一、了解继承
首先我们一起了解下js中继承,其实继承就是后辈继承前辈的属性和方法。
二、继承的方法
- 从父类继承属性和方法
这是对象冒充的方法,模仿java的继承方法。实现的原理是,通过改变父类的执行环境(也就是this指向子类)进行继承;
// 从父类中继承属性和方法
function Father() {
this.say = 'hi';
this.fn = function () {
return this.say;
}
}
function Son() {
this.name = "a";
//这一条把Father当中了普通的函数,变量赋值给了Son的f属性。其实得到的是Father函数的指针。
//需要注意的是,函数中的this,是谁调用指向谁。此时Father函数内的this指向了子类Son
this.f = Father;
/*继承的关键代码。等价于Father(),得到的结果将会有两个:
1. say="hi" 2. fn=function(){return this.say;}。
从而实现了Son继承Father属性和方法的功能。从而实现了Son继承Father属性和方法的功能。
*/
this.f();
//删除这个指针链接。为了避免后续修改对Father构造函数造成影响
delete this.f;
}
var s = new Son();
//打印结果是"hi"。Son中存在了Father的方法fn,return了say属性。
console.log(s.fn());
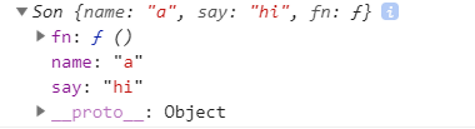
console.log(s);
继承效果展示:
通多console.log(s); 打印结果,即实例s,可以看出子类的继承效果,子类Son继承了父类Father的属性say和方法fn。
2 通过原型链继承
原型链的查找顺序: 先自身查找, 找到就结束, 没有找到就沿着原型链向上查找, 直到找到Object.prototype.proto
function A() {
this.a = "A";
this.fn = function () {
return this.a;
}
}
function B() {
this.a = "B";
}
B.prototype = new A(); //将构造函数A的实例作为B的原型,原来存在于A实例的所有方法和属性,存在于B原型prototype中
var b = new B(); //创建一个构造函数B的实例
console.dir(b);//结果如下图
通过dir方法可以查看到b的实例所有属性和方法。
b实例不但拥有构造函数B的属性a="B",还继承了构造函数A的属性a="A"和方法fn();
并且constructor指向的是构造函数A。

3 class继承extends
class C {
constructor(name) {
//构造函数
this.name = name; //给新的对象添加一个name属性
}
// sayName相当于 A.prototype.sayName = function(){return this.name}
sayName() {
return this.name;
}
}
class D extends C { //D类,该类通过extends关键字,继承了C类的所有属性和方法
}
var newc = new D("haode");
//通过打印结果可以看出,实例继承了C类的属性和方法
console.log(newc.name); //"haode"
console.log(newc.sayName()); //"haode"