开机启动程序,在很多场合都会用到,尤其是那种在后台运行的程序。
效果图:

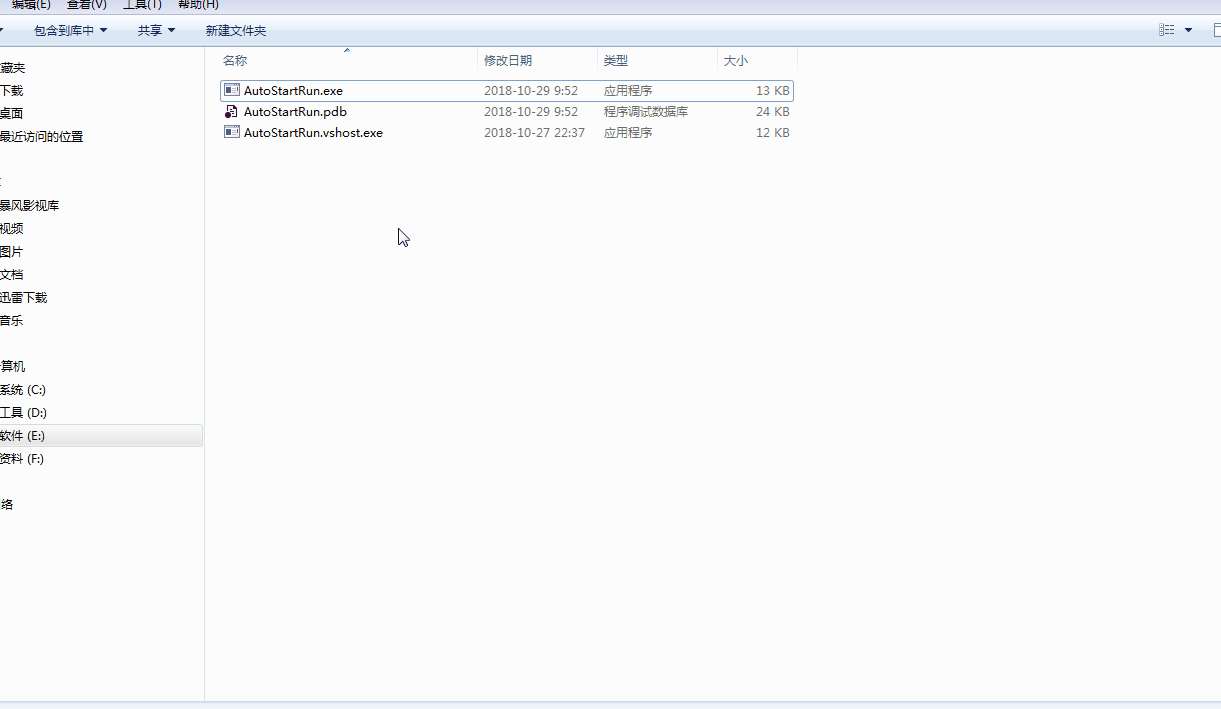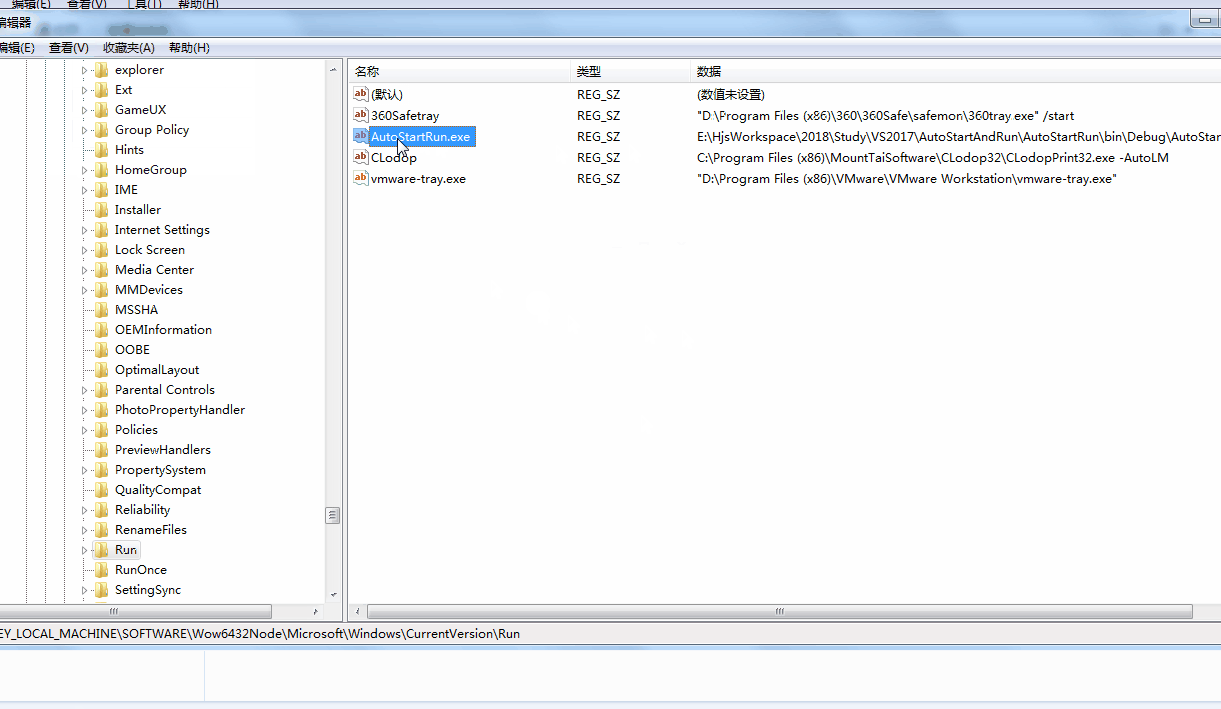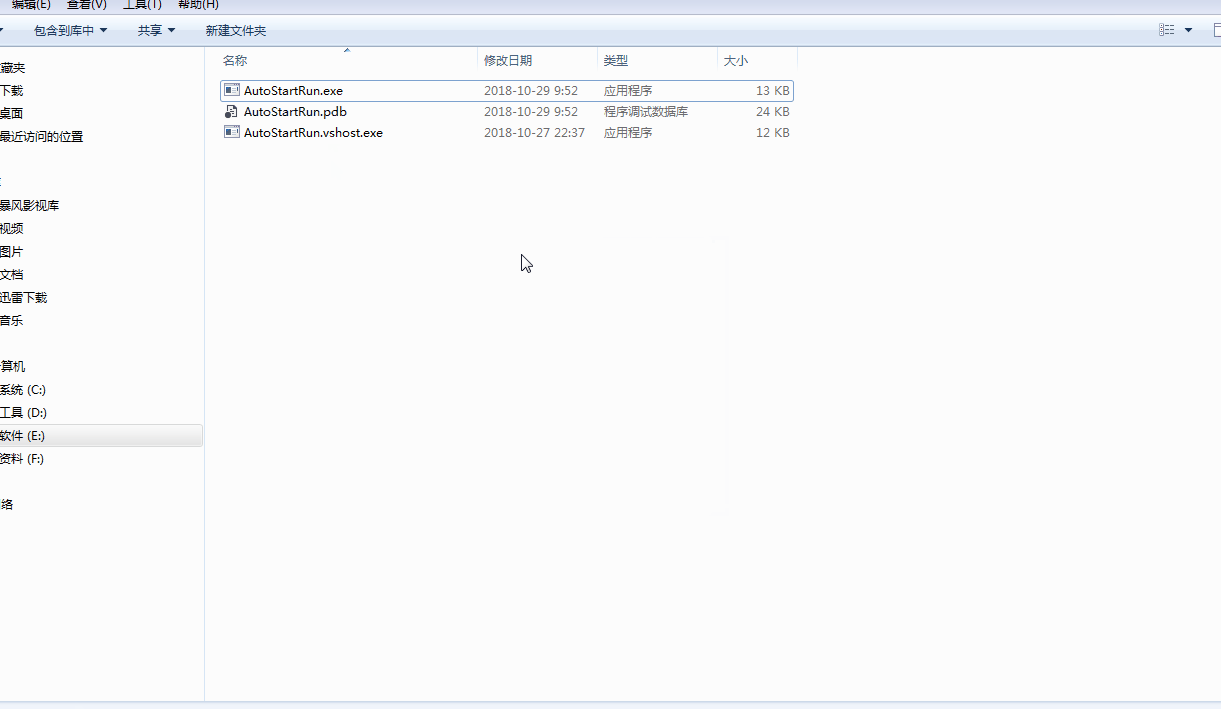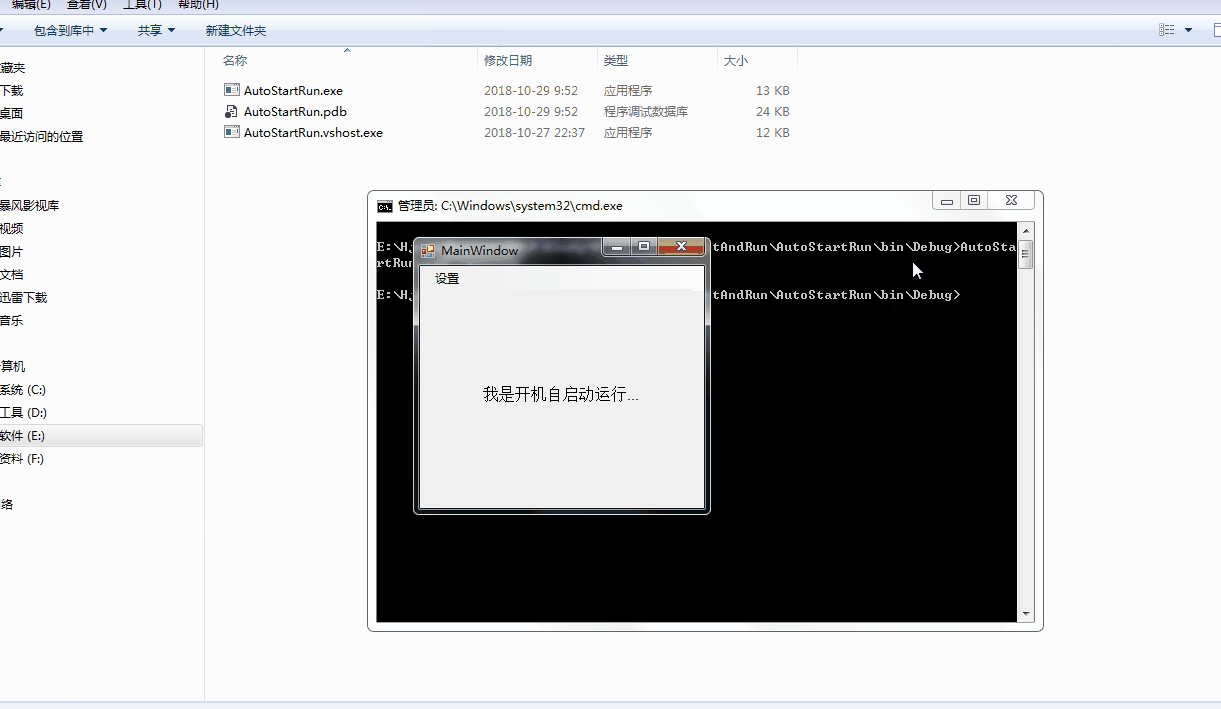
以上两幅图都用到了命令行启动程序,为了模拟开机启动或者其他程序调用此程序。
第一幅图:程序启动可以根据不同参数,执行不同的操作。如果是双击启动,就自动运行逻辑代码,如果是带特定参数启动,就自动运行逻辑代码。
第二幅图:winform 程序设置开机启动,模拟双击启动和开机启动的不同效果。
开机启动并自动运行方法:其实思路很简单,就是将程序添加到注册表中,这设置值的时候,加一个参数就可以了。然后程序在入口函数处判断启动参数,如果有启动参数,就走自动运行逻辑代码,如果没有,就只是程序启动,并不运行逻辑代码。
【Main参数】
在C/C++中,我们很明确的知道 main(int argc, char *argv[]/*, char *envp[]*/) 函数有两(三)个参数,第三个参数一般用得少,我是还没用到过。所以常见的都是用两个参数。第一个是参数个数,非负数。第二个是表示从执行环境传递给程序的各个实参。也就是说,我们要用程序入口参数,只需要判断argc的值,然后使用数组取argv的值就行。
那么到了C#就变的更简单了。直接变成 string[] 了。那么你只要遍历这个字符串数组就可以了。
我们用VS创建命令行工程的时候,如果是命令行程序那么VS会默认使用带参数的main函数:void Main(string [] args);如果是winform工程,VS是默认使用void Main()。其实无论默认使用哪个都无所谓,主要是自己要清楚main函数的格式,以及代表的含义。main函数不光有参数,还可以有返回值。其实我们平时写的C#工程中main函数看似没有返回值,其实是可以带有int类型的返回值的。如果你不清楚这一块,传送门。
那如果我们用的是 void Main() 这种形式我们怎么获取程序入库参数?这里其实是只是一个表面现象。别以为你不带参数,我就获取不到了 ^_^ 。微软为我们提供了一个类:Environment。这个类比较强大。如果你还不清楚怎么用,那去 MSDN 搜一下就会了。获取命令行参数也就一个函数而已: string[] Environment.GetCommandLineArgs();使用这个方法需要注意就是返回值是数组类型,第一个元素包含正在执行的程序的文件名,从第二个参数开始,才是命令行参数。其实这个办法就刚好解决了 winform 程序中获取命令行参数的问题。
【注册表操作】
将程序启动写入注册表实现开机启动,这个感觉没什么好说的。使用固定方法操作就行。不过用有一点需要注意就是在访问注册表的时候可能会提示没有权限,你这个网上百度有好多方法。但是MSDN中也给出了方法。就是在工程的中添加应用程序文件清单中修改一句就可以了。
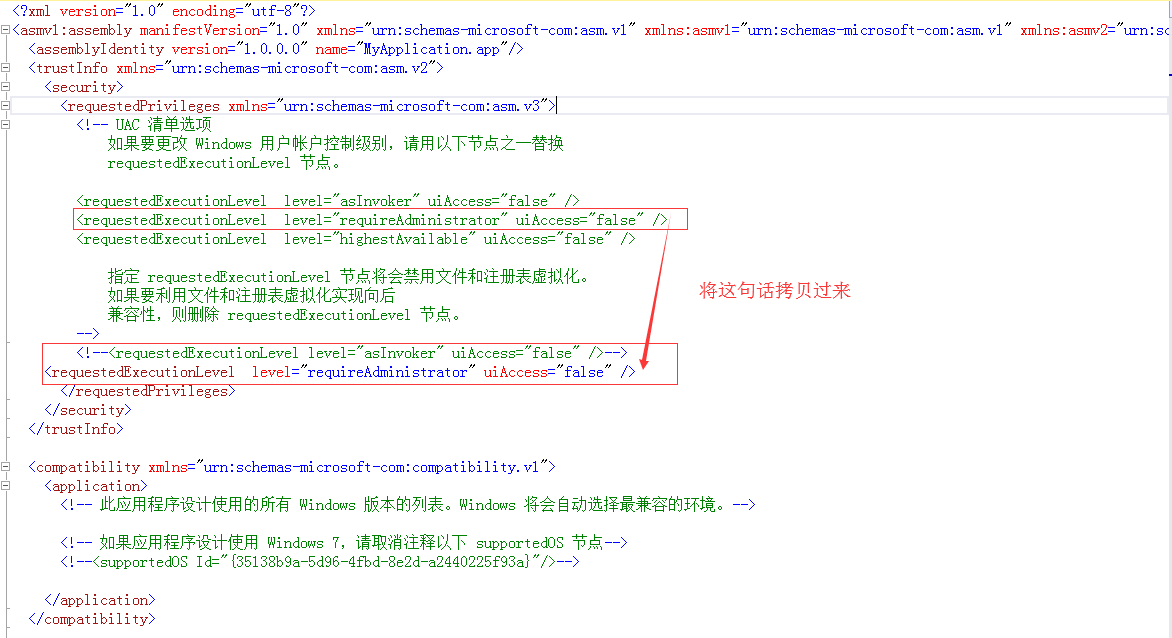
核心代码:
using System; using Microsoft.Win32; namespace AutoStartRun { public sealed class SystemHelper { private SystemHelper() { } /// <summary> /// 设置程序开机启动 /// </summary> /// <param name="strAppPath">应用程序exe所在文件夹</param> /// <param name="strAppName">应用程序exe名称</param> /// <param name="bIsAutoRun">自动运行状态</param> public static void SetAutoRun(string strAppPath, string strAppName, bool bIsAutoRun) { try { if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(strAppPath) || string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(strAppName)) { throw new Exception("应用程序路径或名称为空!"); } RegistryKey reg = Registry.LocalMachine; RegistryKey run = reg.CreateSubKey(@"SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run"); if (bIsAutoRun) { run.SetValue(strAppName, strAppPath); } else { if (null != run.GetValue(strAppName)) { run.DeleteValue(strAppName); } } run.Close(); reg.Close(); } catch (Exception ex) { throw new Exception(ex.Message, ex); } } /// <summary> /// 判断是否开机启动 /// </summary> /// <param name="strAppPath">应用程序路径</param> /// <param name="strAppName">应用程序名称</param> /// <returns></returns> public static bool IsAutoRun(string strAppPath, string strAppName) { try { RegistryKey reg = Registry.LocalMachine; RegistryKey software = reg.OpenSubKey(@"SOFTWARE"); RegistryKey run = reg.OpenSubKey(@"SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run"); object key = run.GetValue(strAppName); software.Close(); run.Close(); if (null == key || !strAppPath.Equals(key.ToString())) { return false; } return true; } catch (Exception ex) { throw new Exception(ex.Message, ex); } } } }
调用方法:
/// <summary> /// 设置程序开机自启动 /// </summary> private void SetAutoRun() { string strFilePath = Application.ExecutablePath; string strFileName = System.IO.Path.GetFileName(strFilePath); try { SystemHelper.SetAutoRun(strFilePath + " -autostart", strFileName, !menuAutoRun.Checked); menuAutoRun.Checked = !menuAutoRun.Checked; } catch (Exception ex) { MessageBox.Show(this, ex.Message, "错误提示", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error); } }
设置开机启动就是如此简单。
【开机启动并运行】
那这个就不用说了,将命令行参数和开机注册表操作结合起来就可以了。
示例代码:
/// <summary> /// 检查是否开机启动,并设置控件状态 /// </summary> private void CheckAutoRun() { string strFilePath = Application.ExecutablePath; string strFileName = System.IO.Path.GetFileName(strFilePath); if (SystemHelper.IsAutoRun(strFilePath + " -autostart", strFileName)) { menuAutoRun.Checked = true; } else { menuAutoRun.Checked = false; } } private void AutoRun() { if (menuAutoRun.Checked) { string[] strArgs = Environment.GetCommandLineArgs(); if (strArgs.Length >= 2 && strArgs[1].Equals("-autorun")) { labText.Text = "我是开机自启动运行..."; } } }
献上 demo