1.概念:
异步通知机制:一旦设备就绪,则主动通知应用程序,这样应用程序根本就不需要查询设备状态,是一种“信号驱动的异步I/O”。信号是在软件层次上对中断机制的一种模拟,在原理上,一个进程收到一个信号与处理器收到一个中断请求可以说是一样的。信号是异步的,一个进程不必通过任何操作来等待信号的到达,事实上,进程也不知道信号到底什么时候会到达。
2.我们试图通过两个方面来分析异步通知机制:
从用户程序的角度考虑:为了启动文件的异步通知机制,用户程序必须执行两个步骤。首先,他们指定一个进程作为文件的“属主(owner)”。当进程使用fcntl系统调用执行
F_SETOWN命令时,属主进程的进程ID号就被保存在filp->f_owner中。这一步是必需的,目的是为了让内核知道应该通知哪个进程。 然后为了真正启动异步通知机制,用户程序还必须
在设备中设置FASYNC标志,这通过fcntl的F_SETFL命令完成的。 执行完这两个步骤之后,输入文件就可以在新数据到达时请求发送一个SIGIO信号。该信号被发送到存放在filp-
>f_owner中的进程(如果是负值就是进程组)。
在用户程序中,为了捕获信号,可以使用signal()函数来设置对应信号的处理函数:
1 void (*signal(int signum, void (*handler))(int)))(int);
该函数原型较难理解, 它可以分解为:
1 typedef void (*sighandler_t)(int); //消息处理函数 2 sighandler_t signal(int signum, sighandler_t handler)); //连接信号与消息处理函数
第一个参数指定信号的值,第二个参数指定针对前面信号值的处理函数,若为SIG_IGN,表示忽略该信号;若为SIG_DFL,表示采用系统默认方式处理信号;若为用户自定义的函
数,则信号被捕获到后,该函数将被执行。如果signal()调用成功,它返回最后一次为信号signum绑定的处理函数的handler值,失败则返回SIG_ERR。
1 fcntl(STDIN_FILENO, F_SETOWN, getpid()); //设置本进程为STDIN_FILENO文件的拥有者,没有这一步,内核不会知道应该将信号发给哪个进程 2 oflags = fcntl(STDIN_FILENO, F_GETFL); //获取设备文件的f_flags 3 fcntl(STDIN_FILENO, F_SETFL, oflags | FASYNC); //为了启用异步通知机制,还需对设备设置FASYNC标志
我们先通过内核源码,剖析上面的实现原理。
1 app:fcntl() 2 kernel:sys_fcntl() 3 do_fcntl() 4 switch (cmd) { 5 …… 6 case F_GETFL: 7 err = filp->f_flags; //返回文件标志 8 break; 9 case F_SETFL: 10 err = setfl(fd, filp, arg); //转调用setfl函数 11 break; 12 …… 13 case F_SETOWN: 14 err = f_setown(filp, arg, 1); //转调用f_setown函数 15 break; 16 …… 17 default: 18 break; 19 } 20 return err;
//来看看f_setown函数的内部实现:设置文件的属主进程
1 int f_setown(struct file *filp, unsigned long arg, int force) 2 { 3 ... 4 pid = find_pid(who); //获取当前进程的pid 5 result = __f_setown(filp, pid, type, force); //内部主要调用f_modown函数 6 ... 7 } 8 static void f_modown(struct file *filp, struct pid *pid, enum pid_type type,uid_t uid, uid_t euid, int force) 9 { 10 ... 11 if (force || !filp->f_owner.pid) { //设置对应的pid,uid,euid 12 put_pid(filp->f_owner.pid); 13 filp->f_owner.pid = get_pid(pid); 14 filp->f_owner.pid_type = type; 15 filp->f_owner.uid = uid; 16 filp->f_owner.euid = euid; 17 } 18 ... 19 }
//再来看看setfl函数的内部实现:
1 static int setfl(int fd, struct file * filp, unsigned long arg) 2 { 3 ... 4 if ((arg ^ filp->f_flags) & FASYNC) { //也就是说FASYNC标志从0变为1的时候,才为真。 5 if (filp->f_op && filp->f_op->fasync) { 6 error = filp->f_op->fasync(fd, filp, (arg & FASYNC) != 0); //调用的就是驱动程序的fasync()函数 7 if (error < 0) 8 goto out; 9 } 10 } 11 ... 12 }
从驱动程序角度考虑:
应用程序在执行F_SETFL启用FASYNC时,调用驱动程序的fasync方法。只要filp->f_flags中的FASYNC标识发生了变化,就会调用该方法,以便把这个变化通知驱动程序,使其能
正确响应。文件打开时,FASYNC标志被默认为是清除的。当数据到达时,所有注册为异步通知的进程都会被发送一个SIGIO信号。
Linux的这种通用方法基于一个数据结构和两个函数:
1 extern int fasync_helper(int, struct file *, int, struct fasync_struct **); 2 //当一个打开的文件的FASYNC标志被修改时,调用驱动程序的fasync方法间接调用fasync_helper函数以便将当前进程加入到驱动程序的异步通知等待队列中。 3 extern void kill_fasync(struct fasync_struct **, int, int); 4 //当设备可访问时,可使用kill_fasync函数发信号所有的相关进程。进程进而调用绑定的消息处理函数。
//分析fasync_helper的内部实现
1 int fasync_helper(int fd, struct file * filp, int on, struct fasync_struct **fapp) 2 { 3 struct fasync_struct *fa, **fp; 4 struct fasync_struct *new = NULL; 5 int result = 0; 6 if (on) { 7 new = kmem_cache_alloc(fasync_cache, SLAB_KERNEL);//创建对象,slab分配器 8 if (!new) 9 return -ENOMEM; 10 } 11 write_lock_irq(&fasync_lock); 12 //遍历整个异步通知队列,看是否存在对应的文件指针 13 for (fp = fapp; (fa = *fp) != NULL; fp = &fa->fa_next) { 14 if (fa->fa_file == filp) {//已存在 15 if(on) { 16 fa->fa_fd = fd;//文件描述符赋值 //注:不明白为什么这里只需要更新文件描述符,而不需要更新文件指针 17 kmem_cache_free(fasync_cache, new);//销毁刚创建的对象 18 } else { 19 *fp = fa->fa_next;//继续遍历 20 kmem_cache_free(fasync_cache, fa);//删除非目标对象 此用于应用程序屏蔽异步通知. 21 result = 1; 22 } 23 goto out;//找到了 24 } 25 } 26 //看到下面可以得知,所谓的把进程添加到异步通知队列中 27 //实则是将文件指针关联到异步结构体对象,然后将该对象挂载在异步通知队列中(等待队列也是这个原理) 28 //那么最后发送信号又是怎么知道是哪个进程的呢?我们看后面的kill_fasync函数。 29 if (on) {//不存在 30 new->magic = FASYNC_MAGIC; 31 new->fa_file = filp;//指定文件指针 32 new->fa_fd = fd;//指定文件描述符 33 new->fa_next = *fapp;//挂载在异步通知队列中 34 *fapp = new;//挂载 35 result = 1; 36 } 37 out: 38 write_unlock_irq(&fasync_lock); 39 return result; 40 }
//看看kill_fasync函数是怎么将信号通知指定进程的:
1 void __kill_fasync(struct fasync_struct *fa, int sig, int band) 2 { 3 while (fa) { 4 ... 5 fown = &fa->fa_file->f_owner;//这里便是回答上面的问题,如果知道是哪个进程的,通过异步对象的文件指针知道其属主进程 6 /* Don't send SIGURG to processes which have not set a queued signum: SIGURG has its own default signallingmechanism. */ 7 if (!(sig == SIGURG && fown->signum == 0)) 8 send_sigio(fown, fa->fa_fd, band);//发送信号 9 fa = fa->fa_next; 10 ... 11 } 12 }
总结:应用程序使用fcntl()设置当前进程的pid和FASYNC标志。进而调用驱动程序的fasync(),即fasync_helper()。然后申请和设置fasync_struct结构,将此结构挂载到驱动程序
的fasync_struct结构链表中。当设备可用时,驱动程序会使用kill_fasync(),从fasync_struct链表中,查找所有的等待进程,然后调用send_sigio发送相应的消息给进程。进程接收到
消息,就会跳转到与消息绑定的消息处理函数中。
实例:基于<<Linux设备驱动开发详解:基于最新的Linux4.0内核.pdf>>第9.3章节
驱动程序源码.

1 #include <linux/module.h> 2 #include <linux/fs.h> 3 #include <linux/init.h> 4 #include <linux/cdev.h> 5 #include <linux/slab.h> 6 #include <linux/uaccess.h> 7 #include <linux/poll.h> 8 9 #define GLOBALMEM_SIZE 0x1000 10 //#define GLOBALMEM_SIZE 0x10 11 #define GLOBALMEM_MAJOR 230 12 #define GLOBALMEM_MAGIC 'g' 13 //#define MEM_CLEAR _IO(GLOBALMEM_MAGIC,0) 14 #define MEM_CLEAR (0x01) 15 static int globalfifo_major = GLOBALMEM_MAJOR; 16 module_param(globalfifo_major, int, S_IRUGO); 17 18 struct globalfifo_dev { 19 struct cdev cdev; 20 unsigned int current_len; 21 unsigned char mem[GLOBALMEM_SIZE]; 22 struct mutex mutex; 23 wait_queue_head_t r_wait; 24 wait_queue_head_t w_wait; 25 struct fasync_struct *queue; 26 }; 27 28 struct globalfifo_dev *globalfifo_devp; 29 30 static int globalfifo_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) 31 { 32 filp->private_data = globalfifo_devp; 33 return 0; 34 } 35 36 static ssize_t globalfifo_read(struct file *filp, char __user * buf, size_t size, 37 loff_t * ppos) 38 { 39 unsigned int count = size; 40 int ret = 0; 41 struct globalfifo_dev *dev = filp->private_data; 42 DECLARE_WAITQUEUE(wait, current); 43 44 mutex_lock(&dev->mutex); 45 add_wait_queue(&dev->r_wait, &wait); 46 47 while(dev->current_len ==0){ 48 if(filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK){ 49 ret = -EAGAIN; 50 goto out; 51 } 52 53 set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE); 54 mutex_unlock(&dev->mutex); 55 56 schedule(); 57 if(signal_pending(current)){ 58 ret = -ERESTARTSYS; 59 goto out2; 60 } 61 mutex_lock(&dev->mutex); 62 63 } 64 65 if (count > dev->current_len) 66 count = dev->current_len; 67 68 if (copy_to_user(buf, dev->mem, count)) { 69 ret = -EFAULT; 70 goto out; 71 } else { 72 memcpy(dev->mem, dev->mem+count, dev->current_len - count); 73 dev->current_len -=count; 74 printk(KERN_INFO "read %d bytes(s) current_len %d ", count, dev->current_len); 75 wake_up_interruptible(&dev->w_wait); 76 77 if(dev->queue){ 78 kill_fasync(&dev->queue, SIGIO, POLL_OUT); 79 printk(KERN_DEBUG "%s kill SIGIO ", __func__); 80 } 81 ret = count; 82 } 83 out: 84 mutex_unlock(&dev->mutex); 85 out2: 86 remove_wait_queue(&dev->r_wait, &wait); 87 set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING); 88 89 return ret; 90 } 91 92 static ssize_t globalfifo_write(struct file *filp, const char __user * buf, 93 size_t size, loff_t * ppos) 94 { 95 unsigned int count = size; 96 int ret = 0; 97 struct globalfifo_dev *dev = filp->private_data; 98 DECLARE_WAITQUEUE(wait, current); 99 100 mutex_lock(&dev->mutex); 101 add_wait_queue(&dev->w_wait, &wait); 102 103 while(dev->current_len == GLOBALMEM_SIZE){ 104 if(filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK){ 105 ret = -EAGAIN; 106 goto out; 107 } 108 109 set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE); 110 mutex_unlock(&dev->mutex); 111 schedule(); 112 if(signal_pending(current)){ 113 ret = -ERESTARTSYS; 114 goto out2; 115 } 116 mutex_lock(&dev->mutex); 117 118 } 119 120 if (count > (GLOBALMEM_SIZE - dev->current_len)) 121 count = (GLOBALMEM_SIZE - dev->current_len); 122 123 if (copy_from_user(dev->mem + dev->current_len, buf, count)){ 124 ret = -EFAULT; 125 goto out; 126 } 127 else { 128 dev->current_len += count; 129 wake_up_interruptible(&dev->r_wait); 130 ret = count; 131 printk(KERN_INFO "written %d bytes(s) current_len %d ", count, dev->current_len); 132 133 if(dev->queue){ 134 kill_fasync(&dev->queue, SIGIO, POLL_IN); 135 printk(KERN_DEBUG "%s kill SIGIO ", __func__); 136 } 137 } 138 out: 139 mutex_unlock(&dev->mutex); 140 out2: 141 remove_wait_queue(&dev->w_wait, &wait); 142 set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING); 143 return ret; 144 } 145 static loff_t globalfifo_llseek(struct file *filp, loff_t offset, int orig) 146 { 147 loff_t ret = 0; 148 switch (orig) { 149 case 0: /* ´ÓÎļþ¿ªÍ·Î»ÖÃseek */ 150 if (offset< 0) { 151 ret = -EINVAL; 152 break; 153 } 154 if ((unsigned int)offset > GLOBALMEM_SIZE) { 155 ret = -EINVAL; 156 break; 157 } 158 filp->f_pos = (unsigned int)offset; 159 ret = filp->f_pos; 160 break; 161 case 1: /* ´ÓÎļþµ±Ç°Î»ÖÿªÊ¼seek */ 162 if ((filp->f_pos + offset) > GLOBALMEM_SIZE) { 163 ret = -EINVAL; 164 break; 165 } 166 if ((filp->f_pos + offset) < 0) { 167 ret = -EINVAL; 168 break; 169 } 170 filp->f_pos += offset; 171 ret = filp->f_pos; 172 break; 173 default: 174 ret = -EINVAL; 175 break; 176 } 177 return ret; 178 } 179 static long globalfifo_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, 180 unsigned long arg) 181 { 182 struct globalfifo_dev *dev = filp->private_data; 183 switch (cmd) { 184 case MEM_CLEAR: 185 mutex_lock(&dev->mutex); 186 memset(dev->mem, 0, GLOBALMEM_SIZE); 187 dev->current_len =0; 188 printk(KERN_INFO "globalfifo is set to zero "); 189 mutex_unlock(&dev->mutex); 190 break; 191 default: 192 return -EINVAL; 193 } 194 195 return 0; 196 } 197 static unsigned int globalfifo_poll(struct file * filp, poll_table * wait) 198 { 199 unsigned int mask =0; 200 struct globalfifo_dev *dev = filp->private_data; 201 202 mutex_lock(&dev->mutex); 203 204 poll_wait(filp, &dev->w_wait, wait); 205 poll_wait(filp, &dev->r_wait, wait); 206 207 if(dev->current_len != 0) 208 mask |=POLLIN | POLLRDNORM; 209 if(dev->current_len != GLOBALMEM_SIZE) 210 mask |=POLLOUT | POLLWRNORM; 211 212 mutex_unlock(&dev->mutex); 213 return mask; 214 } 215 216 static int globalfifo_fasync(int fd, struct file *filp, int on) 217 { 218 struct globalfifo_dev *dev = filp->private_data; 219 220 return fasync_helper(fd, filp, on, &dev->queue); 221 } 222 223 static int globalfifo_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) 224 { 225 globalfifo_fasync(-1, filp, 0); 226 return 0; 227 } 228 static const struct file_operations globalfifo_fops = { 229 .owner = THIS_MODULE, 230 .llseek = globalfifo_llseek, 231 .read = globalfifo_read, 232 .write = globalfifo_write, 233 .unlocked_ioctl = globalfifo_ioctl, 234 .open = globalfifo_open, 235 .poll = globalfifo_poll, 236 .release = globalfifo_release, 237 .fasync = globalfifo_fasync, 238 }; 239 static void globalfifo_setup_cdev(struct globalfifo_dev *dev, int index) 240 { 241 int err, devno = MKDEV(globalfifo_major, index); 242 cdev_init(&dev->cdev, &globalfifo_fops); 243 dev->cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE; 244 err = cdev_add(&dev->cdev, devno, 1); 245 if (err) 246 printk(KERN_NOTICE "Error %d adding globalfifo%d", err, index); 247 } 248 static int __init globalfifo_init(void) 249 { 250 int ret; 251 dev_t devno = MKDEV(globalfifo_major, 0); 252 253 if (globalfifo_major) 254 ret = register_chrdev_region(devno, 1, "globalfifo"); 255 else { 256 ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devno, 0, 1, "globalfifo"); 257 globalfifo_major = MAJOR(devno); 258 } 259 if (ret < 0) 260 return ret; 261 262 globalfifo_devp = kzalloc(sizeof(struct globalfifo_dev), GFP_KERNEL); 263 if (!globalfifo_devp) { 264 ret = -ENOMEM; 265 goto fail_malloc; 266 } 267 globalfifo_setup_cdev(globalfifo_devp, 0); 268 269 mutex_init(&globalfifo_devp->mutex); 270 init_waitqueue_head(&globalfifo_devp->r_wait); 271 init_waitqueue_head(&globalfifo_devp->w_wait); 272 return 0; 273 274 fail_malloc: 275 unregister_chrdev_region(devno, 1); 276 return ret; 277 } 278 279 static void __exit globalfifo_exit(void) 280 { 281 cdev_del(&globalfifo_devp->cdev); 282 kfree(globalfifo_devp); 283 unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(globalfifo_major, 0), 1); 284 } 285 module_init(globalfifo_init); 286 module_exit(globalfifo_exit); 287 288 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");
应用程序源码.

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <fcntl.h> 3 #include <errno.h> 4 #include <signal.h> 5 #include <sys/types.h> 6 #include <unistd.h> 7 8 9 void signal_handler(int signalNum) 10 { 11 printf("signalNum:0x%x ",signalNum); 12 } 13 14 int main(int argc, char **argv) 15 { 16 int fd; 17 int err; 18 19 fd = open("/dev/globalfifo", O_RDONLY); 20 if(fd == -1) 21 printf("open fail "); 22 else{ 23 signal(SIGIO, signal_handler); 24 fcntl(fd, F_SETOWN, getpid()); 25 int oflags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL); 26 fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, oflags | FASYNC); 27 while(1) 28 sleep(100); 29 } 30 return 0; 31 }
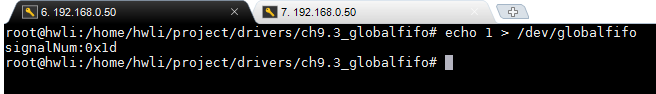
结果:
当echo 1 >/dev/globalfifo时
此文源码基于内核源码版本为linux-2.6.22.6
