sklearn 是 python 下的机器学习库。
scikit-learn的目的是作为一个“黑盒”来工作,即使用户不了解实现也能产生很好的结果。
其功能非常强大,当然也有很多不足的地方,就比如说神经网络就只有一个RBM(不是人民币哈)。但是,不管怎样,首荐!!
这个例子比较了几种分类器的效果,并直观的显示之
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap #from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split #废弃!! from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler from sklearn.datasets import make_moons, make_circles, make_classification from sklearn.neural_network import BernoulliRBM from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier from sklearn.svm import SVC from sklearn.gaussian_process import GaussianProcess from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, AdaBoostClassifier from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis h = .02 # step size in the mesh names = ["Nearest Neighbors", "Linear SVM", "RBF SVM", "Decision Tree", "Random Forest", "AdaBoost", "Naive Bayes", "QDA", "Gaussian Process","Neural Net", ] classifiers = [ KNeighborsClassifier(3), SVC(kernel="linear", C=0.025), SVC(gamma=2, C=1), DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=5), RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=5, n_estimators=10, max_features=1), AdaBoostClassifier(), GaussianNB(), QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis(), #GaussianProcess(), #BernoulliRBM(), ] X, y = make_classification(n_features=2, n_redundant=0, n_informative=2, random_state=1, n_clusters_per_class=1) rng = np.random.RandomState(2) X += 2 * rng.uniform(size=X.shape) linearly_separable = (X, y) datasets = [make_moons(noise=0.3, random_state=0), make_circles(noise=0.2, factor=0.5, random_state=1), linearly_separable ] figure = plt.figure(figsize=(27, 9)) i = 1 # iterate over datasets for ds_cnt, ds in enumerate(datasets): # preprocess dataset, split into training and test part X, y = ds X = StandardScaler().fit_transform(X) X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=.4, random_state=42) x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - .5, X[:, 0].max() + .5 y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - .5, X[:, 1].max() + .5 xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h)) # just plot the dataset first cm = plt.cm.RdBu cm_bright = ListedColormap(['#FF0000', '#0000FF']) ax = plt.subplot(len(datasets), len(classifiers) + 1, i) if ds_cnt == 0: ax.set_title("Input data") # Plot the training points ax.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c=y_train, cmap=cm_bright) # and testing points ax.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c=y_test, cmap=cm_bright, alpha=0.6) ax.set_xlim(xx.min(), xx.max()) ax.set_ylim(yy.min(), yy.max()) ax.set_xticks(()) ax.set_yticks(()) i += 1 # iterate over classifiers for name, clf in zip(names, classifiers): ax = plt.subplot(len(datasets), len(classifiers) + 1, i) clf.fit(X_train, y_train) score = clf.score(X_test, y_test) # Plot the decision boundary. For that, we will assign a color to each # point in the mesh [x_min, m_max]x[y_min, y_max]. if hasattr(clf, "decision_function"): Z = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]) else: Z = clf.predict_proba(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])[:, 1] # Put the result into a color plot Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape) ax.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=cm, alpha=.8) # Plot also the training points ax.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c=y_train, cmap=cm_bright) # and testing points ax.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c=y_test, cmap=cm_bright, alpha=0.6) ax.set_xlim(xx.min(), xx.max()) ax.set_ylim(yy.min(), yy.max()) ax.set_xticks(()) ax.set_yticks(()) if ds_cnt == 0: ax.set_title(name) ax.text(xx.max() - .3, yy.min() + .3, ('%.2f' % score).lstrip('0'), size=15, horizontalalignment='right') i += 1 plt.tight_layout() plt.show()
效果图:
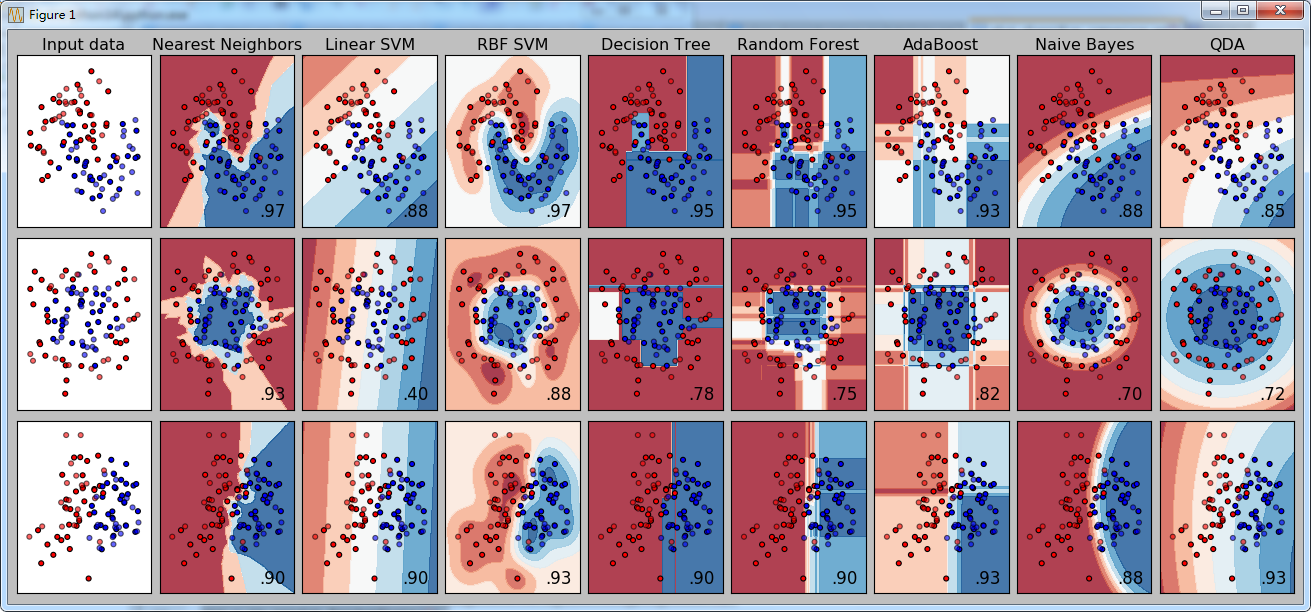
说明:

1.原始数据(三组)
2.分类器名称(八个)
3.对应的成绩 (score)