A Binary Search Tree (BST) is recursively defined as a binary tree which has the following properties:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than or equal to the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
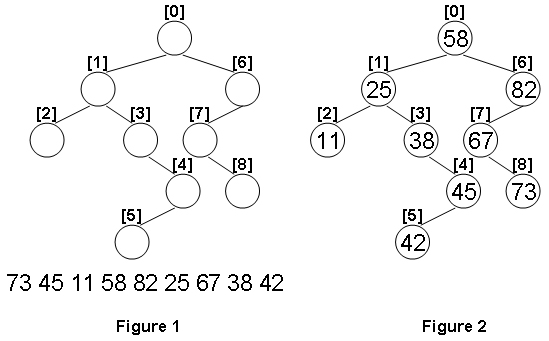
Given the structure of a binary tree and a sequence of distinct integer keys, there is only one way to fill these keys into the tree so that the resulting tree satisfies the definition of a BST. You are supposed to output the level order traversal sequence of that tree. The sample is illustrated by Figure 1 and 2.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤) which is the total number of nodes in the tree. The next N lines each contains the left and the right children of a node in the format left_index right_index, provided that the nodes are numbered from 0 to N−1, and 0 is always the root. If one child is missing, then − will represent the NULL child pointer. Finally N distinct integer keys are given in the last line.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in one line the level order traversal sequence of that tree. All the numbers must be separated by a space, with no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
9
1 6
2 3
-1 -1
-1 4
5 -1
-1 -1
7 -1
-1 8
-1 -1
73 45 11 58 82 25 67 38 42
Sample Output:
58 25 82 11 38 67 45 73 42题意:
将一个构建好的Binary Search Tree按照层序遍历的方式输出。
思路:
我的思路就是先按照题目给的条件将BST给构建好,用sor()函数将所给的数字从小到大排序,将排序好的数字从左到右依次插入到各个结点之中(BST的结点从左到右依次递增),最后在按照层序遍历的方法将其输出。
无论是构建的时候还是插入数字的时候,都需要用到在一个二叉树中查找给定数值的这一结点这样的一个函数的变形,刚开始的时候一种写不出来这个函数(估计是被递归给绕晕了),后来看了一下别人的代码,也写出来了。后来发现这种函数的重点在于先确定函数的边界(也就是什么时候跳出函数),然后就是怎样将递归函数的值返回。
node find_node(node t, int n) {
if (t == NULL) return NULL;
if (t->num == n) return t;
node ret = find_dummy(t->left, n);
if (ret != NULL) return ret;
ret = find_dummy(t->right, n);
if (ret != NULL) return ret;
else return NULL;
}
Code:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
typedef struct Node *node;
struct Node {
int num;
int data;
node left;
node right;
bool filled = false;
};
node BST = (node)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
void level_traver(node t) {
node tmp;
queue<node> q;
q.push(t);
tmp = q.front();
q.pop();
if (tmp->left) q.push(tmp->left);
if (tmp->right) q.push(tmp->right);
cout << tmp->data;
while (!q.empty()) {
tmp = q.front();
q.pop();
if (tmp->left) q.push(tmp->left);
if (tmp->right) q.push(tmp->right);
cout << " " << tmp->data;
}
}
node insert(node t) {
if (t == NULL) return NULL;
if (!t->left && !t->filled) return t;
node ret = insert(t->left);
if (ret != NULL) return ret;
if (t->left && t->left->filled && !t->filled) return t;
ret = insert(t->right);
if (ret != NULL) return ret;
else return NULL;
}
node find_dummy(node t, int n) {
if (t == NULL) return NULL;
if (t->num == n) return t;
node ret = find_dummy(t->left, n);
if (ret != NULL) return ret;
ret = find_dummy(t->right, n);
if (ret != NULL) return ret;
else return NULL;
}
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
BST->num = 0;
node dummy, ptr;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
ptr = BST;
dummy = find_dummy(ptr, i);
int left_index, right_index;
cin >> left_index >> right_index;
if (left_index > 0) {
node temp = (node)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp->num = left_index;
dummy->left = temp;
} else dummy->left = NULL;
if (right_index > 0) {
node temp = (node)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp->num = right_index;
dummy->right = temp;
} else dummy->right = NULL;
}
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int x;
cin >> x;
v.push_back(x);
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
ptr = BST;
node tmp = insert(ptr);
tmp->data = v[i];
tmp->filled = true;
}
level_traver(BST);
return 0;
}
提交的时候有两组数据显示“Segmentation Fault”,虽然说这样可以将问题解决,但是感觉还是太麻烦,也容易出错。
看大佬的博客,发现他的代码并没有用链表来表示BST,而是用的数组,虽然浪费空间,但是因为本题的数据量不大,可以用,而且看上去也简洁不少。
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40550018/article/details/83589085
https://www.liuchuo.net/archives/2173