1.变量
原文:https://www.runoob.com/csharp/csharp-variables.html
一个变量只不过是一个供程序操作的存储区的名字。在 C# 中,每个变量都有一个特定的类型,类型决定了变量的内存大小和布局。范围内的值可以存储在内存中,可以对变量进行一系列操作。
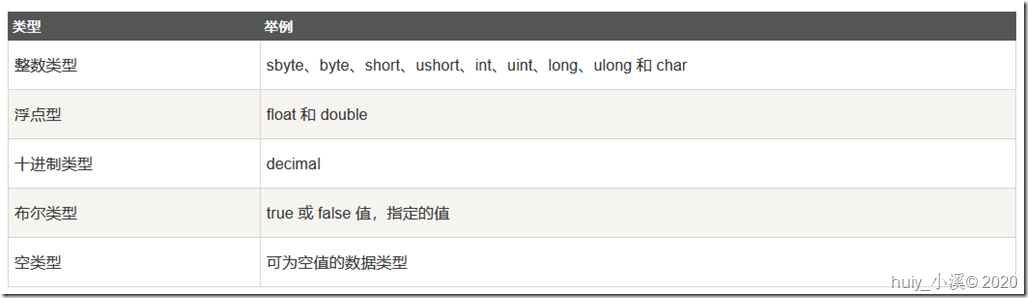
我们已经讨论了各种数据类型。C# 中提供的基本的值类型大致可以分为以下几类:
C# 允许定义其他值类型的变量,比如 enum,也允许定义引用类型变量,比如 class。这些我们将在以后的章节中进行讨论。
2.常量
原文:https://www.runoob.com/csharp/csharp-constants.html
常量是固定值,程序执行期间不会改变。常量可以是任何基本数据类型,比如整数常量、浮点常量、字符常量或者字符串常量,还有枚举常量。
常量可以被当作常规的变量,只是它们的值在定义后不能被修改。
整数常量
整数常量可以是十进制、八进制或十六进制的常量。前缀指定基数:0x 或 0X 表示十六进制,0 表示八进制,没有前缀则表示十进制。
整数常量也可以有后缀,可以是 U 和 L 的组合,其中,U 和 L 分别表示 unsigned 和 long。后缀可以是大写或者小写,多个后缀以任意顺序进行组合。
这里有一些整数常量的实例:
212 /* 合法 */ 215u /* 合法 */ 0xFeeL /* 合法 */ 078 /* 非法:8 不是一个八进制数字 */ 032UU /* 非法:不能重复后缀 */
85 /* 十进制 */ 0213 /* 八进制 */ 0x4b /* 十六进制 */ 30 /* int */ 30u /* 无符号 int */ 30l /* long */ 30ul /* 无符号 long */
字符常量
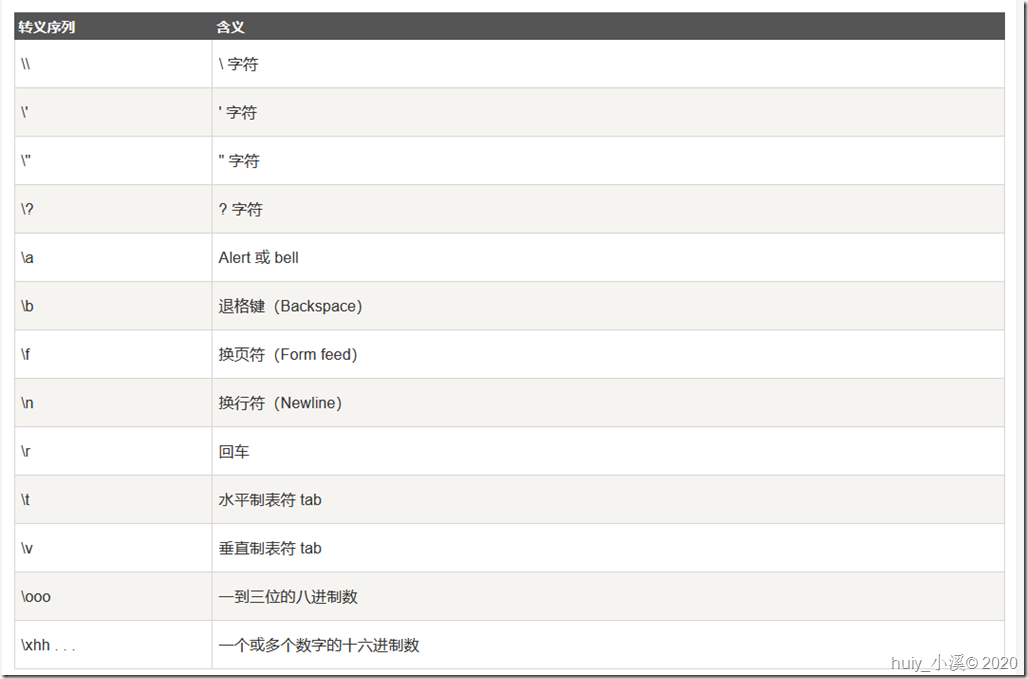
字符常量是括在单引号里,例如,'x',且可存储在一个简单的字符类型变量中。一个字符常量可以是一个普通字符(例如 'x')、一个转义序列(例如 ' ')或者一个通用字符(例如 'u02C0')。
在 C# 中有一些特定的字符,当它们的前面带有反斜杠时有特殊的意义,可用于表示换行符( )或制表符 tab( )。在这里,列出一些转义序列码:
以下是一些转义序列字符的实例:
namespace EscapeChar { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Hello World "); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Hello World
字符串常量
字符串常量是括在双引号 "" 里,或者是括在 @"" 里。字符串常量包含的字符与字符常量相似,可以是:普通字符、转义序列和通用字符
使用字符串常量时,可以把一个很长的行拆成多个行,可以使用空格分隔各个部分。
这里是一些字符串常量的实例。下面所列的各种形式表示相同的字符串。
string a = "hello, world"; // hello, world string b = @"hello, world"; // hello, world string c = "hello world"; // hello world string d = @"hello world"; // hello world string e = "Joe said "Hello" to me"; // Joe said "Hello" to me string f = @"Joe said ""Hello"" to me"; // Joe said "Hello" to me string g = "\\server\share\file.txt"; // \serversharefile.txt string h = @"\serversharefile.txt"; // \serversharefile.txt string i = "one two three"; string j = @"one two three";
定义常量
常量是使用 const 关键字来定义的 。定义一个常量的语法如下:
const <data_type> <constant_name> = value;using System; public class ConstTest { class SampleClass { public int x; public int y; public const int c1 = 5; public const int c2 = c1 + 5; public SampleClass(int p1, int p2) { x = p1; y = p2; } } static void Main() { SampleClass mC = new SampleClass(11, 22); Console.WriteLine("x = {0}, y = {1}", mC.x, mC.y); Console.WriteLine("c1 = {0}, c2 = {1}", SampleClass.c1, SampleClass.c2); } }
x = 11, y = 22 c1 = 5, c2 = 10