis 用法
ngx.exec 用法
END