探究ElasticSearch中的线程池实现
ElasticSearch里面各种操作都是基于线程池+回调实现的,所以这篇文章记录一下java.util.concurrent涉及线程池实现和ElasticSearch中如何自定义自己的线程池的。因为我们自己开发写代码,也经常会用到线程池,一般很少有机会自己去扩充实现一个自己的线程池,比如下面是我经常用的套路,其中SidSearchExceptionHandler和SidSearchRejectExecutionHandler都只是简单地记录日志。
//任务队列
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1024);
//线程在执行过程中的异常处理器
private SidSearchExceptionHandler exceptionHandler = new SidSearchExceptionHandler();
//向线程池提交任务时,拒绝策略
private SidSearchRejectExecutionHandler rejectExecutionHandler = new SidSearchRejectExecutionHandler();
//借助Guava包中的ThreadFactoryBuild创建线程工厂(主要是方便指定线程的名称,debug起来清晰)
private ThreadFactory threadFactory = new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("audio-%d").setUncaughtExceptionHandler(exceptionHandler).build();
//创建线程池
private ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads, 1, TimeUnit.DAYS, taskQueue, threadFactory, rejectExecutionHandler);
比如下面这个自定义线程执行时异常处理策略,在线程执行过程中抛出异常时,只是简单地打印日志:
public class SidSearchExceptionHandler implements Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler {
public static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SidSearchExceptionHandler.class);
@Override
public void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e) {
logger.error("sid search thread pool execution error,thread name:{},cause:{},msg:{}",
t.getName(), e.getCause(), e.getMessage());
}
}
因此,看ES自定义的线程池实现,看下大神们是如何继承ThreadPoolExecutor,定义异常处理策略的。
线程池基础知识
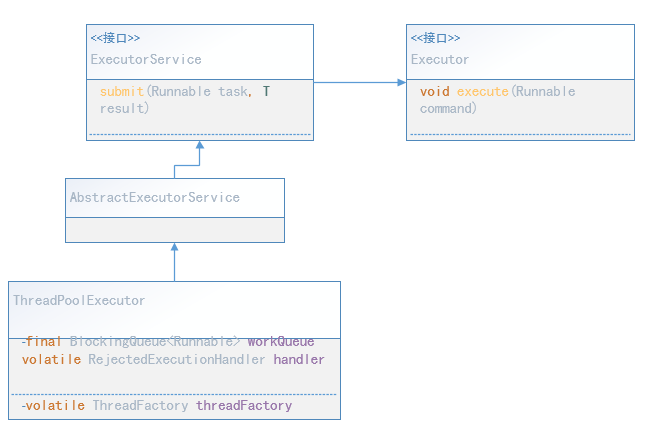
1. 定义任务
想要执行:任务、或者叫业务逻辑的载体是:通过定义一个类,implements Runnable接口,Override Runnable接口的run()方法,在run()方法里面写业务逻辑处理代码(比如将数据写入到数据库、向ElasticSearch提交查询请求……)
2. 提交任务
执行 java.util.concurrent.Executor的 execute(Runnable runnable)方法,就能提交任务,线程池中某个具体的线程会执行提交的任务。
当所有的任务执行完成后,线程池是否要关闭?如果需要执行可返回结果的任务怎么办?于是乎ExecutorService 就扩展Executor接口:public interface ExecutorService extends Executor ,提供了这些功能。
3. 执行任务
相比于ExecutorService,ThreadPoolExecutor添加了两个方法,这样可以在任务执行前和执行完成后做一些处理。
protected void beforeExecute(Thread t, Runnable r) { }
protected void afterExecute(Runnable r, Throwable t) { }
ElasticSearch中的EsThreadPoolExecutor.java就实现了这两个方法。
而真正的任务执行是在ThreadPoolExecutor的内部类Worker中run()方法实现
private final class Worker extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer implements Runnable
{
// 接受一个Runnable任务,然后执行ThreadFactory newThread()创建线程执行任务
Worker(Runnable firstTask) {
setState(-1); // inhibit interrupts until runWorker
this.firstTask = firstTask;
this.thread = getThreadFactory().newThread(this);
}
/** Delegates main run loop to outer runWorker */
public void run() {
runWorker(this);
}
}
Work implements Runnable,调用ThreadPoolExecutor的 final void runWorker(Worker w)执行任务。
来看一下runWorker方法中的部分代码:
final void runWorker(Worker w) {
Thread wt = Thread.currentThread();
Runnable task = w.firstTask;
try {
//任务执行前做一些处理
beforeExecute(wt, task);
Throwable thrown = null;
try {
//任务执行
task.run();
} catch (RuntimeException x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (Error x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (Throwable x) {
thrown = x; throw new Error(x);
} finally {
//任务执行完成后做一些处理
afterExecute(task, thrown);
}
任务是由具体的线程来执行的,因此还需要考虑线程是如何创建的。ThreadFactory定义了创建线程池的方法newThread
public interface ThreadFactory {
/**
* Constructs a new {@code Thread}. Implementations may also initialize
* priority, name, daemon status, {@code ThreadGroup}, etc.
*
* @param r a runnable to be executed by new thread instance
* @return constructed thread, or {@code null} if the request to
* create a thread is rejected
*/
Thread newThread(Runnable r);
}
在Executors工具类里面定义了具体的工厂类,用来创建线程池
/**
* The default thread factory
*/
static class DefaultThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
private static final AtomicInteger poolNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final ThreadGroup group;
private final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final String namePrefix;
DefaultThreadFactory() {
SecurityManager s = System.getSecurityManager();
group = (s != null) ? s.getThreadGroup() :
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
namePrefix = "pool-" +
poolNumber.getAndIncrement() +
"-thread-";
}
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(group, r,
namePrefix + threadNumber.getAndIncrement(),
0);
if (t.isDaemon())
t.setDaemon(false);
if (t.getPriority() != Thread.NORM_PRIORITY)
t.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
return t;
}
}
ElasticSearch 源码线程池实现
1. EsThreadFactory创建线程
EsExecutors的内部类EsThreadFactory
static class EsThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
final ThreadGroup group;
final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
final String namePrefix;
EsThreadFactory(String namePrefix) {
this.namePrefix = namePrefix;
SecurityManager s = System.getSecurityManager();
group = (s != null) ? s.getThreadGroup() :
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
}
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(group, r,
namePrefix + "[T#" + threadNumber.getAndIncrement() + "]",
0);
t.setDaemon(true);
return t;
}
}
线程组、线程数量、线程名称
在创建线程时,一般会为之指定一个线程执行的异常处理策略。惊奇的是EsThreadFactory里面并没有显示地定义线程执行时的异常处理策略(可能在其他代码中,通过匿名内部类的方式定义了异常处理策略吧)。而是使用ThreadGroup中定义的默认异常处理策略:
public class ThreadGroup implements Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler {
如果要自定义线程执行过程中出现异常的处理策略,只需要 implements Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler并且重写它的uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e)方法即可。如果未提供线程执行过程中出现异常的处理策略,那么就使用该默认的异常处理策略。
看java.lang.ThreadGroup里面的uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e)方法的注释:
Called by the Java Virtual Machine when a thread in this thread group stops because of an uncaught exception, and the thread does not have a specific Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler installed.
The uncaughtException method of ThreadGroup does the following:
If this thread group has a parent thread group, the uncaughtException method of that parent is called with the same two arguments.
Otherwise, this method checks to see if there is a Thread.getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler default uncaught exception handler installed, and if so, its uncaughtException method is called with the same two arguments.
如果在创建线程工厂的时候指定了UncaughtExceptionHandler,通过Thread.getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler 就能获取到。
//在创建线程工厂时调用setUncaughtExceptionHandler方法设置一个自定义的:UncaughtExceptionHandler
//若在线程执行过程中出现了异常,那么 exceptionHandler 对象的uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e) 方 //法就会被调用
private ThreadFactory threadFactory = new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("audio-%d").setUncaughtExceptionHandler(exceptionHandler).build();
Otherwise, this method determines if the Throwable argument is an instance of ThreadDeath. If so, nothing special is done. Otherwise, a message containing the thread's name, as returned from the thread's Thread.getName method, and a stack backtrace,using the Throwable's Throwable.printStackTrace method, is printed to the System err
当未指定异常处理器时,若参数Throwable e是一个ThreadDeath对象,那么什么也不做。
如果参数Throwable e不是一个ThreadDeath对象,那么就会通过方法Throwable.printStackTrac打印异常
2.EsThreadPoolExecutor 创建线程池
public class EsThreadPoolExecutor extends ThreadPoolExecutor {
private final ThreadContext contextHolder;
private volatile ShutdownListener listener;
A ThreadContext is a map of string headers and a transient map of keyed objects that are associated with a thread. It allows to store and retrieve header information across method calls, network calls as well as threads spawned from a thread that has a ThreadContext associated with.
从它的构造方法中可看出,多了个ThreadContext(多了保存一些线程执行上下文信息的功能)
EsThreadPoolExecutor(String name, int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory, XRejectedExecutionHandler handler,
ThreadContext contextHolder) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue, threadFactory, handler);
this.name = name;
this.contextHolder = contextHolder;
}
再看EsThreadPoolExecutor Override ThreadPoolExecutor 的execute()方法:
@Override
public void execute(final Runnable command) {
doExecute(wrapRunnable(command));
}
protected void doExecute(final Runnable command) {
try {
super.execute(command);
} catch (EsRejectedExecutionException ex) {
if (command instanceof AbstractRunnable) {
// If we are an abstract runnable we can handle the rejection
// directly and don't need to rethrow it.
try {
((AbstractRunnable) command).onRejection(ex);
} finally {
((AbstractRunnable) command).onAfter();
}
} else {
throw ex;
}
}
}
doExecute()先执行super.execute(command);在这里面有任务拒绝策略的检查逻辑,如果任务被拒绝了,就会调用EsAbortPolicy的rejectedExecution()
if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) {
int recheck = ctl.get();
if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command))
//调用拒绝策略
reject(command);
else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
/**
* Invokes the rejected execution handler for the given command.
* Package-protected for use by ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor.
*/
final void reject(Runnable command) {
//handler 就是在new ThreadPoolExecutor对象 时传递的 RejectedExecutionHandler对象
handler.rejectedExecution(command, this);
}
然后可以在doExecute()里面多做一些额外的处理:((AbstractRunnable) command).onRejection(ex);任务被拒绝之后发个消息通知啥的。
ElasticSearch中的拒绝策略实现EsAbortPolicy:
public class EsAbortPolicy implements XRejectedExecutionHandler {
private final CounterMetric rejected = new CounterMetric();
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
if (r instanceof AbstractRunnable) {
//判断任务是否要强制执行
if (((AbstractRunnable) r).isForceExecution()) {
BlockingQueue<Runnable> queue = executor.getQueue();
//创建ThreadPoolExecutor指定的 任务队列 类型是SizeBlockingQueue
if (!(queue instanceof SizeBlockingQueue)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("forced execution, but expected a size queue");
}
try {
//尽管任务执行失败了,还是再一次把它提交到任务队列,这样拒绝的任务又可以有执行机会了
((SizeBlockingQueue) queue).forcePut(r);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw new IllegalStateException("forced execution, but got interrupted", e);
}
return;
}
}
rejected.inc();
throw new EsRejectedExecutionException("rejected execution of " + r + " on " + executor, executor.isShutdown());
}
@Override
public long rejected() {
return rejected.count();
}
}
public interface XRejectedExecutionHandler extends RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* The number of rejected executions.
*/
long rejected();
}
XRejectedExecutionHandler统计任务被拒绝的次数。用的是java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAdder,又发现了一个新的计数器:关于LongAdder与AtomicLong的对比
看完这个实现,是不是下次也可以模仿实现:当向 线程池 提交任务被拒绝了,也能够失败重试~
前面讲了这么多,都是在对比ElasticSearch中的线程池与JDK并发包中的线程池背后执行的一些原理。ElasticSearch中的自定义线程池就是基于JDK并发包中的线程池实现的。
下面来正式分析下ElasticSearch源码中线程池创建流程。
在节点启动过程中,org.elasticsearch.node.Node.java 开始创建线程池:
final ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(settings, executorBuilders.toArray(new ExecutorBuilder[0]));
看ThreadPool源码:里面有很多实例变量,如下:
public class ThreadPool extends AbstractComponent implements Scheduler, Closeable {
private Map<String, ExecutorHolder> executors = new HashMap<>();
static final ExecutorService DIRECT_EXECUTOR = EsExecutors.newDirectExecutorService();
private final Map<String, ExecutorBuilder> builders;
private final ThreadContext threadContext;
private final ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor scheduler;
比如说:ExecutorService DIRECT_EXECUTOR = EsExecutors.newDirectExecutorService();就是一个线程池。还有一些线程池是通过ExecutorBuilder来创建的(Map<String, ExecutorBuilder> builders)
线程池类型:ThreadPool的内部类ThreadPoolType
public enum ThreadPoolType {
DIRECT("direct"),
FIXED("fixed"),
FIXED_AUTO_QUEUE_SIZE("fixed_auto_queue_size"),
SCALING("scaling");
一个HashMap存储线程池名称,以及相应的类型。
static {
HashMap<String, ThreadPoolType> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(Names.SAME, ThreadPoolType.DIRECT);
map.put(Names.GENERIC, ThreadPoolType.SCALING);
map.put(Names.LISTENER, ThreadPoolType.FIXED);
map.put(Names.GET, ThreadPoolType.FIXED);
map.put(Names.ANALYZE, ThreadPoolType.FIXED);
map.put(Names.INDEX, ThreadPoolType.FIXED);
map.put(Names.WRITE, ThreadPoolType.FIXED);
map.put(Names.SEARCH, ThreadPoolType.FIXED_AUTO_QUEUE_SIZE);
map.put(Names.MANAGEMENT, ThreadPoolType.SCALING);
map.put(Names.FLUSH, ThreadPoolType.SCALING);
map.put(Names.REFRESH, ThreadPoolType.SCALING);
map.put(Names.WARMER, ThreadPoolType.SCALING);
map.put(Names.SNAPSHOT, ThreadPoolType.SCALING);
map.put(Names.FORCE_MERGE, ThreadPoolType.FIXED);
map.put(Names.FETCH_SHARD_STARTED, ThreadPoolType.SCALING);
map.put(Names.FETCH_SHARD_STORE, ThreadPoolType.SCALING);
THREAD_POOL_TYPES = Collections.unmodifiableMap(map);
}
而真正创建线程池的代码,是在ThreadPool的构造方法中的for循环final ExecutorHolder executorHolder = entry.getValue().build(executorSettings, threadContext);,这行语句的build方法。
for (@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") final Map.Entry<String, ExecutorBuilder> entry : builders.entrySet()) {
final ExecutorBuilder.ExecutorSettings executorSettings = entry.getValue().getSettings(settings);
final ExecutorHolder executorHolder = entry.getValue().build(executorSettings, threadContext);
if (executors.containsKey(executorHolder.info.getName())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("duplicate executors with name [" + executorHolder.info.getName() + "] registered");
}
logger.debug("created thread pool: {}", entry.getValue().formatInfo(executorHolder.info));
executors.put(entry.getKey(), executorHolder);
}

前面枚举类 ThreadPoolType 中有四种类型的线程池,对应着上图的三个ExecutorBuild类,看org.elasticsearch.threadpool.FixedExecutorBuilder的build方法:创建线程池需要参数FixedExecutorSettings,需要保存线程上下文 ThreadContext
@Override
ThreadPool.ExecutorHolder build(final FixedExecutorSettings settings, final ThreadContext threadContext) {
int size = settings.size;
int queueSize = settings.queueSize;
final ThreadFactory threadFactory = EsExecutors.daemonThreadFactory(EsExecutors.threadName(settings.nodeName, name()));
final ExecutorService executor =
EsExecutors.newFixed(settings.nodeName + "/" + name(), size, queueSize, threadFactory, threadContext);
final String name;
if ("write".equals(name()) && Booleans.parseBoolean(System.getProperty("es.thread_pool.write.use_bulk_as_display_name", "false"))) {
name = "bulk";
} else {
name = name();
}
final ThreadPool.Info info =
new ThreadPool.Info(name, ThreadPool.ThreadPoolType.FIXED, size, size, null, queueSize < 0 ? null : new SizeValue(queueSize));
return new ThreadPool.ExecutorHolder(executor, info);
}
其中的这两行代码:
final ThreadFactory threadFactory = EsExecutors.daemonThreadFactory(EsExecutors.threadName(settings.nodeName, name()));
构建线程工厂。
final ExecutorService executor =
EsExecutors.newFixed(settings.nodeName + "/" + name(), size, queueSize, threadFactory, threadContext);
构建线程池。
至此,ElasticSearch构建线程池整个流程就是这样了。
构建出来的线程池被封装在ThreadPool.ExecutorHolder类中new ThreadPool.ExecutorHolder(executor, info);
final ThreadPool.Info info =
new ThreadPool.Info(name, ThreadPool.ThreadPoolType.FIXED, size, size, null, queueSize < 0 ? null : new SizeValue(queueSize));
return new ThreadPool.ExecutorHolder(executor, info);
当所有的线程池构造完成后,在节点启动过程中初始化各种服务时,new 这些对象时,都需要传一个ThreadPool 参数,各个服务就可以使用线程池来执行任务了。org.elasticsearch.node.Node.java 中代码:
//构造好各种线程池
final ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(settings, executorBuilders.toArray(new ExecutorBuilder[0]));
//clusterService 用到了threadPool
final ClusterService clusterService = new ClusterService(settings, settingsModule.getClusterSettings(), threadPool,
ClusterModule.getClusterStateCustomSuppliers(clusterPlugins));
//monitorService 用到了threadPool
final MonitorService monitorService = new MonitorService(settings, nodeEnvironment, threadPool, clusterInfoService);
//actionModule
ActionModule actionModule = new ActionModule(false, settings, clusterModule.getIndexNameExpressionResolver(),
settingsModule.getIndexScopedSettings(), settingsModule.getClusterSettings(), settingsModule.getSettingsFilter(),
threadPool, pluginsService.filterPlugins(ActionPlugin.class), client, circuitBreakerService, usageService);
//...在new 很多其他 XXXService时,都需要传一个ThreadPool参数。
因此,可以说ThreadPool在ElasticSearch各种操作中无处不在。哈哈。
总结
这篇文章写得有点乱,主要两个方面:一个是JDK包中原生线程池相关功能介绍,然后对比ElasticSearch中如何实现自定义的线程池。分析了ElasticSearch中自定义线程池任务提交时的拒绝策略和线程执行过程中抛出异常时的异常处理策略。然后大概分析下ElasticSearch中线程池的创建流程:从org.elasticsearch.node.Node开始:
主要涉及到以下类:
org.elasticsearch.common.util.concurrent.EsThreadPoolExecutor
org.elasticsearch.threadpool.ExecutorBuilder的三个子类:
org.elasticsearch.threadpool.FixedExecutorBuilderorg.elasticsearch.threadpool.AutoQueueAdjustingExecutorBuilderorg.elasticsearch.threadpool.ScalingExecutorBuilder
org.elasticsearch.threadpool.ThreadPool