一、线程的状态:
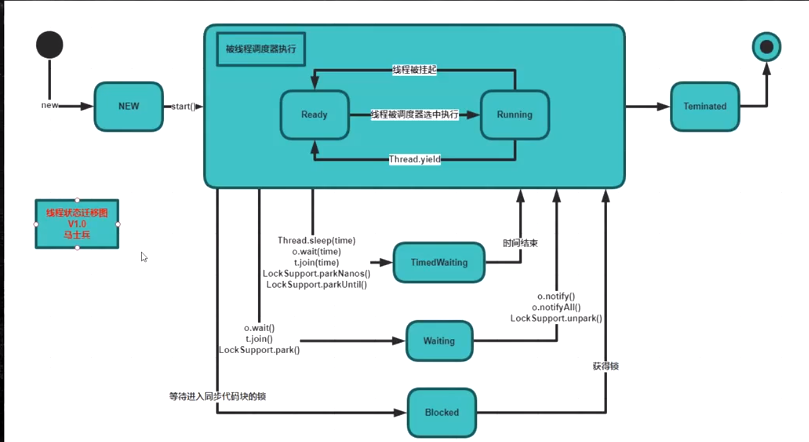
新建状态(NEW):线程刚被创建,还没被启动。
Runable状态:线程对象调用start方法,被线程调度器来执行。
1.就绪状态(Ready):线程被启动,加入CPU等待队列,等待CPU运行。
2.运行状态(Running):在CPU上运行。
结束状态(Terminated):线程正常结束。线程正常结束以后,不能再次调用start方法,会抛出异常:java.lang.IllegalThreadStateException
TimedWaiting等待、Waiting等待、Blocked阻塞
测试线程状态:
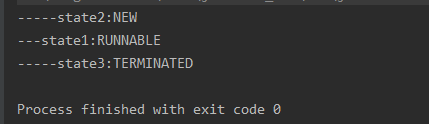
public class T04_ThreadState { static class MyThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("---state1:" + this.getState()); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } public static void main(String[] args) { MyThread t1 = new MyThread(); System.out.println("-----state2:"+t1.getState()); t1.start(); //启动线程 try { t1.join();//main方法等待线程结束 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("-----state3:"+t1.getState()); } }
二、线程常见的几种方法:
1.Sleep:线程睡眠,暂停一段时间让给其他线程去执行,到时间后复活
/** * 线程睡眠,暂停一段时间让给其他线程去执行,到时间后复活 */ static void testSleep(){ new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++){ System.out.println("-------->T"+i); if(i % 5 == 0){ try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }).start(); }
2.Yield:线程回到等待队列,等待再次被调度
/** * yield():线程回到等待队列,等待再次被调度 */ static void testYield(){ new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 1; i < 101; i++){ System.out.println("-------->A"+i); if(i % 10 == 0){ Thread.yield(); } } }).start(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++){ System.out.println("-------->B"+i); if(i % 10 == 0){ Thread.yield(); } } }).start(); }
3.Join:当前线程加入调用join方法的线程,本线程等待,等A运行完了以后,B继续执行。
/** * join(): 当前线程加入调用join方法的线程,本线程等待,等A运行完了以后,B继续执行。 */ static void testJoin(){ Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { System.out.println("------>A0"+i); } }); t1.start(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++){ if(i == 4){ try { t1.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println("B0"+i); } }).start(); }
执行结果如下: