弦截法:
若 ![]() 在区间
在区间 ![]() 上连续且
上连续且 ![]() ,则
,则 ![]() 在区间
在区间 ![]() 有解。不妨假设其解为
有解。不妨假设其解为 ![]() ,当
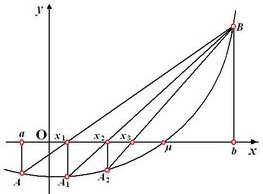
,当![]() 不是简单多项式时,无法求出其精确解,这时可以利用弦截法来求其近似解。由于过
不是简单多项式时,无法求出其精确解,这时可以利用弦截法来求其近似解。由于过 ![]() 和
和 ![]() 两点的直线
两点的直线 ![]() 的方程为
的方程为 ![]() ,将直线与
,将直线与 ![]() 轴交点的横坐标
轴交点的横坐标 ![]() 取作方程
取作方程 ![]() 在含根区间
在含根区间 ![]() 上解
上解 ![]() 的近似值,然后不断地迭代直到近似解满足所需的精度即可。
的近似值,然后不断地迭代直到近似解满足所需的精度即可。
如图所示:
cpp 实现:
// CppDemo.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 // #include "stdafx.h" #include<iostream> #include<iomanip> #include<math.h> using namespace std; float f(float x) // 求 y 函数 { float y; y = ((x - 5.0)*x + 16.0)*x - 80.0; return y; } float newx(float x1, float x2) // 求 x 的下一迭代值 { float x; x = (x1*f(x2) - x2*f(x1)) / (f(x2) - f(x1)); return x; } float root(float x1, float x2) // 求根函数 { float x, y, y1; y1 = f(x1); // 先固定(x1,y1),并不断调整(x2,y2) for(y = y1; fabs(y) >= 0.001; ) // 循环求解,判断精度是否满足需求 { x = newx(x1, x2); // 下一迭代值 x y = f(x); // x 对应的 y 值 if(y*y1 > 0) // 如果新点(x,y)和(x1,y1)在 x 轴的同侧,则替换(x1,y1) { y1 = y; x1 = x; } else { x2 = x; } } return x; } int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { float x1, x2, f1, f2, x; do{ cout<<"请输入 x1, x2 按空格分割:"<<endl; cin>>x1>>x2; f1 = f(x1); f2 = f(x2); }while(f1*f2 >= 0); x = root(x1, x2); cout<<"此方程的根是"<<x<<endl; return 0; }
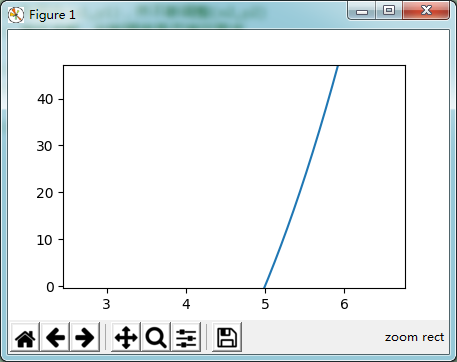
python 近似图:
#运行此程序需先安装 matplotlib 包 #python -m pip install -U pip #python -m pip install -U matplotlib import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np x=np.linspace(-10,10,10000) y=((x - 5.0)*x + 16.0)*x - 80.0 plt.plot(x,y) plt.show()
附件:心形图(来自抖音视频)
#运行此程序需先安装 matplotlib 包 #python -m pip install -U pip #python -m pip install -U matplotlib import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np x=np.linspace(-1.816,1.816,100000) y=np.power(x*x,1/3)+0.9*np.power((3.3-x*x),1/2)*np.sin(128*x)
plt.title(' ',color='red') plt.plot(x,y,color='red') plt.show()
参考资料:
cpp程序来源:《Visual c++编程从基础到应用》 第3章末尾
弦截法图片来源:https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E5%BC%A6%E6%88%AA%E6%B3%95/1195626?fr=aladdin
matplotlib 下载地址:https://matplotlib.org/users/installing.html
https://www.jianshu.com/p/538b5e776405
https://realpython.com/python-matplotlib-guide/