http://blog.csdn.net/significantfrank/article/details/7712053
1. Command Pattern
基本定义: 把Command(Request)封装成对象,把发出命令(Invoker)的责任和执行命令(Receiver)的责任分割开,委派给不同的对象。
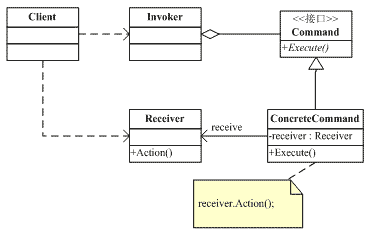
责任划分有什么好处?
责任约单一,内聚性越高,可重用的可能性越大,试想下,如果服务员不仅要点菜,还要去做菜,会是什么情景。
为什么把Invoker和Receiver解耦好处多?
类之间的耦合越低,可扩展的可能性越高。解耦后,更换一个服务员并不会影响厨师的工作
那么把Request封装成对象具体是什么意思呢?
在遥控器Remote Control例子中,比如我有一个‘开灯’的Request,那么就应该对应有一个LightOnCommand对象,关灯就应该有LightOffCommand
在Web应用中,我有一个add user的Request,那么就应有一个AddUserCommand去处理请求, 或者用struts的name convention就是AddUserAction.
那么在Struts中又是怎么运用Command Pattern的呢?
Client : FilterDispatcher Servlet
Invoker: ActionInvocation
Command: Action (not a must in Struts2)
ConcreteCommand:AddUserAction
Receiver: ServiceImpl (not a must, depends how many logic you want to put into concreteCommand)
Struts,你什么时候调用的setCommand()?
用户定义了Action Mapping在struts.xml里,在web container启动时,ConfigurationManager 就装载了struts.xml,当Request过来时,Struts Framework会根据当前的URL去找ConfigurationManager所对应的concreteCommand/Action, 然后这个Action会被set到ActionInvocation
Command Interface是必须的吗?
在struts1中,有一个Interface,所有的Action都必须是它的实现。但是在Struts2中,Action可以是任意的POJO,因为在Runtime的时候,具体的Action是什么,该调用它的什么方法,都可以通过配置文件(MetaData)+ Java Reflection来实现。这种新方式的好处是POJO Action没有了对框架的依赖,测试将会更加容易。缺点是因为没有interface的约束,调用Action的什么方法完全取决于默认值(比如execute)或是配置文件中的配置。若设置不妥,只有在Runtime的时候才能发现错误。
Receiver 是必须得吗?
不是,取决于你Action的厚度,如果你想让Action很轻的话,那么通常你会在Action中使用UserService.addUser()去做事情,此时的UserService就是Receiver。把Action设计的厚点,直接把addUser的logic放在Action中也是可以的。
Struts2中运用了command的思想,但并没有严格的按照其经典模型实现,而是做了些变通,这些变通乍看起来可能是有点违背设计原则,比如说取消了Action Interface,这不是反模式吗,反面向接口的编程吗,但仔细想想,这里我们真的需要这个接口吗?通过配置文件+Reflection,我们同样可以做到在Runtime的时候给ActionInvocation注入不同的Action的目的。而接口却增加了用户实现对框架的依赖,降低了程序的可测性,所以这样的变通其实是有积极意义的,虽然我们损失了一点点接口作为契约所带来的好处。
2. Interceptor Pattern
于其说这是模式,不如说这是AOP和Pipeline思想的结合,只不过Struts2中的实现非常的精巧,我不得不说这应该作为一个模式来推广。
AOP : 所谓的AOP就是preProcess and postProcess, 系统应用中,许多地方是需要面向切面的,比如log,authentication,etc...。看过一些实现,如Java Dynamic,但不够优雅。
Pipeline:分层就是把复杂的问题分层多个层次,每一层只处理问题的一小部分。通信的7层模型就是典型的范例
Interceptor Pattern 不仅为系统进行分层,而且还提供了AOP的处理,此外,还以一种plug-in的方式为用户提供了无限扩展的可能。
应该怎么实现?
Interceptor的调用过程类似于一个栈式调用,所以想到递归是很自然的,这既避免了像Dynamic Proxy那样的hack,又提供了更好的扩展性。
还是以Struts中的类作为例子,其类图如下:
调用过程:
Pseudo 代码:
ActionInvocation
- public Result invoke(){
- if( interceptors.hasNext() ){
- Interceptor interceptor = interceptors.next();
- result = interceptor.intercept(this);
- }
- else {
- action.execute();//如果没有更多的Interceptor,停止递归,调用action
- }
- }
public Result invoke(){
if( interceptors.hasNext() ){
Interceptor interceptor = interceptors.next();
result = interceptor.intercept(this);
}
else {
action.execute();//如果没有更多的Interceptor,停止递归,调用action
}
}
InterceptorImpl
- public SomeInterceptor implements Interceptor{
- public Result intercept(ActionInvocation actionInvocation){
- //pre-processing
- // 递归调用
- result = actionInvocation.invoke();
- //post-processing
- return result;
- }
- }
public SomeInterceptor implements Interceptor{
public Result intercept(ActionInvocation actionInvocation){
//pre-processing
// 递归调用
result = actionInvocation.invoke();
//post-processing
return result;
}
}
More: http://www.cnblogs.com/west-link/archive/2011/06/22/2086591.html
http://bosy.dailydev.org/2007/04/interceptor-design-pattern.html
Struts2 架构图
Struts 2 framework: http://viralpatel.net/blogs/introduction-to-struts-2-framework/