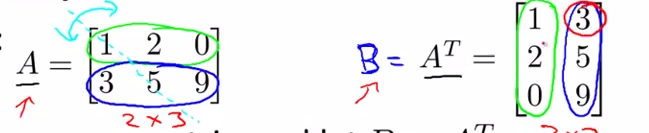Notes - Coursera MachineLearning by Andrew NG - Week1
Week1-2014/03/07-hphp欢迎赐教、讨论、转载,转载请注明原文地址~
Machine Learning Introduction
- GeneralSpeaking - lecture 1,2
- Many Application
- Amazaon, Netfilx recommend system
- Arthur Samuel, made a machine learn how to check. checkers , made a program play chess with itself , and know better of how to win .
- Popular
- and well .. currently large demands of talents. as one of the top 12 computer skill
- Different types of learning algorithms
- famous partial methods : supervised learning , unsupervised learning,
- Course Main Goal
- how to develop the best machine learning systems to get better performance.
- Supervise learning - lecture 3
- Regression: Predict continous valued output
- Classification problem ,
- tumor size Vs malignant
- Tumor size , age , Vs malignant or benign ,
- could use more features to predict ( or regression ) : uniformity of cell shape , cell size ......
- Statistically
- compromized : 妥协的
- Unsupervised Learning - lecture 4
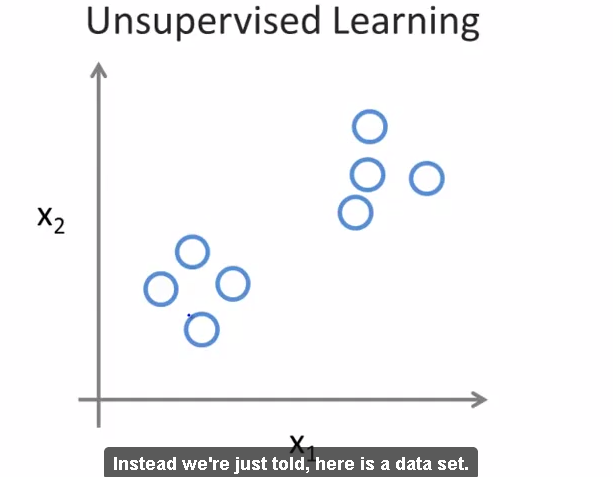
- clustering problem
- google news , with one news , several diff urls are laid.
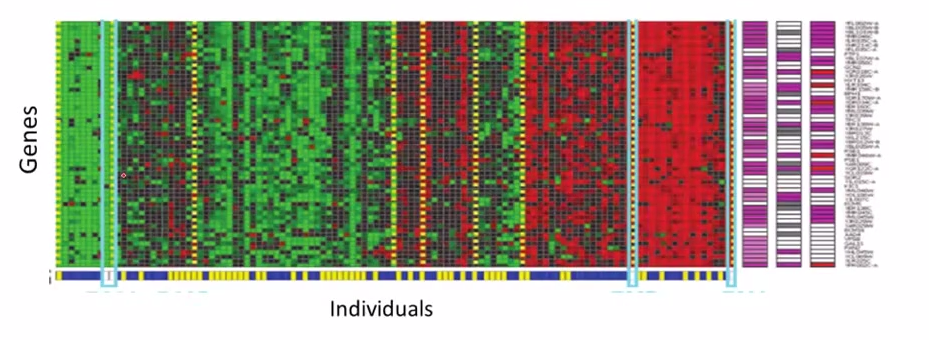
- astronomical data analysis
- Cocktail party problem
- seperate voice source

- use octave , could solve the problem quickly and briefly
Linear Regression with one variable
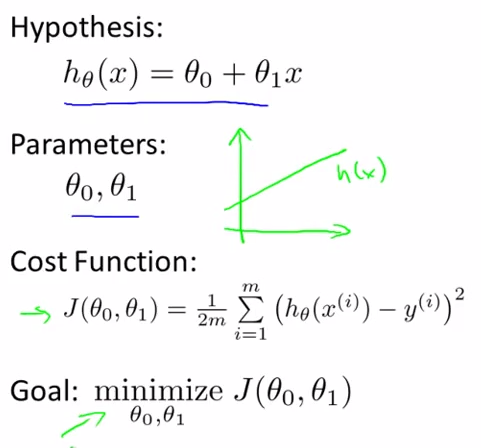
- Model representation - lecture 5
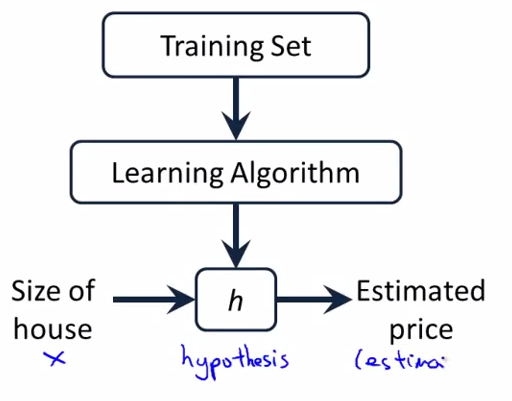
Training set : m : number of training examples , x : input , y : output variable ,
y = h(x) , h : hypothesis
How do we represent H?
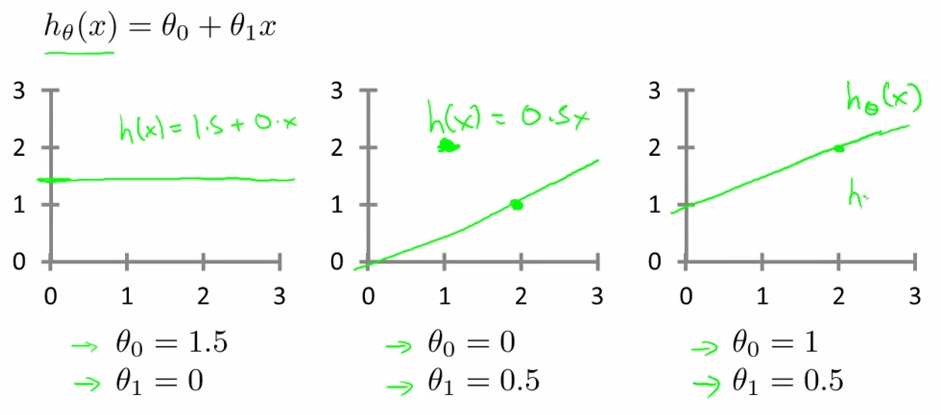
htheta(x) = theta0 + theta1(x)
univariant -- linear regression (a fancy name)
- Cost Function - lecture 6
htheta(x) = theta0 + theta1(x)
how to choose two theta s
choose thetas so that h(x) is close to given examples.
m
minimize = 1/2m Sum ( h(xi) - yi ) 2
theta0, theta 1 1
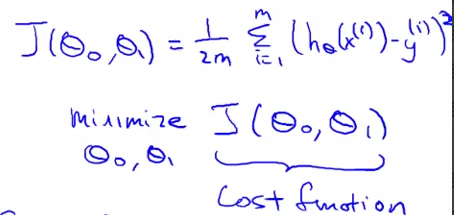
squared error function -- the most common coss function in regression .
- Cost function intuition I - lecture 7
get better intuition what cost function is doing , and why we want to use it.
recap : focus , say briefly
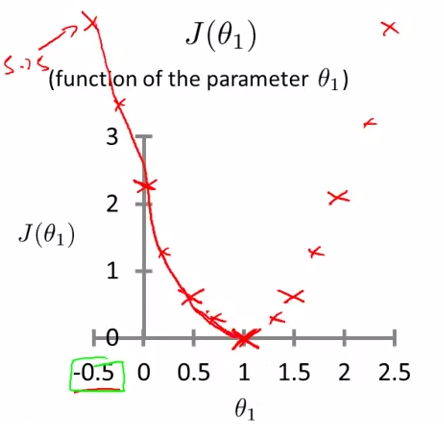
simplified : theta 0 = 0
h(x) = theta1 * x
J(theta1) = 1/2m * Sum[i:1-m](theta1xi - yi) 2
when theta1 = 1 , J ( theta1 ) = 0
theta1 = 0.5 , J ( theta1 ) = 0.5 , J ( 0 ) = 14/6
- Cost function intuition II - lecture 8
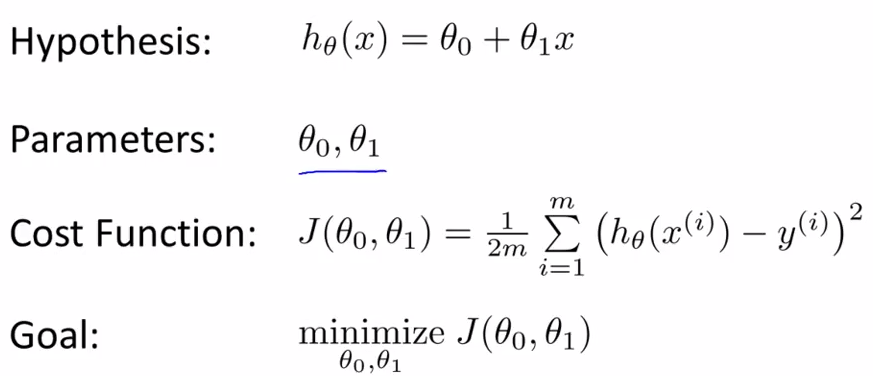
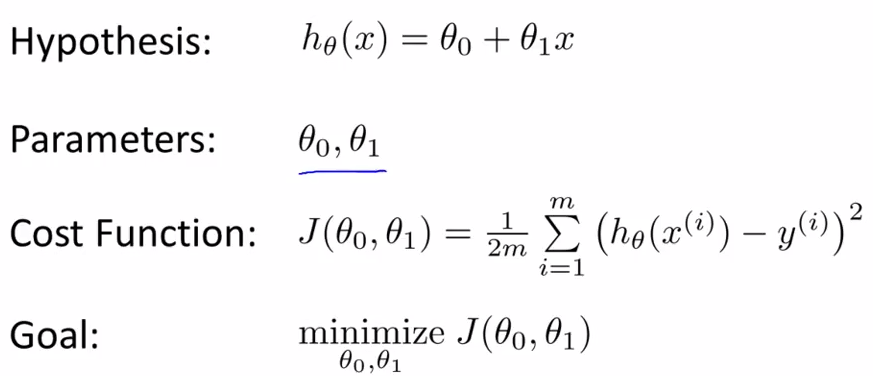
- contour plots : outline
- theta0, theta1 != (0, x) or (x, 0) , with the cost function act as a 3D bowl , below
- contour plots : outline
- theta0, theta1 != (0, x) or (x, 0) , with the cost function act as a 3D bowl , below
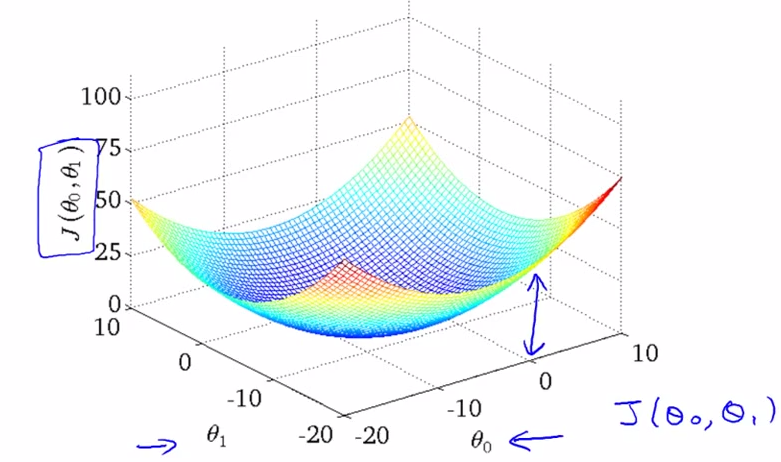
- using : contour plots ( or contour figures ) .
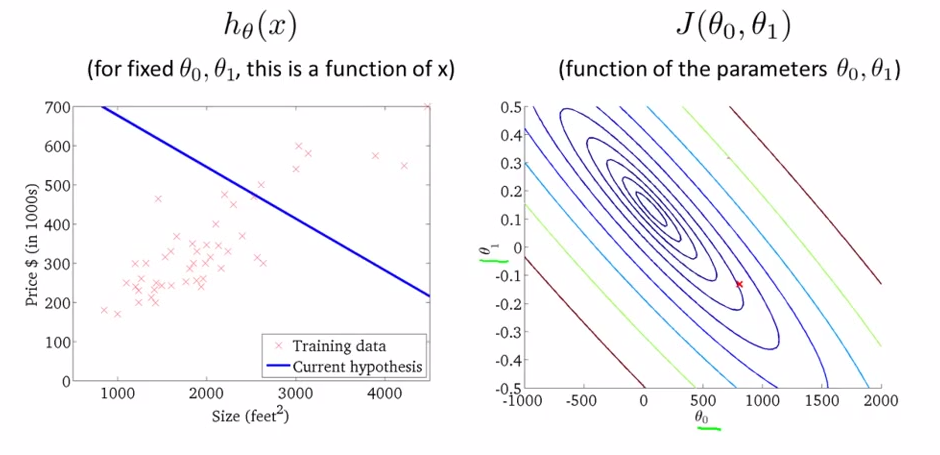

- using : contour plots ( or contour figures ) .

- Gradient descent algorithm - lecture 9
- it is used all over machine learning
- could minimizing arbitrary functions besides cost function
- Basic Thoughts
- it is used all over machine learning
- could minimizing arbitrary functions besides cost function
- Basic Thoughts
 - surface ->
- surface ->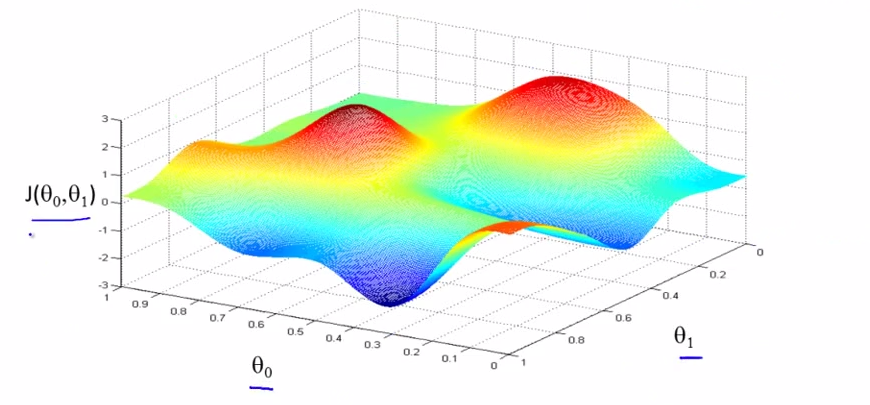
- EG: start at some point on the surface,
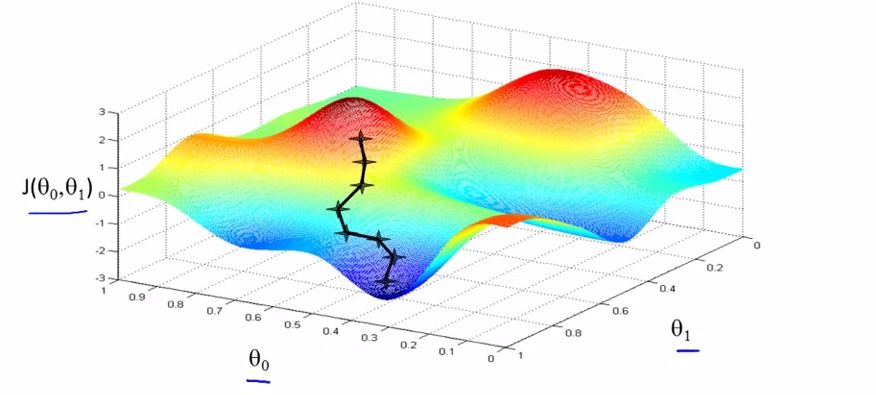 VS
VS 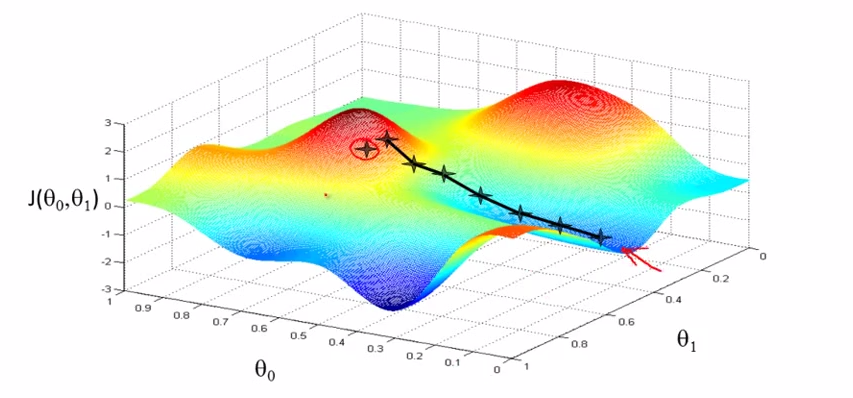
- ==> start with diff starts , end in diff ends.[it is a property of Gradient descent algorithm ]
- detailed description
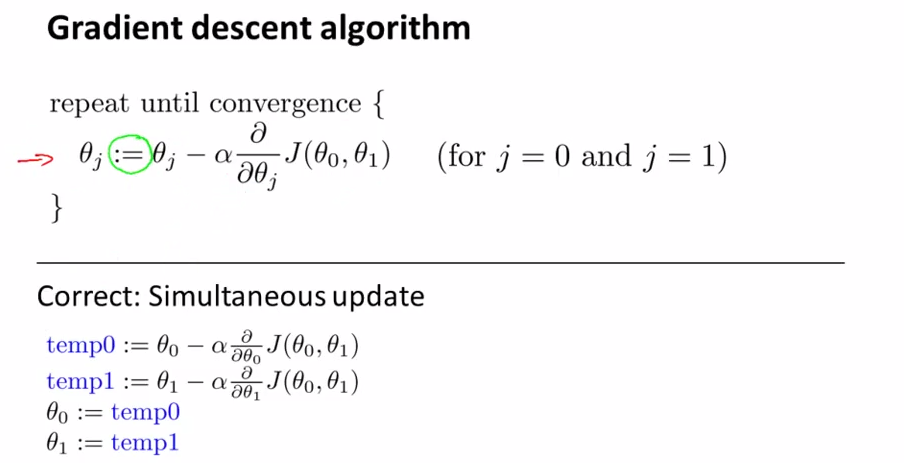
- alpha : learning rate [ if alpha is large , aggressive ]
- calculus and derivative
- keep in mind : simultaneously, at the same time
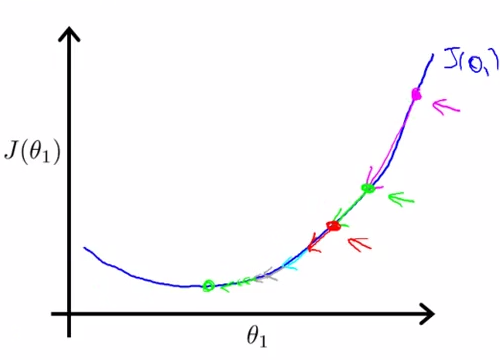
- Gradient descent intuition - lecture 10
- partial derivative vs derivative , different in mathematics , seems same in MachineLearning
- tangent , slope of line
- converge and diverge : using different alpha
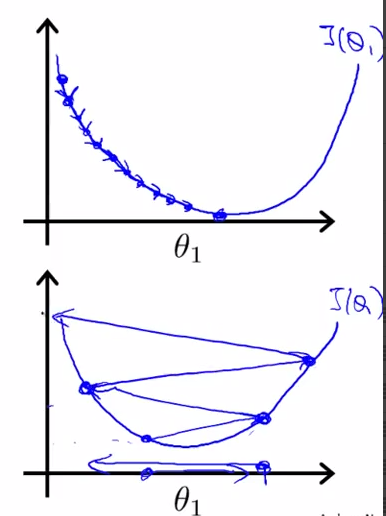
- when we get theta1 to a local minimum location , it will stop changing.
- gradient descent algorithm could converge to a local minimum
- if alpha is fixed , smaller and smaller steps , and no need to decrease alpha
- Gradient descent for Linear Regression - lecture 11
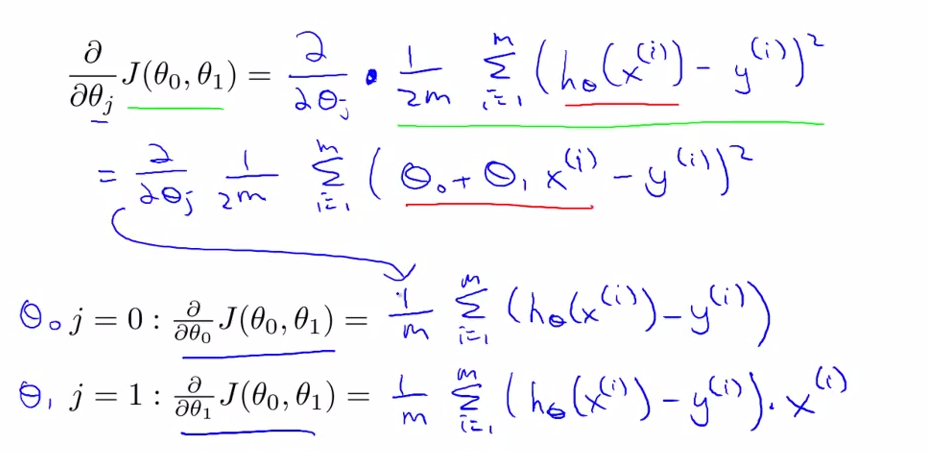
- use the basic algorithm to get minimum theta0, theta1.
- cost function of linear function will always be a bowl-shaped function ==> convex function
- above algorithm also called "Batch" Gradient Descent Algorithm
- "Batch" : each step use all of the training data.
What's next - lecture 12
- Extensions of the Gradient descent / Linear Regression ideas
- how to choose alpha ,
- how act using more features ?
- harder to plot features.
- Use Linear Algebra

- matrix/ vector addition , substraction, multiplication
- matrix inverse, matrics transpose
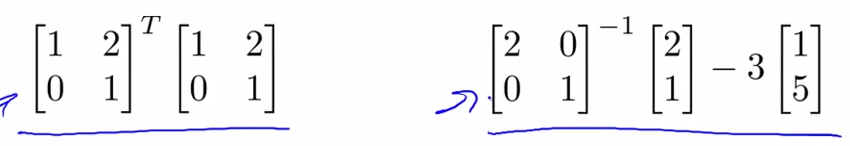
- Matrices and Vectors
- Dimension of matrix : row * column , Aij = matrix A ith row , jth colum
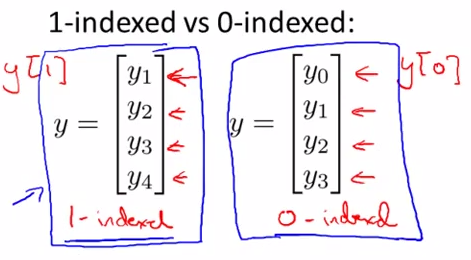
- vector : only one column matrix , yi = the ith element ; as below 1-index as usual inference
- Additions and Substractions
- simple addition and substraction
- scalar Multiplication
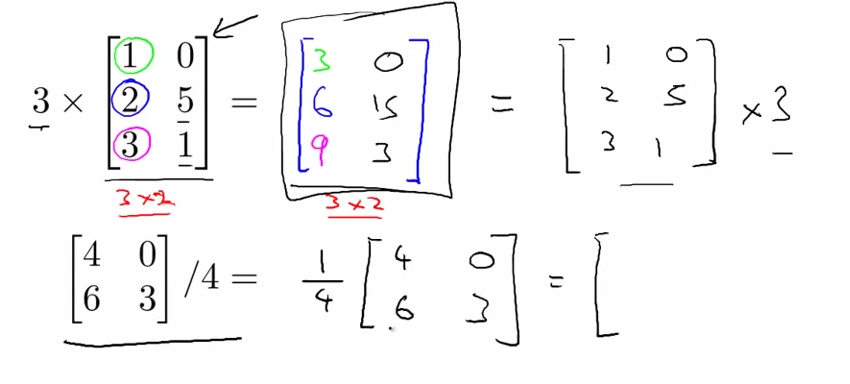
- combination of oprands
- Multiplication of matrix and vector
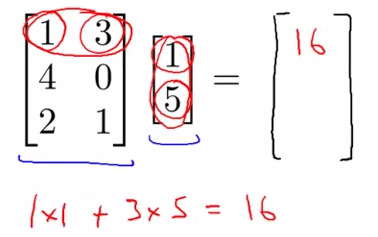
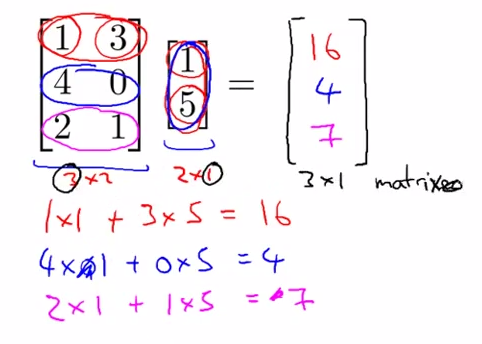
- Details
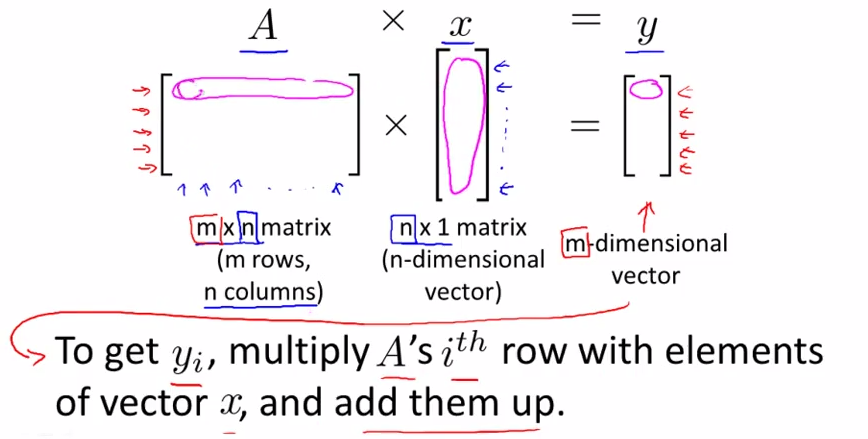
- m*n ---> n * 1 ====> m * 1
- the ith row multiply with corresponding column , then add whole up
- Linear Regression
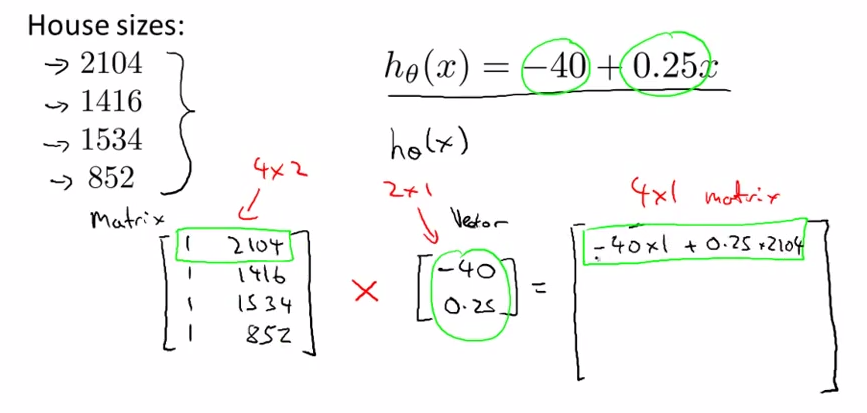 -- >
-- > 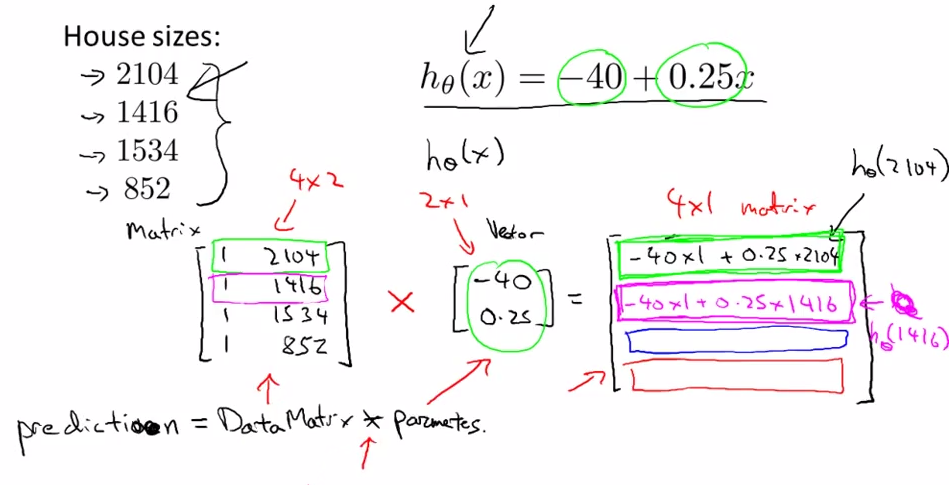
- prediction = DataMatrix * Parameters
- dfdsfds , the matrix computation will get more computation effecient than the simply loop in previous way.
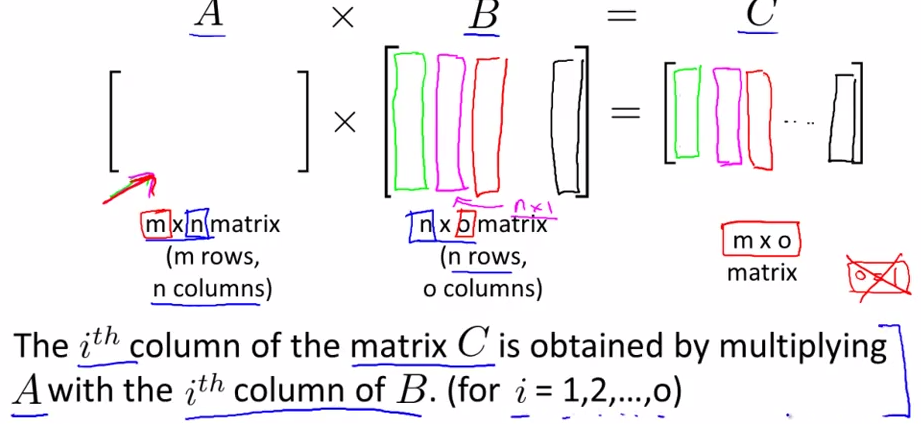
- Matrix - Matrix multiplication
- An Example
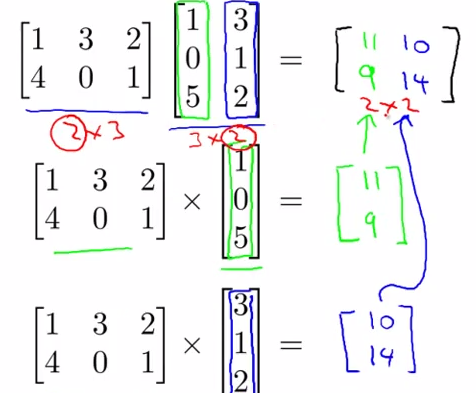
- Details
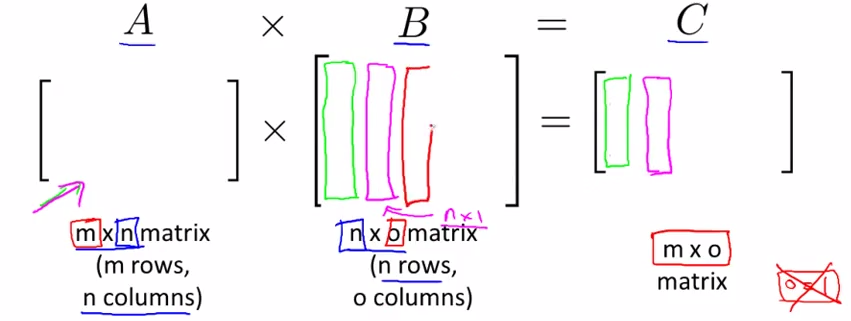
as the A multiply with B's each vector, and these new vectors combine to a new matrix C
- the house affair
 a good way to see hypothesis with different theta0, theta1s
a good way to see hypothesis with different theta0, theta1s- great program languages ( top 10 popular language [ ?? How do they tell ] ) ---- have lots of linear algebra libraries
- Matrix multiplication properties.
- commutative property
- a*b = b*a
- does not match in matrix-multiplication ==> A * B != B * A
- associative property
- a * b * c = a * ( b * c )
- A * B * C = A * ( B * C )
- proven
- Identity Matrix
- Denoted I ( I n*n )
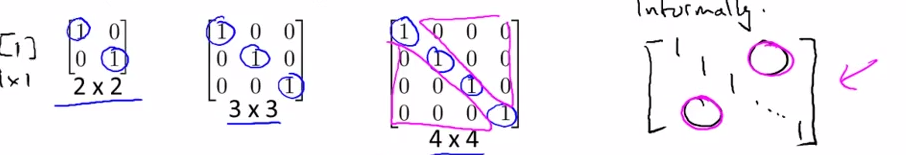
- For any matrix A , A * I = I * A = A
- 单位矩阵
- Matrix inverse and transpose
- Inverse
- start with Identity : 1
- 3 * ( 1/ 3 ) or 3 * 3 -1 = 1
- 0 -1 ---> undefined
- SO if A is a m*m matrix and , and have an inverse A -1 , then -- > A * A-1 = I (m*m)
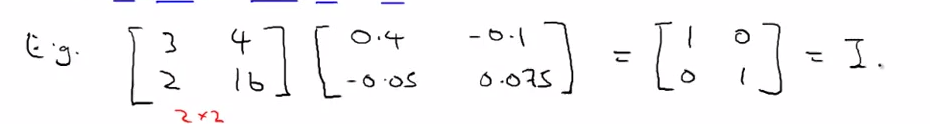
- How to compute inverse ?
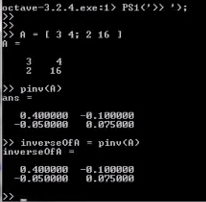
- How to tell if a matrix have an inverse ??
- such that like [0 0 , 0 0 ] have no inverse
- but in machine learning algorithms , we will get to deal with this situation later .
- matrix transpose
- eg:

- terminology : Transpose
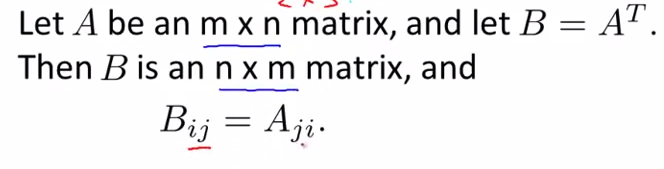
- intuition
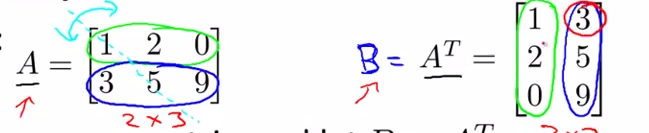
 - surface ->
- surface ->
- EG: start at some point on the surface,
 VS
VS 
- ==> start with diff starts , end in diff ends.[it is a property of Gradient descent algorithm ]
- detailed description

- alpha : learning rate [ if alpha is large , aggressive ]
- calculus and derivative
- keep in mind : simultaneously, at the same time
- partial derivative vs derivative , different in mathematics , seems same in MachineLearning
- tangent , slope of line
- converge and diverge : using different alpha

- when we get theta1 to a local minimum location , it will stop changing.
- gradient descent algorithm could converge to a local minimum
- if alpha is fixed , smaller and smaller steps , and no need to decrease alpha

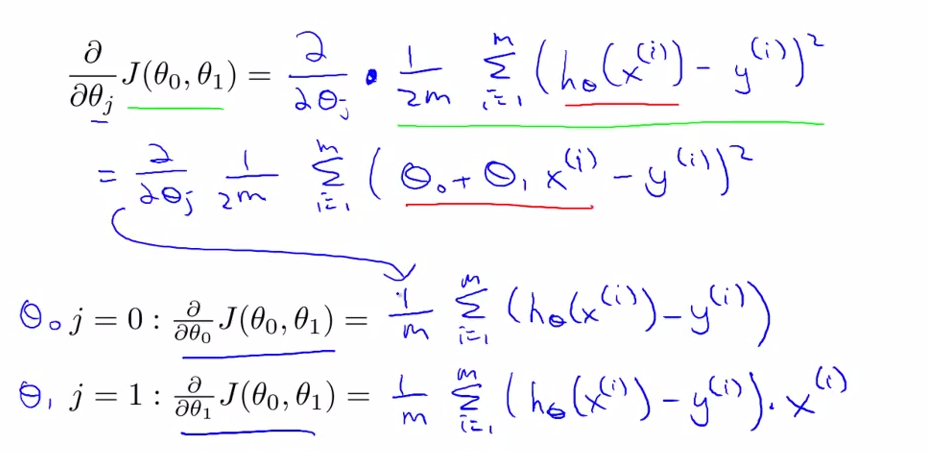
- use the basic algorithm to get minimum theta0, theta1.
- cost function of linear function will always be a bowl-shaped function ==> convex function
- above algorithm also called "Batch" Gradient Descent Algorithm
- "Batch" : each step use all of the training data.
What's next - lecture 12
- Extensions of the Gradient descent / Linear Regression ideas
- how to choose alpha ,
- how act using more features ?
- harder to plot features.
- Use Linear Algebra

- matrix/ vector addition , substraction, multiplication
- matrix inverse, matrics transpose

- Matrices and Vectors
- Dimension of matrix : row * column , Aij = matrix A ith row , jth colum
- vector : only one column matrix , yi = the ith element ; as below 1-index as usual inference

- Additions and Substractions
- simple addition and substraction
- scalar Multiplication
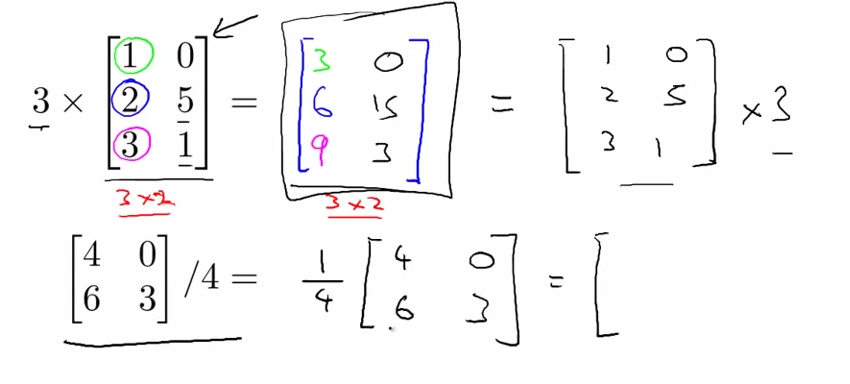
- combination of oprands
- Multiplication of matrix and vector
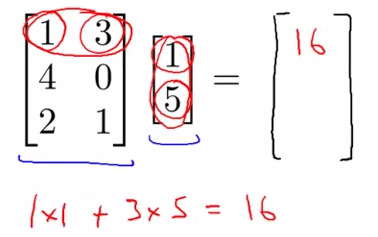
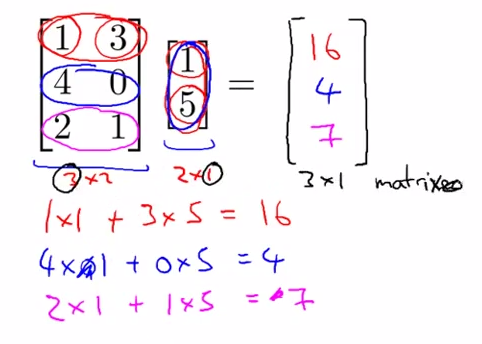
- Details

- m*n ---> n * 1 ====> m * 1
- the ith row multiply with corresponding column , then add whole up
- Linear Regression
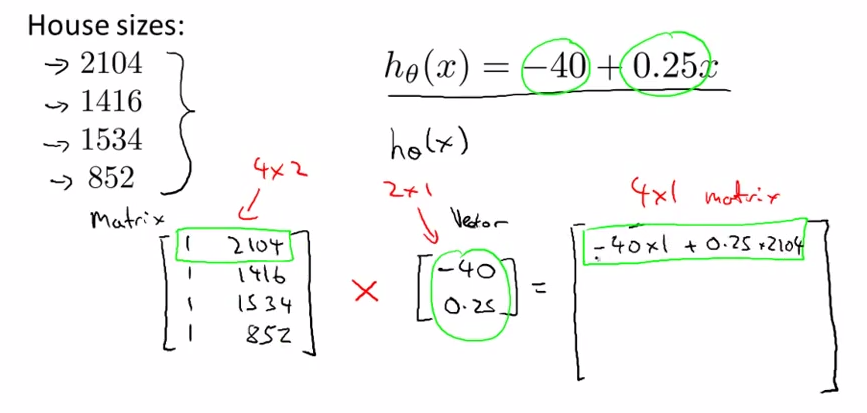 -- >
-- > 
- prediction = DataMatrix * Parameters
- dfdsfds , the matrix computation will get more computation effecient than the simply loop in previous way.
- Matrix - Matrix multiplication
- An Example

- Details


- the house affair

- great program languages ( top 10 popular language [ ?? How do they tell ] ) ---- have lots of linear algebra libraries
- Matrix multiplication properties.
- commutative property
- a*b = b*a
- does not match in matrix-multiplication ==> A * B != B * A
- associative property
- a * b * c = a * ( b * c )
- A * B * C = A * ( B * C )
- proven
- Identity Matrix
- Denoted I ( I n*n )

- For any matrix A , A * I = I * A = A
- 单位矩阵
- Matrix inverse and transpose
- Inverse
- start with Identity : 1
- 3 * ( 1/ 3 ) or 3 * 3 -1 = 1
- 0 -1 ---> undefined
- SO if A is a m*m matrix and , and have an inverse A -1 , then -- > A * A-1 = I (m*m)
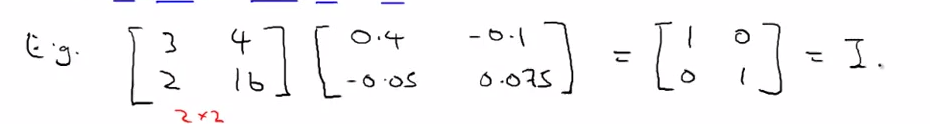
- How to compute inverse ?

- How to tell if a matrix have an inverse ??
- such that like [0 0 , 0 0 ] have no inverse
- but in machine learning algorithms , we will get to deal with this situation later .
- matrix transpose
- eg:

- terminology : Transpose
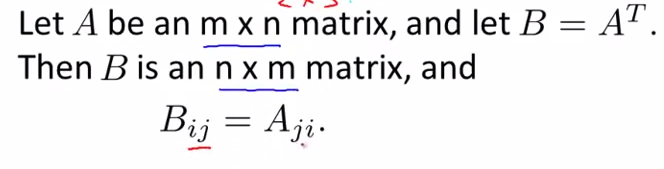
- intuition