2.0 注释
python的注释方法
"""
多行注释 可实现换行
"""
#单行注释
2.1 变量
- 问:为什么要有变量?
- 为某个值创建一个“外号”,以后在使用时候通过此外号就可以直接调用。
- 创建一个变量
name = "gkf" #name是变量名 等号就是声明(或赋值) "gkf"是变量的值
age = 18 #age是标量名 等号就是声明(或赋值) 18是变量的值
2.2 变量名命名规范
-
可以使用字母数字下滑线组合 如: name ="gkf" num_1 = 318 或 _hobby = "美女"
-
不能以数字不能开头
-
不能使用python关键字
#python的关键字有 [False', 'None', 'True', 'and', 'as', 'assert', 'break', 'class', 'continue', 'def', 'del',
'elif', 'else', 'except', 'finally', 'for', 'from', 'global', 'if', 'import', 'in', 'is', 'lambda',
'nonlocal', 'not', 'or', 'pass', 'raise', 'return', 'try', 'while', 'with', 'yield']
- 建议 见名知意,尽量使用下划线连接,不要使用拼音,避免大小写交替(驼峰体)
- 正确示范: user_name = "gkf666"
- 全局变量全部大写
### 2.3 常量
- 不允许修改的值,Python中执行约定。(不常使用)
### 2.4 输入 input
- input (input默认输入是字符串,如要需要可以进行转换)
```python
name = input("请输入姓名") #python3
name = raw_input("请输入姓名") #python2
- 执行结果:

- 注意 v = input("输入") v的类型是字符串,当我们在使用变量v的时候,要考虑是否要进行类型转换
v = input("输入一个数字")
print(v,type(v)) #type(v) 查看v的类型 #注意代码中所有的字符必须是英文格式,不然会报错
#执行结果
输入一个数字6
6 <class 'str'> #6是str(字符串类型)
Process finished with exit code 0
- 强行翻译一波input源码注释
"""
Read a string from standard input. The trailing newline is stripped.
The prompt string, if given, is printed to standard output without a
trailing newline before reading input.
If the user hits EOF (*nix: Ctrl-D, Windows: Ctrl-Z+Return), raise EOFError.
On *nix systems, readline is used if available.
"""
从标准输入中读取字符串。删除尾随换行符。如果给出了提示字符串,则在读取输入之前将其打印到标准输出而没有尾随换行符。
如果用户点击EOF(* nix:Ctrl-D,Windows:Ctrl-Z + Return),则引发EOFError。在* nix系统上,如果可用,则使用readline。
2.5 输出 print
-
print (输出/打印 你要的东西) 在print2版本里面 print "你好"中间加空格。
print("hello word") # py版本 3 print "hello word" # py版本 2 #结合input一起使用 name = input("请输入姓名") sex = input("请输入性别") print("%s,%s"%(name,sex)) #%s是字符串占位符,用来拼接内容 -
执行结果:
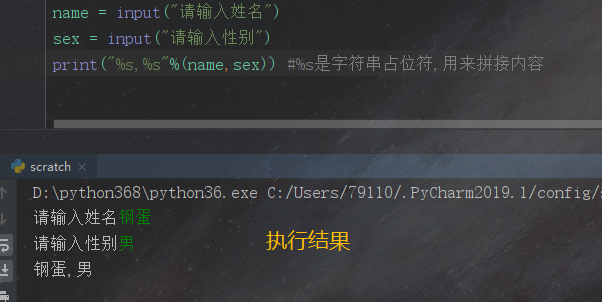
- 在Python中print默认是换行的,end=' '',默认有一个空格sep=' '
#在Python中print默认是换行的
n = '你'
m = '好'
print(n,m)
#你 好 执行结果
print(n,m,sep='')#默认有个空格 sep=' ',sep=''去掉空格
#你好 执行结果
print(n,end='')#end=""去除默认的换行符
print(m) #print 默认有一个 end="
"换行
#你好 执行结果
print(value,...,sep ='',end =' n',file = sys.stdout,flush = False)默认情况下,将值打印到流或sys.stdout。
可选的关键字参数:file:类文件对象(stream); 默认为当前的sys.stdout。sep:在值之间插入的字符串,默认为空格。
end:在最后一个值后附加的字符串,默认为换行符。flush:是否强制刷新流。
st = """支持换行
我是行
"""
st1 ='''支持换行
我是行
'''
print(st)
print(st1)
# 执行结果
支持换行
我是行
支持换行
我是行
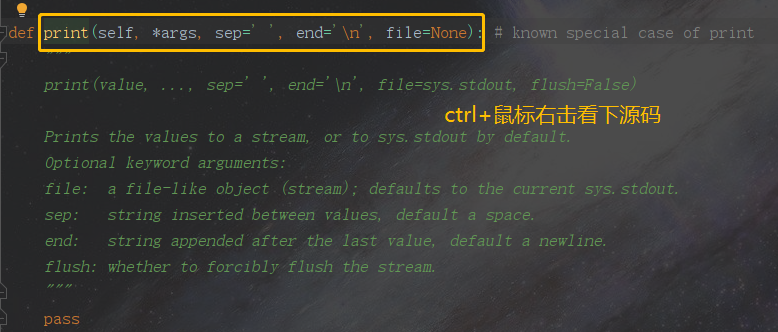
- 强行翻译一波print源码注释
"""
print(value, ..., sep=' ', end='
', file=sys.stdout, flush=False)
Prints the values to a stream, or to sys.stdout by default.
Optional keyword arguments:
file: a file-like object (stream); defaults to the current sys.stdout.
sep: string inserted between values, default a space.
end: string appended after the last value, default a newline.
flush: whether to forcibly flush the stream.
"""
2.6 关于开发工具
- python开发工具我这里使用的是pycharm
- 大家可以参考这篇文章,选择自己喜欢的开发工具点击查看